栈和队列的定义和实现
- 栈和队列的定义
栈是一种线性的数据结构,只能在一端进行插入和删除,其中的元素满足先进后出的规则。队列也是一种线性数据结构,只能在一端插入,另一端删除,其中元素满足先进先出的规则。


- 栈和队列的java实现
- 首先定义一个可以在同时在两端进行插入和删除的线性表,然后通过限制该线性表只能在一端进行插入和删除来构建栈和队列
//
public class Code03_DoubleEndsQueueToStackAndQueue {
// 线性表节点
public static class Node<T> {
public T value;
// 节点有两个指针,last指向线性表的上一个节点,next指向线性表的下一个节点
public Node<T> last;
public Node<T> next;
public Node(T data) {
value = data;
}
}
public static class DoubleEndsQueue<T> {
public Node<T> head;
public Node<T> tail;
// 从头部增加节点
public void addFromHead(T value) {
Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);
if (head == null) {
head = cur;
tail = cur;
} else {
cur.next = head;
head.last = cur;
head = cur;
}
}
// 从尾部增加节点
public void addFromBottom(T value) {
Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);
if (head == null) {
head = cur;
tail = cur;
} else {
cur.last = tail;
tail.next = cur;
tail = cur;
}
}
// 从头部弹出节点
public T popFromHead() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 记录要被弹出的节点
Node<T> cur = head;
if (head == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
head = head.next;
cur.next = null;
head.last = null;
}
return cur.value;
}
// 从尾部弹出节点
public T popFromBottom() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 记录要被弹出的节点
Node<T> cur = tail;
if (head == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
