1、永远小表驱动大表,即小的数据集驱动大的数据集。
原理:
select * from a where id in (select id from b)
# 等价于
for select id from b
for select * from a where a.id = b.id
当b表的数据集小于a表的数据集时,用in优于exists;
select * from a where exists (select 1 from b where b.id = a.id)
# 等价于
for select * from a
for select * from b where b.id = a.id
当a表的数据集小于b表的数据集时,用exists优于in。
公式:
select ... from table where exists (subquery)
即:将主查询的数据,放在子查询中做条件验证,根据验证结果(TRUE或FALSE)决定主查询的数据结果是否得以保留。
提示:exists (subquery)只返回TRUE或FALSE,因此子查询中的select *也可以是select 1或select ‘X’,官方说法是实际执行时会忽略select清单,因此没有区别。
2、order by关键字优化:
(1)order by子句,尽量使用Using index方式排序,避免使用Using filesort方式排序;
① create table:
create table tblA(
age int,
birth TIMESTAMP not null
);
insert into tblA(age,birth) values (22,now());
insert into tblA(age,birth) values (23,now());
insert into tblA(age,birth) values (24,now());
create index idx_a_ageBirth on tbla(age, birth);
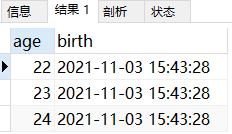
select * from tbla;
② case:
explain select * from tbla where age > 20 order by age;

explain select * from tbla where age > 20 order by age, birth;
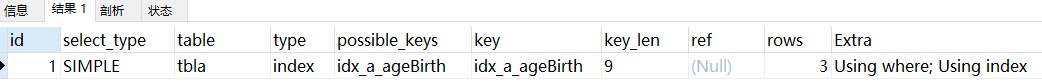
explain select * from tbla where age > 20 order by birth;

explain select * from tbla where age > 20 order by birth, age;

explain select * from tbla where age > 20 order by age asc, birth desc;

MySQL支持两种方式的排序,Using filesort(文件排序)和Using index(扫描有序索引排序),index效率高,它指MySQL扫描索引本身完成排序。filesort方式效率较低。
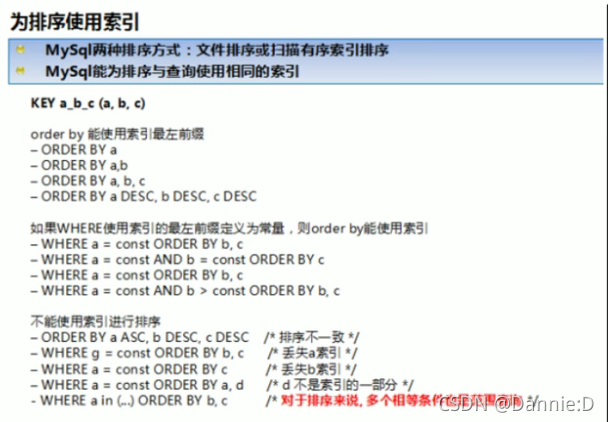
(2)尽可能在索引列上完成排序操作,遵照索引建的最佳左前缀;
order by满足两种情况,会使用index方式排序:
a. order by语句使用索引最左前列;
b. 使用where子句与order by子句条件列组合满足索引最左前列。
(3)若不在索引列上,mysql就要启动filesort的两种算法:双路排序(MySQL4.1之前,两次I/O)和单路排序(MySQL4.1后,一次I/O操作,但需使用更多空间);
提高order by效率:
(1)忌select *;
(2)尝试提高sort_buffer_size;
(3)尝试提高max_length_for_sort_data。
总结:
3、group by关键字优化:
(1) group by实质是先排序后分组,遵照索引建的最佳左前缀;
(2) 当无法使用索引列,增大max_length_for_sort_data参数的设置,增大sort_buffer_size参数的设置;
(3)where高于having,尽量使用where限定。





















 1455
1455

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








