JAVA实现简单的计算器
该计算器(没有处理)错误的情况,只能处理输入正确的运算,实现加减乘除和取余的功能,还可以进行小数的运算,处理了乘法除法取余优先于加减法的运算。用简单的方法写的,但是代码有点长(主要是不会大佬们写这个计算器的方法)。关于这个计算器的写法代码中几乎每步都有注释。
下图就是创建的计算器。
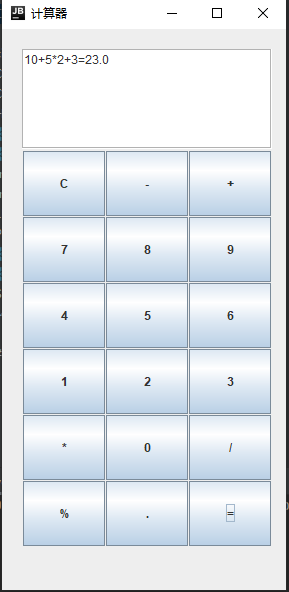
这个部分是主函数的部分
public class Event {
public static void main(String[] args){
CalculatorImpl calculator = new CalculatorImpl();
}
}
下面的是CalulatorImpl类的代码
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class CalculatorImpl extends JFrame {
private String[] str = {"C", "-", "+", "7", "8", "9", "4", "5", "6", "1", "2", "3", "*", "0", "/", "%", ".", "="};//计算器上的按钮
private JButton strs[] = new JButton[str.length];//建立按钮,并确定个数
private JPanel p = new JPanel();//建立装载按钮的容器
private JTextArea text = new JTextArea();//建立输入框和结果框
private String stnum[] = new String[100];//存放最多100组数据
private char chstr[] = new char[100];//存放最多100组数据
private int a = 0;//标记这是第几个数
private int b = 0;//标记这是第几个运算符号
private double num;//结果
private String show ="";//记录要输出的内容
private int l;//用于乘法和除法优先于加减法的运算
private boolean bo1 = false;//用于乘法和除法优先于加减法的运算
private boolean bo2 = false;//用于乘法和除法优先于加减法的运算
public CalculatorImpl() {
super("计算器");//给这个JFrame命名
p.setBounds(20, 120, 250, 400);//确定装载按钮的位置、宽度和高度
p.setLayout(new GridLayout(6, 3, 1, 1));//用GridLayout的方式对按钮布局
text.setLayout(null);//确定输入框和结果框的布局
text.setBounds(20, 20, 250, 100);//确定输入框和结果框的位置、宽度和高度
text.setAlignmentX(RIGHT_ALIGNMENT);//让输入框和结果框的数据向右对齐
text.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());//建立输入框和结果框的边框,让其更加美观
text.setEditable(false);//使文本框不能从键盘输入
Definition(stnum);//给数组初始化定义
Definitionch(chstr);//给数组初始化定义
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
strs[i] = new JButton();//创建每个按钮
strs[i].setText(str[i]);//给每个按钮加上该有的名字
p.add(strs[i]);//将按钮放入JPanel容器中
strs[i].addActionListener(new Impl());//给每个按钮加上点击事件
}
this.setLayout(null);//定义JFrame的布局
this.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 600);//确定JFrame容器的位置、宽度和高度
this.add(text);//将输入框和结果框加入
this.add(p);//将装载按钮的容器加入
this.setVisible(true);//让JFrame可以看见
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//点击计算器关闭按钮的时候程序退出
}
class Impl implements ActionListener {//定义按钮的点击事件
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String label = e.getActionCommand();//获取点击的按钮
char ch = label.charAt(0);//将按到的值转换为char型
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' || ch == '.') {//按钮为数字和‘.’的情况
stnum[a] = stnum[a] + ch;//记录数字
show = show+ch;//将数字加入到要输出的内容中
text.setText(show);//输入到输入框和结果框
}//确定0~9数字的点击事件
else if (ch == 'C') {
Definition(stnum);//给字符串数组初始化定义
Definitionch(chstr);//给符号数组初始化定义
a = 0;//让标记数字的位置变为0
b = 0;//将标记符号的位置变为0
num = 0;//将结果变为0
show = "";//展示的值清空
text.setText(show);//将输入框和结果框清空
bo1 = false;//将判断优先级的条件变为初始值
bo2 = false;//将判断优先级的条件变为初始值
} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '/' || ch == '*' || ch == '%') {
chstr[b] = ch;//记录符号
show = show+chstr[b];//将符号假如要输出的内容中
text.setText(show);//将该字符输入到输入框和结果框
a++;//让记录数字的位置向后移动一位
b++;//让记录字符的位置向后移动一位
} else if (ch == '=') {
show = show+'=';//将等号放入要输出的内容中
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
if (chstr[i] == '+') {
l = i;//将该记录该位置的数字赋值给l
while(l<a&&chstr[l+1]!='+'&&chstr[l+1]!='-'&&chstr[l+1]!='=') {//用while循环判断加号或者减号前面是否有*/%
if (chstr[l + 1] == '*' || chstr[l + 1] == '/' || chstr[l + 1] == '%') {//判断加号或者减号前面是否有*/%
if (chstr[l + 1] == '*') {//乘号的情况
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 1]) * Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 2]);//让加号后面的两个数先进行乘法运算
stnum[l + 2] = String.valueOf(num);//让后面的数赋予num的值
}
if (chstr[l + 1] == '/') {
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 1]) / Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 2]);//让加号后面的两个数先进行除法运算
stnum[l + 2] = String.valueOf(num);//让后面的数赋予num的值
}
if (chstr[l + 1] == '%') {
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 1]) % Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 2]);//让加号后面的两个数先进行取余运算
