Crashing Robots
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 5708 | Accepted: 2492 |
Description
In a modernized warehouse, robots are used to fetch the goods. Careful planning is needed to ensure that the robots reach their destinations without crashing into each other. Of course, all warehouses are rectangular, and all robots occupy a circular floor space with a diameter of 1 meter. Assume there are N robots, numbered from 1 through N. You will get to know the position and orientation of each robot, and all the instructions, which are carefully (and mindlessly) followed by the robots. Instructions are processed in the order they come. No two robots move simultaneously; a robot always completes its move before the next one starts moving.
A robot crashes with a wall if it attempts to move outside the area of the warehouse, and two robots crash with each other if they ever try to occupy the same spot.
A robot crashes with a wall if it attempts to move outside the area of the warehouse, and two robots crash with each other if they ever try to occupy the same spot.
Input
The first line of input is K, the number of test cases. Each test case starts with one line consisting of two integers, 1 <= A, B <= 100, giving the size of the warehouse in meters. A is the length in the EW-direction, and B in the NS-direction.
The second line contains two integers, 1 <= N, M <= 100, denoting the numbers of robots and instructions respectively.
Then follow N lines with two integers, 1 <= Xi <= A, 1 <= Yi <= B and one letter (N, S, E or W), giving the starting position and direction of each robot, in order from 1 through N. No two robots start at the same position.
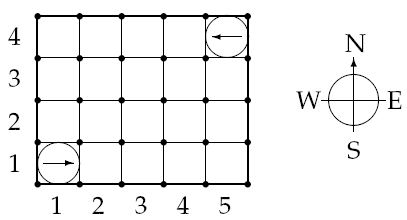
Figure 1: The starting positions of the robots in the sample warehouse
Finally there are M lines, giving the instructions in sequential order.
An instruction has the following format:
< robot #> < action> < repeat>
Where is one of
and 1 <= < repeat> <= 100 is the number of times the robot should perform this single move.
The second line contains two integers, 1 <= N, M <= 100, denoting the numbers of robots and instructions respectively.
Then follow N lines with two integers, 1 <= Xi <= A, 1 <= Yi <= B and one letter (N, S, E or W), giving the starting position and direction of each robot, in order from 1 through N. No two robots start at the same position.