tail = tail.last;
tail.next = null;
cur.last = null;
}
return cur.value;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
}
// 构建栈结构
public static class MyStack<T> {
private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();
}
// 只能从头部压入节点
public void push(T value) {
queue.addFromHead(value);
}
// 只能从头部弹出节点
public T pop() {
return queue.popFromHead();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
// 构建队列
public static class MyQueue<T> {
private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;
public MyQueue() {
queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();
}
// 从一端压入数据
public void push(T value) {
queue.addFromHead(value);
}
// 从另一端弹出数据
public T poll() {
return queue.popFromBottom();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
}
栈和队列的简单问题
- 用固定大小的数组实现栈和队列
- 固定大小数组实现栈
用固定数据实现栈比较简单,只需要用一个index变量指向数组中栈顶元素的下一个位置,在入栈的时候,直接将元素放到index的位置,然后index++,在出栈的时候,返回index-1位置的元素,然后将index–。过程示意图如下:

- 固定大小数组实现队列
用固定大小的数组实现队列比栈要复杂,因为队列需要两个变量来分别来控制队首元素的出队和队尾元素的入队,当队尾指针指向数组尾部最大边界,而数组头部又有空位时,此时如果有元素入队,队尾指针需要移动到数组的头部;队首指针也会遇到这种问题。所以为了简便的控制这两个指针,这里引入size和limit两个参数,size记录当前队列中的元素,limit存储数组的最大容量,具体过程如下示意图:
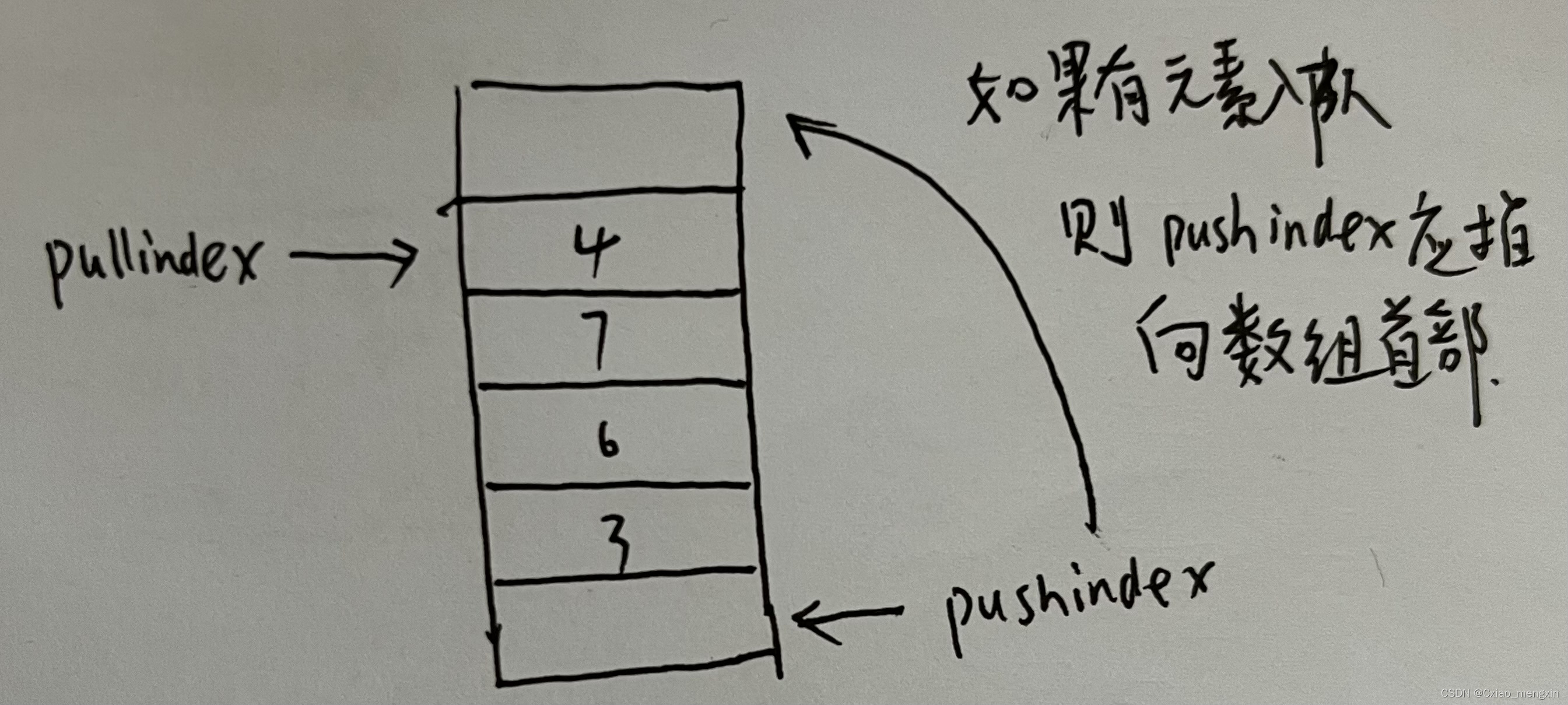
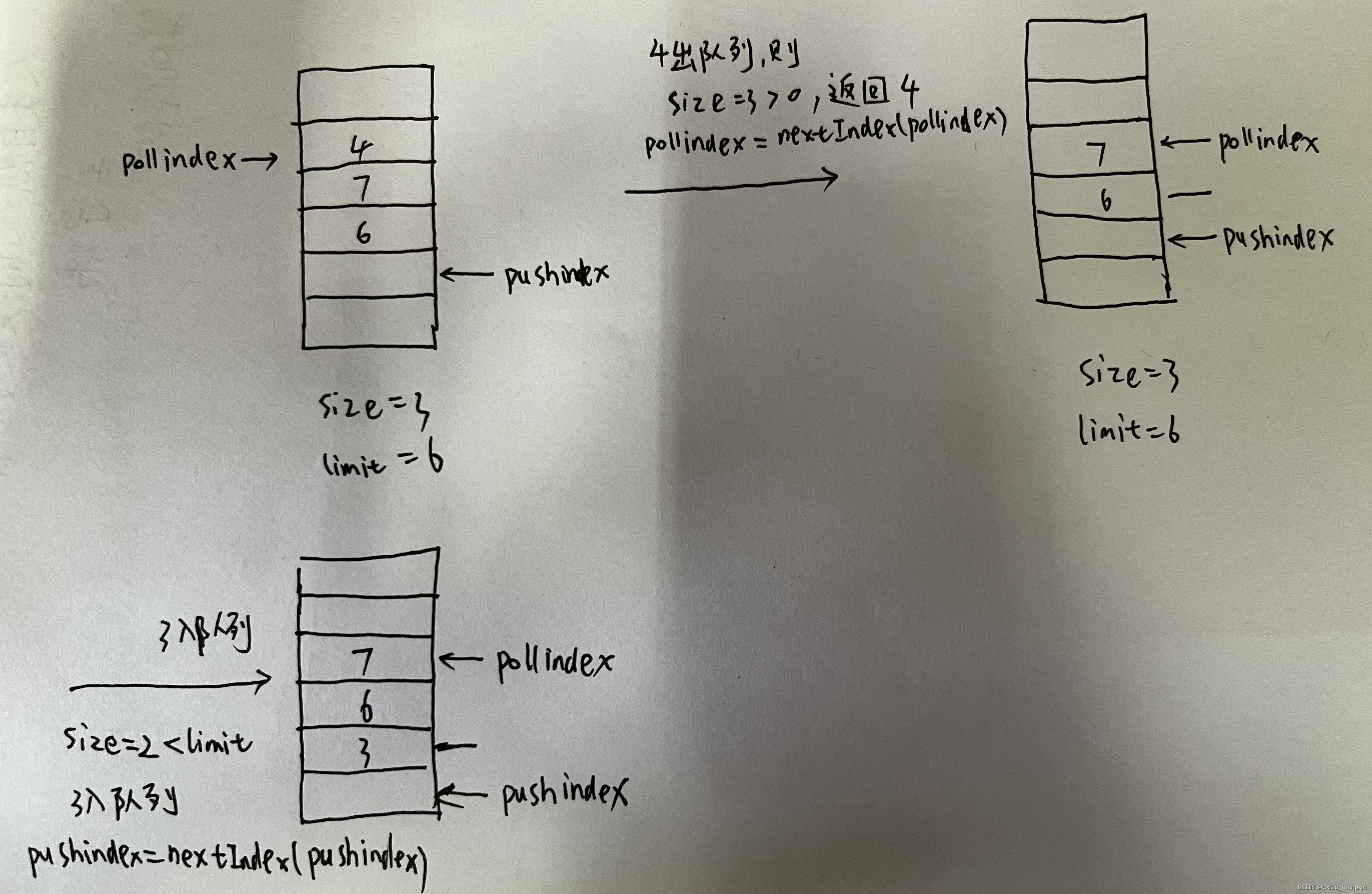
java代码实现如下
public class RingArray {
public static class MyQueue {
private int[] arr;
