第一节 复习
反射技术 :
Class类 --》反射技术的入口
a)如何获取一个类的Class对象 , 最常用的方式Class.forName(“完整的包名+类名”);
举例:Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”);
b)Class是所以使用class声明的数据类型[类类型]的模板
一个类需要具备 1)属性 2)方法 3)构造方法
使用Class对象获取任意一个类的属性 -->属性对象 Field 对象
使用Class对象获取任意一个类的方法 --> 方法对象 Method对象 ,在Method类有一个非常重要的方法 invoke (…)
使用Class对象获取任意一个类的构造方法 -->构造方法对象 Constructor 对象,在,Constructor类有一个非常重要的方法 newInstance().,用于创建类的对象
第二节 注解
2.1 注解的简介
注解的作用
①不是程序本身,可以对程序作出解释。(这一点跟注释没什么区别)
②可以被其他程序(比如:编译器等)读取。(注解信息处理流程,是注解和注释的重大区别,如果没有注解信息处理流程,则注解毫无意义)
注解的格式
注解是以”@注释名”在代码中存在,还可以添加一些参数值,例如@SuppressWarnings(value=”unchecked”)。
注解在哪里使用
可以附加在package,class,method,field等上面,相当于给它们添加了额外的辅助信息,我们可以通过反射机制编程实现对这些元素的访问。
内置的注解
①@Override :标识方法是重写的方法
② @Deprecated :标识的方法不建议使用
③ @SuppressWarnings:用来抑制编译时的警告信息
④@SuppressWarinings需要提供参数才能正常使用,这些参数都是已经定义好的,我们只需要选择就可以了。

举例:
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
@SuppressWarnings(value={“unchecked”,“deprecation”})
自定义注解的语法
使用@interface定义自定义注解时,自动继承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口
【1】@interface 用来声明一个注解
【2】其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数
◆ 方法的名称就是参数的名称
◆ 返回值类型就是参数类型(返回值类型只能是基本类型、Class、String、enum)
◆ 可以通过default来声明参数的默认值
◆ 如果只有一个成员,一般参数名为value
注意事项:注解元素必须要有值。我们定义注解元素时,经常使用空字符串,0作为默认值。
也经常使用负数(比如-1)表示不存在的含义
元注解
元注解的作用就是负责注解其他注解。在Java中定义了4个标准的meta-annotation类型,它们被用来提供对其它annotation类型作说明
这些类型和它们所支持的类在java.lang.annotation包中可以找到
◆@Target
◆@Retention
◆@Documented
◆@Inherited
@Target
作用:用于描述注解的使用范围(即被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)

@Retention
作用:表示需要在什么级别保存该注解信息,用于描述注解的生命周期

2.2 自定义注解及使用
自定义注解
package com.bjsxt.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.*;
/**
* 自定义注解
*/
@Target({TYPE,METHOD,FIELD}) //@Target说明自定义注解MyAnnotation 的适用范围 是类,接口,。。方法,属性
@Retention(RUNTIME) //@Retention说明自定义的的注解MyAnnotation的使用时机,是程序运行时
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();//注解的参数
}
使用注解 (将注解应用到类上,属性上,方法上)
package com.bjsxt.annotation;
/**
*给MyUser类添加注解
*/
@MyAnnotation(value = "这是一个用户类") //在类上使用注解
public class MyUser {
@MyAnnotation(value = "用户编号") //在属性上使用注解
private String uid;
@MyAnnotation(value = "这是一个显示用的方法") //在方法上使用注解
public void show(){
}
}
使用反射技在程序运时读取注解
package com.bjsxt.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import static java.lang.Class.forName;
/**
* 使用反射技术在程序运行时读取注释
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class aClass = forName("com.bjsxt.annotation.MyUser");
//
Annotation[] annotations = aClass.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation:annotations) {
Class aClass1 = annotation.annotationType();
System.out.println("注解的类名称"+aClass1.getName());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------我是分割线---------------------------");
MyAnnotation annotation1 = (MyAnnotation) aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("注解上注解的参数值"+annotation1.value());
//
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field:fields) {
MyAnnotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("属性上的注解"+annotation.value());
}
//
Method show = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("show");
MyAnnotation annotation = show.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("注解的参数值"+annotation.value());
}
}
2.3 课堂案例_反射读取注解信息