Figure 1: The starting positions of the robots in the sample warehouse
Finally there are M lines, giving the instructions in sequential order.
An instruction has the following format:
< robot #> < action> < repeat>
Where is one of
- L: turn left 90 degrees,
- R: turn right 90 degrees, or
- F: move forward one meter,
and 1 <= < repeat> <= 100 is the number of times the robot should perform this single move.
Output
Output one line for each test case:
Only the first crash is to be reported.
- Robot i crashes into the wall, if robot i crashes into a wall. (A robot crashes into a wall if Xi = 0, Xi = A + 1, Yi = 0 or Yi = B + 1.)
- Robot i crashes into robot j, if robots i and j crash, and i is the moving robot.
- OK, if no crashing occurs.
Only the first crash is to be reported.
Sample Input
4
5 4
2 2
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 F 7
2 F 7
5 4
2 4
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 F 3
2 F 1
1 L 1
1 F 3
5 4
2 2
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 L 96
1 F 2
5 4
2 3
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 F 4
1 L 1
1 F 20
Sample Output
Robot 1 crashes into the wall
Robot 1 crashes into robot 2
OK
Robot 1 crashes into robot 2
题意:某个仓库很高科技 用机器人搬东西,告诉你机器人的个数 仓库的大小 给你一些让机器人转向或者移动的命令 让你判断机器人在执行这些命令的时候 会不会相撞或者撞墙。
//第一次的代码,改了无数次。麻烦死。没有经验啊。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct node
{
int x,y;
char direction;
}robotn[101];
struct nodeins
{
int num;
char action;
int repeat;
}robotm[101];
int main()
{
int K,A,B,N,M;
int i,j,yushu,just,mx,flag;
scanf("%d",&K);
while(K--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&A,&B);
scanf("%d%d",&N,&M);
for(i=1;i<=N;i++)
scanf("%d%d%*c%c",&robotn[i].x,&robotn[i].y,&robotn[i].direction);
for(i=1;i<=M;i++)
scanf("%d%*c%c%d",&robotm[i].num,&robotm[i].action,&robotm[i].repeat);
for(i=1;i<=M;i++)
{
if(robotm[i].action=='F')
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].y;
robotn[robotm[i].num].y+=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].y>B)
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].y>just&&robotn[j].y<=B)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].y) {mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall\n",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&
robotn[j].y>just&&robotn[j].y<=robotn[robotm[i].num].y)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].y){mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].x;
robotn[robotm[i].num].x+=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].x>A)
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].x>just&&robotn[j].x<=A)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall\n",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x>just&&robotn[j].x<=robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&
robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].y;
robotn[robotm[i].num].y-=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].y<=0)
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].y>=robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].y<just)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].y){mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall\n",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&
robotn[j].y>=robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].y<just)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].y){mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
else
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].x;
robotn[robotm[i].num].x-=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].x<=0)
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].x>=robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].x<just)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0) {printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall\n",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x>=robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].x<just&&
robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
}
else if(robotm[i].action=='L')
{
yushu=robotm[i].repeat%4;
if(yushu==1)
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='W';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='N';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='E';
else robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='S';
}
else if(yushu==2)
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='S';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='W';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='N';
else robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='E';
}
else if(yushu==3)
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='E';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='S';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='W';
else robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='N';
}
}
else
{
yushu=robotm[i].repeat%4;
if(yushu==1)
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='E';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='S';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='W';
else robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='N';
}
else if(yushu==2)
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='S';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='W';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='N';
else robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='E';
}
else if(yushu==3)
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='N')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='W';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='E')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='N';
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=='S')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='E';
else robotn[robotm[i].num].direction='S';
}
}
}
if(i>M) printf("OK\n");
}
return 0;
}
//第二次的代码。对左转,右转简单的处理,一句话就行。把四个方向按0-3编号。//可惜还是不能把代码量缩小,水平还是太低。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct node
{
int x,y;
int direction;
}robotn[101];
struct nodeins
{
int num;
char action;
int repeat;
}robotm[101];
int main()
{
int K,A,B,N,M;
int i,j,just,mx,flag;
char dir;
scanf("%d",&K);
while(K--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&A,&B);
scanf("%d%d",&N,&M);
for(i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%*c%c",&robotn[i].x,&robotn[i].y,&dir);
switch(dir)
{
case 'N':robotn[i].direction=0;break;
case 'E':robotn[i].direction=1;break;
case 'S':robotn[i].direction=2;break;
case 'W':robotn[i].direction=3;break;
}
}
for(i=1;i<=M;i++)
scanf("%d%*c%c%d",&robotm[i].num,&robotm[i].action,&robotm[i].repeat);
for(i=1;i<=M;i++)
{
if(robotm[i].action=='F')
{
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction==0)
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].y;
robotn[robotm[i].num].y+=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].y>B)
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].y>just&&robotn[j].y<=B)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].y) {mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&
robotn[j].y>just&&robotn[j].y<=robotn[robotm[i].num].y)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].y){mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction==1)
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].x;
robotn[robotm[i].num].x+=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].x>A)
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].x>just&&robotn[j].x<=A)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=101;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x>just&&robotn[j].x<=robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&
robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y)
{
if(mx>robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=101){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
else if(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction==2)
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].y;
robotn[robotm[i].num].y-=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].y<=0)
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].y>=1&&robotn[j].y<just)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].y){mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x==robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&
robotn[j].y>=robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].y<just)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].y){mx=robotn[j].y;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
else
{
just=robotn[robotm[i].num].x;
robotn[robotm[i].num].x-=robotm[i].repeat;
if(robotn[robotm[i].num].x<=0)
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y&&robotn[j].x>=1&&robotn[j].x<just)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0) {printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
if(j>N)
{printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall",robotm[i].num);
break;}
}
else
{
mx=0;
for(j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(robotm[i].num!=j&&robotn[j].x>=robotn[robotm[i].num].x&&robotn[j].x<just&&
robotn[j].y==robotn[robotm[i].num].y)
{
if(mx<robotn[j].x){mx=robotn[j].x;flag=j;}
}
}
if(mx!=0){printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d",robotm[i].num,flag);break;}
}
}
}
else if(robotm[i].action=='L')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction-robotm[i].repeat%4+4)%4;
else if(robotm[i].action=='R')
robotn[robotm[i].num].direction=(robotn[robotm[i].num].direction+robotm[i].repeat%4)%4;
}
if(i>M) printf("OK");
if(K) printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}





 本文概述了AI音视频处理领域的关键技术,包括视频分割、语义识别、自动驾驶、AR、SLAM等,并探讨了其在实际应用中的作用。
本文概述了AI音视频处理领域的关键技术,包括视频分割、语义识别、自动驾驶、AR、SLAM等,并探讨了其在实际应用中的作用。
















 901
901

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