stnum[l + 2] = String.valueOf(num);//让后面的数赋予num的值
}
bo1 = true;//表示进行了优先乘法的运算
}
l++;//让符号位置向后移动,判断后面是否还是*/%
}
//退出判断优先运算的循环之后,根据是否进行了优先运算给num赋值
if(bo1==true){
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) +num;
i = l;//让运算跳过优先运算的部分
stnum[i+1] = String.valueOf(num);//为后面的运算赋值
bo1 = false;//让该值变回false
}else{
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) + Double.parseDouble(stnum[i + 1]);//没有进行优先运算,直接后一个数加前一个数
stnum[i + 1] = String.valueOf(num);//把第二个数变为num
}
} else if (chstr[i] == '-') {//减法的原理和加法一样
l = i;
while(l<a&&chstr[l+1]!='+'&&chstr[l+1]!='-'&&chstr[l+1]!='=') {
if (chstr[l + 1] == '*' || chstr[l + 1] == '/' || chstr[l + 1] == '%') {
if (chstr[l + 1] == '*') {
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 1]) * Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 2]);
stnum[l + 2] = String.valueOf(num);
}
if (chstr[l + 1] == '/') {
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 1]) / Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 2]);
stnum[l + 2] = String.valueOf(num);
}
if (chstr[l + 1] == '%') {
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 1]) % Double.parseDouble(stnum[l + 2]);
stnum[l + 2] = String.valueOf(num);
}
bo2 = true;
}
l++;
}
if(bo2==true){
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) - num;
i = l;
stnum[i+1] = String.valueOf(num);
bo2 = false;
}else{
num = Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) - Double.parseDouble(stnum[i + 1]);
stnum[i + 1] = String.valueOf(num);
}
} else if (chstr[i] == '*') {
num = (Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) * Double.parseDouble(stnum[i + 1]));
stnum[i + 1] = String.valueOf(num);
} else if (chstr[i] == '/') {
num = (Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) / Double.parseDouble(stnum[i + 1]));
stnum[i + 1] = String.valueOf(num);
} else if (chstr[i] == '%') {
num = (Double.parseDouble(stnum[i]) % Double.parseDouble(stnum[i + 1]));
stnum[i + 1] = String.valueOf(num);
}
}//实现+-*/%符号,其中的Double.parseDouble(stnum[i])是将String类型转换为double类
show = show+(String.valueOf(num));//将结果加入到要输出的内容中
text.setText(show);//展示
Definition(stnum);//给字符串数组初始化定义
Definitionch(chstr);//给符号数组初始化定义
a = 0;//让标记数字的位置变为0
b = 0;//将标记符号的位置变为0
num = 0;//让结果变为0
show = "";//清空输入框的内容
}
}
}
public void Definition(String st[]) {//定义保存数字数组中的元素
for (int i = 0; i < st.length; i++) {
st[i] = "";
}
}
public void Definitionch(char ch[]) {//定义保存符号数组中的元素
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
ch[i] = ' ';
}
}
}
以上就是所有的代码。
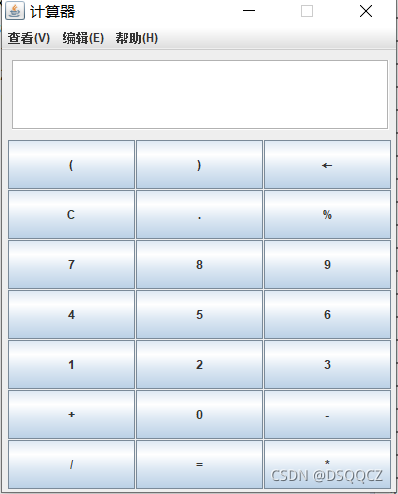
在b站学习的逆波兰计算器,实现了小括号和退格的功能.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Domain {
public static void main(String[] args){
new WindowRtl();
}
public static boolean judge(String item) {
String []strs = {"(",")","+","-","*","/","%"};
boolean []ss = new boolean[strs.length];
for(int i=0;i< strs.length;i++) {
ss[i] = item.equals(strs[i]);
}
if(!ss[0]&&!ss[1]&&!ss[2]&&!ss[3]&&!ss[4]&&!ss[5]&&!ss[6]) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
public static List<String> parseSuffixExpressionList(List<String> li){
Stack<String> st1 = new Stack();
List<String> st2 = new ArrayList<String>();//s2没有pop操作,之后输出时应该逆序输出
for(String item : li) {
if(judge(item)) {
st2.add(item);
}else if(item.equals("(")) {
st1.push(item);
}else if(item.equals(")")) {
while(!st1.peek().equals("(")) {
st2.add(st1.pop());
}
st1.pop();
}else {
while(st1.size()!=0&&Operation.getValue(st1.peek())>=Operation.getValue(item)) {
st2.add(st1.pop());
}
st1.push(item);
}
}
while(st1.size()!=0) {
st2.add(st1.pop());
}
return st2;
}
public static List<String> getListString(String str){
String[] split = str.split(" ");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for(String ele : split) {
list.add(ele);
}
return list;
}
public static List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String s){