有一个Java类名称为Student,使用ORM思想(类和表对应,属性和字段对应,对象和数据行对应)使用注解完成类和表结构的映射关系,在类上使用注解,在程序运行时,通过反射读取注解,在数据库中创建Student类对应的数据表tb_student。
操作步骤
(1)创建Student类
(2)编写注解
a)编写应用在Student类上的注解 ,后期用于数据库中表的名称
b)编写应用在Student类上的属性上的注解,后期用于数据库表中的字段
【一个字段由三部分组成,名称,数据类型,长度】
(3)在Student类和属性上应用注解
(4)准备jdbcutil和jar包
(5)写测试,使用反射读取注解
使用注解完成类和表结构的映射关系,怎么映射呀?发现表名和类名是不对等的,字段名和属性名也有可能对不上,怎么办?就需要使用注解来让他们对应起来。那么我们就做这样一件事情:将java当中Student类使用使用第三方程序(就是我们写的程序)用过读取注解在数据库中创建一张表出来。(也就是在java中有一个Student类,在Student类中使用注解,在程序运行的时候,使用反射读取注解,到数据库当中,把这个表创建出来)
【1】创建Student类
package com.bjsxt.deno;
/**
*bean类
*/
public class Student {
private int stuId;
private String stuName;
private int age;
public int getStuId() {
return stuId;
}
public void setStuId(int stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(int stuId, String stuName, int age) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuId=" + stuId +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
【2】编写注解——— a)编写应用在Student类上的注解 ,后期用于数据库中表的名称
package com.bjsxt.deno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 类的注释
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SxtTable {
String tableName(); //注解的参数
}
【2】编写注解———编写应用在Student类上的属性上的注解,后期用于数据库表中的字段
【一个字段由三部分组成,名称,数据类型,长度】
package com.bjsxt.deno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
*属性注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SxtField {
String name(); //字段名称
int length(); //字段类型的长度
String type(); //字段的数据类型
}
【3】在Student类和属性上应用注解
/**
*bean类
*/
@SxtTable(tableName = "tb_student")
public class Student {
@SxtField(name="stuId",type="int",length=4)
private int stuId;
@SxtField(name="stuName",type="varchar",length=20)
private String stuName;
@SxtField(name="age",type="varchar",length=20)
private int age;
public int getStuId() {
return stuId;
}
public void setStuId(int stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(int stuId, String stuName, int age) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuId=" + stuId +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
【4】准备jdbcutil和jar包
【5】写测试,使用反射读取注解
package com.bjsxt.deno;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*课堂案例:反射读取注解信息
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//【1】获取Student的Class对象
Class aClass = Class.forName("com.bjsxt.deno.Student");
//【2】获取类上的注解
SxtTable annotation =(SxtTable) aClass.getAnnotation(SxtTable.class);
//【3】获取注解中的参数值,这个参数值就是表名
String tableName = annotation.tableName();
//创建一个集合,用于存储属性注解中的参数值,为了后面拼接sql语句使用
HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
//【4】获取Student类的属性对象
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field:declaredFields) {
SxtField annotation1 = field.getAnnotation(SxtField.class); //获取属性上的注解
//属性上的注解由3部分组成,分别是名称、类型、长度
String name = annotation1.name();
String type = annotation1.type();
int length = annotation1.length();
map.put(name,type+"("+length+")");
}
//System.out.println(map);
//拼接sql语句
StringBuilder sql=new StringBuilder();
sql.append("create table");
sql.append(" ");
sql.append(tableName);
sql.append("(");
//获取所有key的集合
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
//遍历集合
for (String key:keys) {
sql.append(key);
sql.append(" ");
sql.append(map.get(key));
sql.append(",");
}
sql.deleteCharAt(sql.length()-1);
sql.append(")");
System.out.println(sql);
//开始操作数据库
Connection conn = JDBCUtil.getConn();
