概述
什么是MQ?
MQ:Message Queue,消息队列。
MQ常见产品有ActiveMQ、RabbitMQ、RocketMQ、Kafka。
为什么会出现MQ?(MQ作用)
- 削峰填谷(主要):没有MQ时,大量请求到来时,系统只能拒绝请求保护自己,MQ可以在中间起到“水库”的作用,洪峰到来时,可以储存一部分水(请求),在河道(下游系统)水位降低后再排水。
- 解耦:MQ在消息发送方和接收方之间起“媒婆”的作用,避免了发送方和接收方的直接交流,防止尴尬。接收方不在线时,MQ可存储消息,等待接收方的上线。
系统引入MQ后有什么新问题?(MQ缺点)
- 增加系统复杂性:系统引入任何一个组件都会增加系统复杂性。复杂性的增加往往降低了系统的可靠性、可维护性等其他质量属性。
- 只能异步调用:MQ增加了系统调用耗时,为了可以削峰填谷,也必须异步调用。所以,MQ更适合耗时较高的业务调用,同时消息发送方必须做业务的异步化。
模式
- 队列(queue)模式:点对点模式,一条消息只能被一个消费者消费。
- 主题(topic)模式:发布/订阅模式,一条消息可以同时被多个消费者消费。
Java API
测试框架(队列模式)
public class JmsTest {
private Connection connection;
private Session session;
private Destination destination;
@Before
public void init() throws JMSException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
this.connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
this.session = this.connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
this.destination = this.session.createQueue("test-queue");
// this.destination = this.session.createTopic("test-topic");
}
@After
public void destroy() throws JMSException {
this.session.close();
this.connection.close();
}
}
发送消息
@Test
public void testSend() throws JMSException {
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(destination);
Message message = new ActiveMQTextMessage() {{
this.setText("Hello, MQ!");
this.setJMSType("String");
}};
producer.send(message);
producer.close();
}
接收消息
@Test
public void testReceive() throws JMSException {
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);
connection.start();
TextMessage message = (TextMessage) consumer.receive();
String text = message.getText();
System.out.println(text);
consumer.close();
}
消息监听器
@Test
public void testListener() throws JMSException, IOException {
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(destination);
connection.start();
consumer.setMessageListener((message) -> {
TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;
try {
System.out.println(textMessage.getText());
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.in.read();
consumer.close();
}
JMS
JMS是什么
JMS:Java Message Service,Java消息服务,定义了消息中间接的API标准。
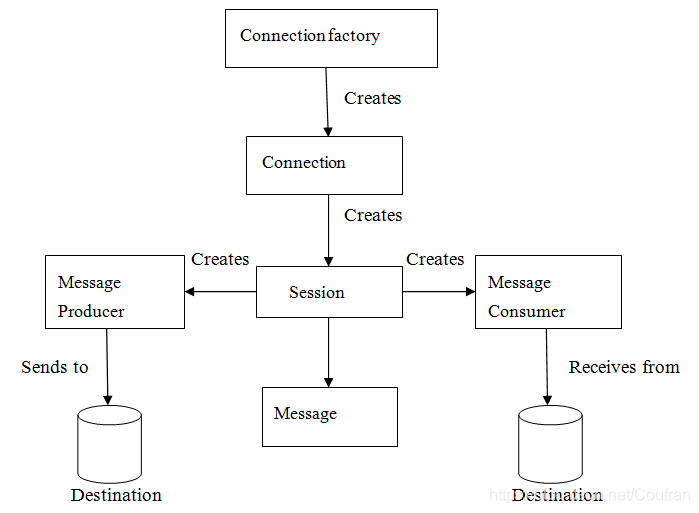
ConnectionFactory:连接工厂,负责创建Connection连接,其维护了创建连接的配置参数。Connection:连接,封装了与JMS Provider的连接。Session:用于生产和消费消息的单线程上下文。MessageProducer:消息生产者。MessageConsumer:消息消费者。Destination:目标。细分为Queue和Topic。
消息(Message)
- 消息头
| 消息头 | 解释 | 设置方 |
|---|---|---|
| JMSDestination | 目的地 | send |
| JMSDeliveryMode | 发送模式(持久化) | send |
| JMSMessageID | 消息ID | send |
| JMSTimestamp | 发送时间 | send |