List<String> li = new ArrayList<String>();
int i = 0;
String s1;
char c;
do {
if((c=s.charAt(i)) < 48|| (c=s.charAt(i)) > 57) {
li.add(""+c);
i++;
}else {
s1 = "";
while( ((c=s.charAt(i))>=48&&(c=s.charAt(i))<=57)||((c=s.charAt(i))==46)) {
s1 += c;
i++;
if(i >= s.length()) {
break;
}
}
li.add(s1);
}
}while(i<s.length());
return li;
}
public static double calculate(List<String> list) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack();
for(String ele : list) {
if(judge(ele)) {
stack.push(ele);
}else {
double res = 0;
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(stack.pop());
double num1 = Double.parseDouble(stack.pop());
if(ele.equals("+")) {
res = num1+num2;
}else if(ele.equals("-")) {
res = num1-num2;
}else if(ele.equals("*")) {
res = num1*num2;
}else if(ele.equals("/")) {
res = num1/num2;
}else if(ele.equals("%")){
int num11 = (int)num1;
int num22= (int)num2;
res = num11%num22;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
stack.push(""+res);
}
}
return Double.parseDouble(stack.pop());
}
}
class Operation{
private static int ADD = 1;//加
private static int SUB = 1;//减
private static int MUL = 2;//乘
private static int DIV = 2;//除
private static int QUM = 2;//取模
public static int getValue(String operation) {
int result = 0;
if(!operation.equals("(")&&!operation.equals(")")) {
switch (operation) {
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = SUB;
break;
case "*":
result = MUL;
break;
case "/":
result = DIV;
break;
case "%":
result = QUM;
break;
default:
System.out.println("不存在该运算符");
break;
}
}
return result;
}
}
另一部分
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.List;
public class WindowRtl extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
private String[] str = {"(",")","←","C",".","%","7","8","9","4","5","6","1","2","3","+","0","-","/","=","*"};
private JPanel jPanel = new JPanel();
private JButton[] strs = new JButton[str.length];
private JTextArea text = new JTextArea();
private String szong = "";
private String []szong1 = new String[1000];
private String szhen = "";
int a = 0;
public WindowRtl(){
super("计算器");
this.setBounds(100,100,400,500);
this.setLayout(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setResizable(false);
JMenuBar bar = new JMenuBar();
JMenu jm = new JMenu("查看(V)");
JMenu jm2 = new JMenu("编辑(E)");
JMenu jm3 = new JMenu("帮助(H)");
bar.add(jm);
bar.add(jm2);
bar.add(jm3);
this.setJMenuBar(bar);
text.setLayout(null);
text.setBounds(10,10,377,70);
text.setAlignmentX(RIGHT_ALIGNMENT);
text.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());
text.setEditable(false);
jPanel.setBounds(5,90,385,350);
jPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(7,3,1,1));
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++){
strs[i] = new JButton();
strs[i].setText(str[i]);
jPanel.add(strs[i]);
strs[i].addActionListener(this);
}
this.add(jPanel);
this.add(text);
this.setVisible(true);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
String label = actionEvent.getActionCommand();
szong = "";
if(label.equals("C")){
szhen = "";
a = 0;
szong = "";
}else if(!label.equals("←")&&!label.equals("=")){
szong1[a] = label;
for(int i=0;i<=a;i++){
szong+=szong1[i];
}
a++;
//sb.append(label);
}else if(!label.equals("C")&&!label.equals("=")){
if(a>0) {
szong1[a - 1] = "";
for (int i = 0; i <= a-1; i++) {
szong += szong1[i];
}
a--;
}
}
text.setText(szong);
if(label.equals("=")){
for (int i = 0; i <= a-1; i++) {
szhen += szong1[i];
}
Domain d = new Domain();
List<String> infixlist = d.toInfixExpressionList(szhen);
List<String> lis = d.parseSuffixExpressionList(infixlist);
double res = d.calculate(lis);
text.setText(""+res);
for (int i = 0; i <= a-1; i++) {
szong1[i] = "";
}
szhen = "";
a = 0;
szong = "";
}
}
}
记录一下成果.




















 732
732

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