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
boolean execute = statement.execute(sql.toString());
//execute()方法只要不是查询返回值都为false
System.out.println(!execute?"成功":"失败");
}
}
第三节 XML文件
3.1 编写XML文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<students>
<student>
<id>1001</id>
<name>张三</name>
<age>21</age>
</student>
<student>
<id>1001</id>
<name>李四</name>
<age>22</age>
</student>
<student>
<id>1003</id>
<name>王五</name>
<age>24</age>
</student>
</students>
编写完xml文件,可以使用浏览器打开 ,如果出错,将显示出错的位置
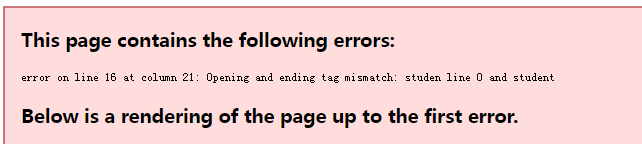
正常则显示如下效果
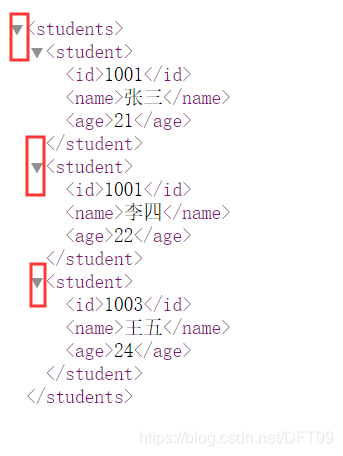
以上的测试,只能测试xml语法是否正确,,但是没有限定编写规则
什么叫限定的编写规则?
指的是根元素students中除了student标签之外,还允许不允许有其它的标签
student的子标签中id,name,age可以出现几次呢?目前没有限制
就需要使用一个名称为DTD的技术 :验证XML文档是否“合法”,
”合法“:指的是程序员定义的规则
3.2 DOM4J解析XML文件
XML文件:通常是应用程序的配置文件(存储的数据是应用程序启动的必备数据)
应用程序启动时,需要从配置文件中读取数据,怎么读?
目前最流行的方式:DOM4J
使用Java解析【读取xml文件中的数据】xml 文件, 有4种方式
(1)DOM 解析
(2)JDOM 解析
(3)SAX解析
(4)DOM4J 解析
四种解析方式的优缺点?
略
3.2.1 使用DOM4J解析XML文件
使用DOM4J的步骤
(1)导包
(2)使用DOM4J
package com.bjsxt.xml;
import com.bjsxt.deno.JDBCUtil;
import com.bjsxt.deno.Student;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws DocumentException, SQLException {
List<Student> list=new ArrayList<>();
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();//创建对象
Document doc = reader.read(new File("student.xml"));
Element rootElement = doc.getRootElement(); //得到根元素对象
//System.out.println(rootElement);
//System.out.println(rootElement.getName()); //得到根的名称
//获取直接子元素
for( Iterator iterator = rootElement.elementIterator();iterator.hasNext();){
//取元素
Element subStudent = (Element)iterator.next();
// System.out.println(subStudent.getName());
//创建Student对象
Student student=new Student();
//继续遍历subStudent的子元素
Iterator iterator1 = subStudent.elementIterator();
for(;iterator1.hasNext();){
Element next = (Element) iterator1.next();
System.out.println(next.getName());
switch (next.getName()){ //判断的是标签的名称
case "id":
student.setStuId(Integer.parseInt(next.getText())); //将String类型转化为int类型
break;
case "name":
student.setStuName(next.getText());
break;
case "age":
student.setAge(Integer.parseInt(next.getText()));
break;
}
}
//将学生对象放到集合中
list.add(student);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
}
//遍历打印
for (Student student:list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
//调用insert方法将数据添加到数据库中
insert(list);
}
public static void insert(List<Student> list) throws SQLException {
int count=0;
for (Student student:list) {
//编写sql语句
String sql="insert into tb_student values(?,?,?)";
//获取连接
Connection conn = JDBCUtil.getConn();
//创建sql语句发送器
PreparedStatement statement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符赋值
statement.setInt(1,student.getStuId());
statement.setString(2,student.getStuName());
statement.setInt(3,student.getAge());
//到数据库执行
statement.executeUpdate();
count++;
}
System.out.println(count>0?"一共插入了"+count+"条数据":"失败");
}
}
第四节 属性文件
认识 :xml文件 -->存储和传递数据
很多应用程序的配置文件,就是使用xml
除了xml文件之外,还有一种类型的文件,也可以存储程序运行的必备数据
称为属性文件 ,对应的是java中的属性类
将属性对象中的数据存储到属性文件
package com.bjsxt.pro;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
*将属性对象中的数据存储到属性文件
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//属性类,对应的是以.properties结尾的属性文件
Properties properties = new Properties(); //创建属性类的对象
//创建属性文件存什么内容?