| JMSCorrelationID | 关联的消息ID | client |
| JMSReplyTo | 消息回复的目的地 | client |
| JMSRedelivered | 是否重复发送 | provider |
| JMSType | 消息类型 | client |
| JMSExpiration | 过期时间(ms) | send |
| JMSPriority | 优先级(0-4普通、5-9高) | send |
- 消息体
| 类型 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| TextMessage | 文本消息 |
| ObjectMessage | 对象消息(对象需实现Serializable接口) |
| BytesMessage | 字节消息 |
| StreamMessage | 流消息 |
| MapMessage | 键值对消息 |
- 消息属性
持久化
- queue默认持久化,是否持久化取决于生产者,通过以下代码设置。
// 注意:手动设置``Message.setJMSDeliveryMode``无效。
producer.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.NON_PERSISTENT); // 设置非持久化
producer.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.PERSISTENT); // 设置持久化
- topic模式默认非持久订阅,是否持久化取决于消费者,通过以下代码设置。
Session.createDurableSubscriber(topic, name); // JMS 1.x 设置持久订阅
Session.createDurableConsumer(topic, name); // JMS 2.x 设置持久订阅
Session.unsubscribe(name); // 取消持久订阅
事务(transacted)
- 事务下的消息是原子性的,要么同时生产/消费成功,要么同时生成/消费失败。
- 事务对消息生产者和消息消费者都有效。
- 事务通过创建
Session时的参数指定,代码如下。
Connection.createSession(true, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); // 第一个参数代表是否启用事务
- 启用事务时,需要通过
Session提交或回滚完成事务,代码如下。
Session.commit(); // 提交事务
Session.rollback(); // 回滚事务
签收(acknowledge)
- 签收针对消息消费者,消息消费者通过签收消息的动作表示消息已被消费。
- 签收模式
AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE:自动签收。
CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE:手动签收。
DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE:自动批量签收。
SESSION_TRANSACTED:事务签收,事务提交时自动签收,事务回滚时不签收。 - 消息通过如下代码签收。
Message.acknowledge(); // 签收消息
Spring、Spring Boot整合JMS
- Spring定义了
JmsTemplate,通过JmsTemplate操作。 - Spring Boot通过
spring-boot-starter-activemq整合。
ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ Broker(Embed ActiveMQ)
Broker:内嵌的ActiveMQ。
BrokerService brokerService = new BrokerService();
brokerService.setUseJmx(true);
brokerService.addConnector("tcp://localhost:61616");
brokerService.start();
System.in.read();
ActiveMQ协议
TCP、NIO、UDP、SSL、HTTP(S)、VM等。
ActiveMQ持久化
KahaDB(默认)、LevelDB、JDBC。
ActiveMQ集群
- Broker集群
- Broker集群中所有单点同时提供服务。
- 主从(Master Slave)
- 该模式提供了高可用的ActiveMQ集群。
- 主从的基本原则是共享持久化存储,分为“共享文件系统”、“JDBC共享数据库”和“自我复制的Level DB”三种方式。
- Slave不对外提供服务,Master宕机后,Slave自动升级为Master,开始对外提供服务。
ActiveMQ高级特性
- 异步发送(Async Sends):Producer不等待Broker的确认,直接返回发送成功。可能丢失消息,所以需要手动确认(可以接收回调),必要时补偿消息。
- 延时/定时投递(Delay and Schedule Message Delivery)
- 重投递策略(Redelivery Policy):投递失败后会间隔指定时间发送多次重新投递,总是投递失败的放到死信队列(DLQ)中
- 死信队列(Dead-Letter Queue,DLQ)
- more…





















 965
965