private int pushi;// 队尾指针
private int polli;// 队首指针
private int size; // 记录当前队列中元素个数
private final int limit; // 数组的最大容量
public MyQueue(int limit) {
arr = new int[limit];
pushi = 0;
polli = 0;
size = 0;
this.limit = limit;
}
public void push(int value) {
if (size == limit) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列满了,不能再加了");
}
size++;
arr[pushi] = value;
pushi = nextIndex(pushi);
}
public int pop() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空了,不能再拿了");
}
size--;
int ans = arr[polli];
polli = nextIndex(polli);
return ans;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 如果现在的下标是i,返回下一个位置
private int nextIndex(int i) {
return i < limit - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;
}
}
}
- 设计一个栈,在实现栈基本功能的基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的功能
要求如下:
- pop, push, getMin 的操作都是O(1)时间复杂度
- 设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构
使用两个栈就可以实现这个功能。将一个栈作为data栈,另一个栈作为min栈。初始时两个栈都为空,此时第一个元素入栈,第一个元素同时入data栈和min栈,即如果两个栈都为空,则元素入栈是同时入两个栈。如果两个栈元素不为空,则元素入栈时,对于data栈直接入栈,对于min栈,如果入栈的元素小于min栈的栈顶,则元素如min栈,否则将min栈栈顶元素再次入min栈。元素出栈时,两个栈的栈顶同时出栈。这样无论何时,min栈的栈顶都是栈中最小元素,这是用空间换时间的做法。
示意图如下:
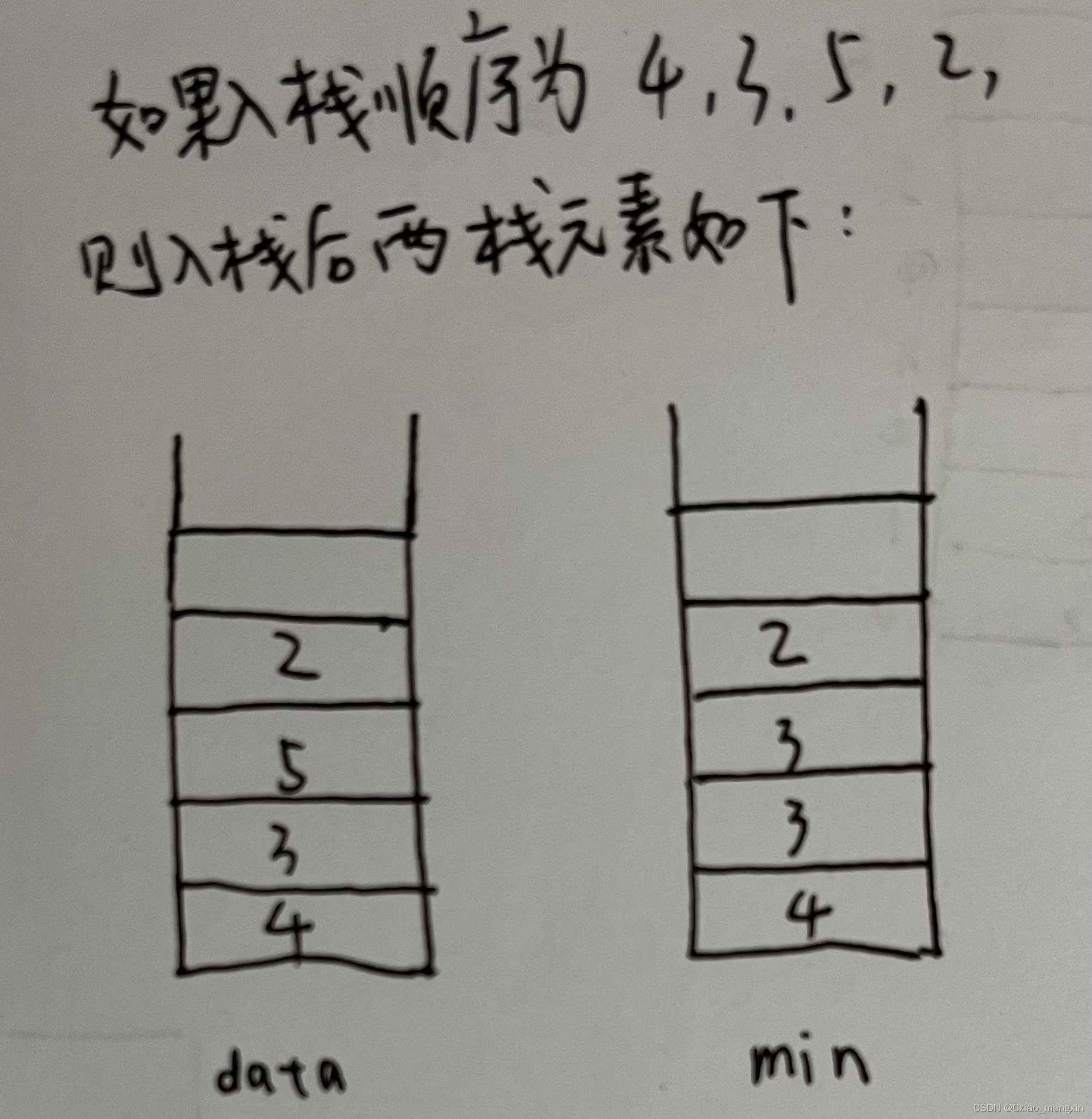
java代码如下
public class GetMinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stackData;
private Stack<Integer> stackMin;
public GetMinStack() {