properties.setProperty("name","marry"); //name-->key,marry -->value,底层调用的是hashtable的put方法
properties.setProperty("id","1001");
properties.setProperty("age","24");
//将属性对象中的值存储到属性文件
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("student.properties"),"学生信息");//第二个参数是对文件的说明
}
}
从属性文件中读取数据
package com.bjsxt.pro;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 将属性对象中的数据存储到属性文件
*/
public class TestRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//(1)创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//(2)从流中加载属性文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream("student.properties"));
//根据key获取值
String id = properties.getProperty("id");
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
String age = properties.getProperty("age");
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+age);
}
}
使用属性文件封装JDBCUtil
package com.bjsxt.pro;
import java.io.*;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
*使用属性文件封装JDBCUtil
*/
public class JDBCUtil2 {
private static String DRIVER ;
private static String URL;
private static String USERNAME ;
private static String PWD ;
//static静态代码块,为类的静态变量赋值
static{
File file=new File("jdbc.properties"); //创建文件
Properties properties = new Properties(); //创建属性对象
if(!file.exists()){ //如果文件不存在,创建
//如果文件不存在,则需要初始化数据(数据库连接字符串的数据),默认连mysql数据库
properties.setProperty("mysqlDriver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
properties.setProperty("mysqlURL","jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/syl1105");
properties.setProperty("mysqlUserName","root");
properties.setProperty("mysqlPassWord","root");
properties.setProperty("type","mysql"); //连接的数据库
//将属性对象中的数据存储到磁盘文件
try {
properties.store(new FileOutputStream(file),"jdbc");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//文件存在,则从文件中读取内容
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream(file)); //从文件中加载
//给静态变量赋值
String type = properties.getProperty("type");
if("mysql".equals(type)){ //说明连接mysql数据库
DRIVER = properties.getProperty("mysqlDriver");
URL = properties.getProperty("mysqlURL");
USERNAME = properties.getProperty("mysqlUserName");
PWD = properties.getProperty("mysqlPassWord");
}else{//连接oracle数据库
DRIVER = properties.getProperty("oracleDriver");
URL = properties.getProperty("oracleURL");
USERNAME = properties.getProperty("oracleUserName");
PWD = properties.getProperty("oraclePassword");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//共享对象是Connection对象
public static Connection getConn(){
Connection connection=null;
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
connection= DriverManager.getConnection(URL,USERNAME,PWD);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getConn());
}
}
jdbc.properties
#jdbc
#Tue Nov 12 17:20:32 CST 2019
mysqlUserName=root
mysqlDriver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type=mysql
mysqlPassWord=root
mysqlURL=jdbc\:mysql\://localhost\:3306/syl1105
oracleDriver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
oracleURL=jdbc\:oracle\:thin\:@192.168.151.241\:1521\:xe
oracleUserName=scott
oraclePassword=tiger





 本文介绍了注解、XML文件和属性文件在程序设计中的应用。详细讲解了注解的作用、格式、内置注解以及自定义注解的使用,并通过案例展示了如何通过反射读取注解信息。接着探讨了XML文件的编写和DOM4J解析,强调了XML文件在应用程序配置中的角色。最后提到了属性文件作为另一种存储程序数据的方式。
本文介绍了注解、XML文件和属性文件在程序设计中的应用。详细讲解了注解的作用、格式、内置注解以及自定义注解的使用,并通过案例展示了如何通过反射读取注解信息。接着探讨了XML文件的编写和DOM4J解析,强调了XML文件在应用程序配置中的角色。最后提到了属性文件作为另一种存储程序数据的方式。
















 1216
1216

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








