一、介绍
HHEM 排行榜评估LLM在总结文档时引入幻觉的频率,使用 HHEM-2.1(商业版) 幻觉检测模型。
排行榜地址: https://huggingface.co/spaces/vectara/leaderboard
github地址: https://github.com/vectara/hallucination-leaderboard
HHEM-2.1 开源版本(HHEM-2.1-Open): https://huggingface.co/vectara/hallucination_evaluation_model
二、使用
排行榜使用的测试数据集地址: https://huggingface.co/datasets/vectara/leaderboard_results,其中 source 为问题,summary 为各模型的回答。对于单个模型,使用 1006 个问题用于测试。
原始数据集: 📎leaderboard_summaries.csv, 使用脚本抽取 1006 个测试问题,并保存成 jsonl 格式文件,用于后续使用模型获取答案。jsonl 文件包含字段 source,model_answer(为空),脚本如下:📎抽取数据集.py,抽取完成后的文件如下:📎leaderboard_summaries.jsonl。该文件用于获取模型答案。
- 下载HHEM-2.1-Open 模型
- 使用脚本获取上面 jsonl 文件模型的答案,模型答案填充到model_answer字段, 脚本如下: 📎获取答案.py, 其中 temperature 取的 0,提示词如下:
You are a chat bot answering questions using data. You must stick to the answers provided solely by the text in the passage provided. You are asked the question 'Provide a concise summary of the following passage, covering the core pieces of information described.' <PASSAGE>' #使用summary字段值替换 PASAGE- 实验分别获取了开源的Qwen3-32B模型的思维模式和非思维模式的答案,结果如下:📎leaderboard_summaries_think.jsonl📎leaderboard_summaries.jsonl
- 根据HHEM-2.1官方示例,获取每个答案的幻觉概率,值越小说明幻觉率概率越高
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
pairs = [ # Test data, List[Tuple[str, str]]
("The capital of France is Berlin.", "The capital of France is Paris."), # factual but hallucinated
('I am in California', 'I am in United States.'), # Consistent
('I am in United States', 'I am in California.'), # Hallucinated
("A person on a horse jumps over a broken down airplane.", "A person is outdoors, on a horse."),
("A boy is jumping on skateboard in the middle of a red bridge.", "The boy skates down the sidewalk on a red bridge"),
("A man with blond-hair, and a brown shirt drinking out of a public water fountain.", "A blond man wearing a brown shirt is reading a book."),
("Mark Wahlberg was a fan of Manny.", "Manny was a fan of Mark Wahlberg.")
]
# Step 1: Load the model
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
'vectara/hallucination_evaluation_model', trust_remote_code=True)
# Step 2: Use the model to predict
model.predict(pairs) # note the predict() method. Do not do model(pairs).
# tensor([0.0111, 0.6474, 0.1290, 0.8969, 0.1846, 0.0050, 0.0543])
- 根据示例,修改相关脚本,使用hallucination_evaluation_model模型获取响应的幻觉率,脚本如下:
import torch
import json
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
# Step 1: Load the model
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
'/root/autodl-tmp/hallucination_evaluation_model', trust_remote_code=True)
# 打开 jsonl 文件
raw_scores = []
with open("leaderboard_summaries_think.jsonl", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for idx, line in enumerate(f):
data = json.loads(line)
pairs = [(data["source"], data["model_answer"])]
print(f"正在执行第 {idx + 1} 个样本")
# 第2步:使用模型进行预测
raw_score = model.predict(pairs).item() # 确保方法调用正确
raw_scores.append(raw_score)
print(raw_scores)
print("个数:" + str(len(raw_scores)))
raw_scores_tensor = torch.tensor(raw_scores)
# pairs = [ # Test data, List[Tuple[str, str]]
# ("The capital of France is Berlin.", "The capital of France is Paris."), # factual but hallucinated
# ('I am in California', 'I am in United States.'), # Consistent
# ('I am in United States', 'I am in California.'), # Hallucinated
# ("A person on a horse jumps over a broken down airplane.", "A person is outdoors, on a horse."),
# ("A boy is jumping on skateboard in the middle of a red bridge.", "The boy skates down the sidewalk on a red bridge"),
# ("A man with blond-hair, and a brown shirt drinking out of a public water fountain.", "A blond man wearing a brown shirt is reading a book."),