this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();
this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int newNum) {
if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {
this.stackMin.push(newNum);
} else if (newNum < this.getmin()) {
this.stackMin.push(newNum);
} else {
int newMin = this.stackMin.peek();
this.stackMin.push(newMin);
}
this.stackData.push(newNum);
}
public int pop() {
if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");
}
this.stackMin.pop();
return this.stackData.pop();
}
public int getmin() {
if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");
}
return this.stackMin.peek();
}
}
- 如何只用队列结构实现栈结构
使用两个队列,其中一个队列是data队列,另一个是help队列。在没有进行任何操作时,data队列中存放当前栈中的所有元素,help队列为空。当元素出栈时,将data队列中的前n-1个元素入help队列(前n-1个元素出data队列,并入help队列),然后将data队列的最后一个元素返回(最后一个元素出data队列),此时data队列为空。然后将help队列改为data队列,data队列改为help队列。当元素入栈时,直接将元素放到data队列的队尾。
public class Code07_TwoQueueImplementStack {
public static class TwoQueueStack<T> {
public Queue<T> queue;
public Queue<T> help;
public TwoQueueStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
help = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(T value) {
queue.offer(value);
}
public T poll() {
while (queue.size() > 1) {
help.offer(queue.poll());
}
T ans = queue.poll();
Queue<T> tmp = queue;
queue = help;
help = tmp;
return ans;
}
// 返回栈顶元素
public T peek() {
while (queue.size() > 1) {
help.offer(queue.poll());
}
T ans = queue.poll();
help.offer(ans);
Queue<T> tmp = queue;
queue = help;
help = tmp;
return ans;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
}
- 如何使用栈结构实现队列结构
使用连个栈,其中一个是push栈,另一个是pop栈。push栈是元素入队时首先进入的栈,pop栈是元素出队前存放的位置。要想用着两个栈实现队列,需要增加一个push栈元素进pop栈的操作,即将push栈中的元素全部入pop栈,但这要遵循两个原则:
1) 只有pop栈为空时,才能将push栈中元素导入pop栈
2) 当向push栈中导元素是,必须将push栈元素全部导空
java代码如下
public static class TwoStacksQueue {
public Stack<Integer> stackPush;
public Stack<Integer> stackPop;
public TwoStacksQueue() {
stackPush = new Stack<Integer>();
stackPop = new Stack<Integer>();
}
// push栈向pop栈倒入数据
private void pushToPop() {
// 只有pop栈为空时,才能导数据
if (stackPop.empty()) {
while (!stackPush.empty()) {
// 将push栈所有元素导入pop栈
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
}
public void add(int pushInt) {
stackPush.push(pushInt);
pushToPop();
}
public int poll() {
if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
}
// 在元素出队前,先将push栈中元素导入pop栈
pushToPop();
return stackPop.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
}
pushToPop();
return stackPop.peek();
}
}







 本文介绍了栈和队列的基本定义和Java实现,包括固定大小数组实现栈和队列,以及如何设计特殊功能的栈(返回最小元素)和仅用队列实现栈的算法。
本文介绍了栈和队列的基本定义和Java实现,包括固定大小数组实现栈和队列,以及如何设计特殊功能的栈(返回最小元素)和仅用队列实现栈的算法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