# ("Mark Wahlberg was a fan of Manny.", "Manny was a fan of Mark Wahlberg.")
# ]
# # Step 2: Use the model to predict
# raw_scores = model.predict(pairs) # note the predict() method. Do not do model(pairs).
# # tensor([0.0111, 0.6474, 0.1290, 0.8969, 0.1846, 0.0050, 0.0543])
# print(raw_scores)
#This is the most end-to-end and out-of-the-box way to use HHEM-2.1-Open. It takes a list of pairs of (premise, hypothesis) as the input and returns a score between 0 and 1 for each pair where 0 means that the hypothesis is not evidenced at all by the premise and 1 means the hypothesis is fully supported by the premise. raw_scores的值越小越幻觉
hallucination_rate = (raw_scores_tensor < 0.5).float().mean().item() #幻觉率
factual_consistency = 1 - hallucination_rate
print(f'幻觉率: {hallucination_rate}')
print(f'事实一致性: {factual_consistency}')其中,幻觉率的阈值并没有公布,我们以0.5为阈值,小于 0.5 则认为是幻觉,所以上述脚本也用的 0.5作为 阈值。
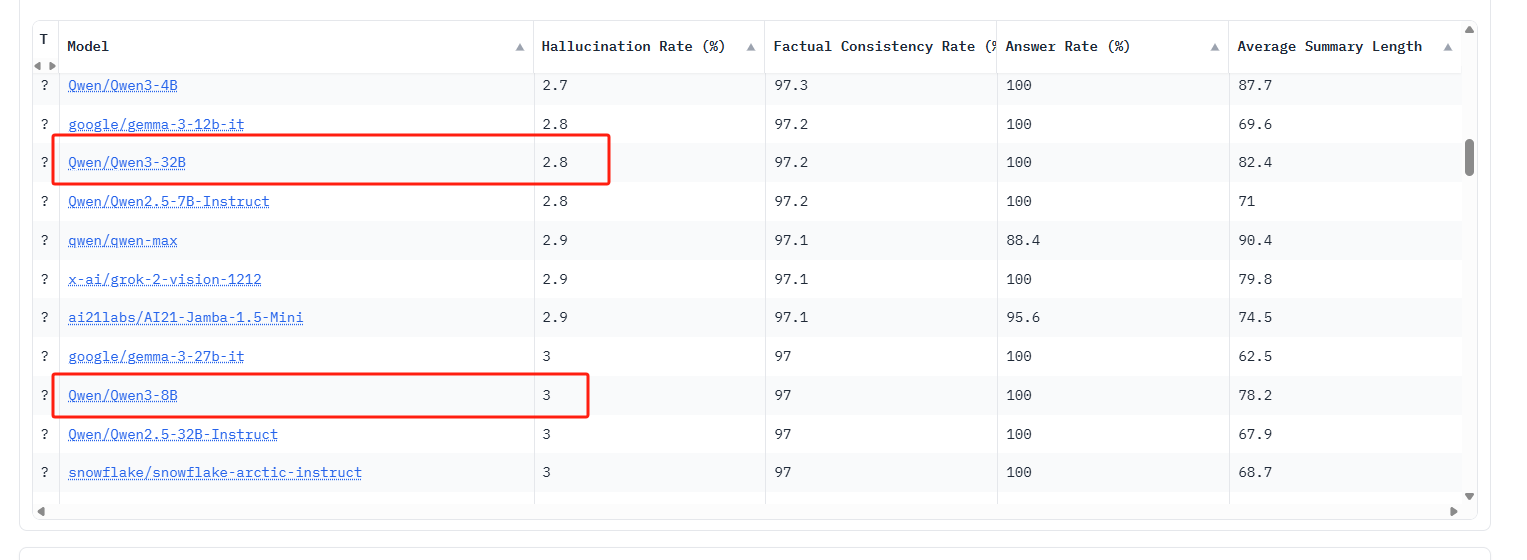
- 使用上述脚本分别对Qwen3-32B模型的推理和非推理情况下的幻觉率做了评估,结果如下:
非推理模型:3.9%
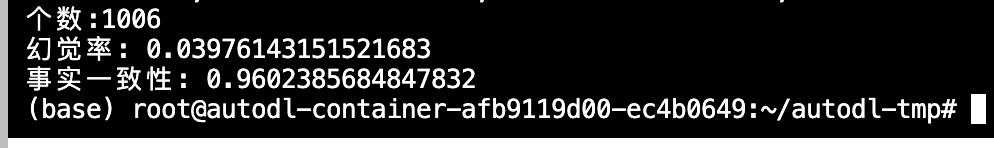
推理模型: 6.5%
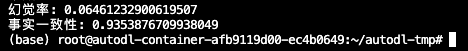
补充: 获取在线的Qwen3-32B模型的非思维模式的答案,结果如下: 📎leaderboard_summaries_online.jsonl
幻觉率评估结果:4.9%
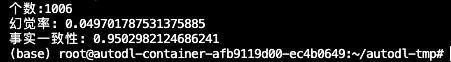
获取在线的Qwen3-8B模型的非思维模式的答案,结果如下:
📎leaderboard_summaries_8b_online.jsonl
幻觉率评估结果:3.4%
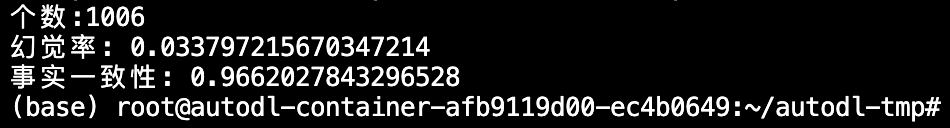
官网榜单:

























 741
741

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








