Factoring
So far we’ve been using the product of small primes for the modulus, but small primes aren’t much good for RSA as they can be factorised using modern methods.
What is a “small prime”? There was an RSA Factoring Challenge with cash prizes given to teams who could factorise RSA moduli. This gave insight to the public into how long various key sizes would remain safe. Computers get faster, algorithms get better, so in cryptography it’s always prudent to err on the side of caution.
These days, using primes that are at least 1024 bits long is recommended—multiplying two such 1024 primes gives you a modulus that is 2048 bits large. RSA with a 2048-bit modulus is called RSA-2048.
Some say that to really remain future-proof you should use RSA-4096 or even RSA-8192. However, there is a tradeoff here; it takes longer to generate large prime numbers, plus modular exponentiations are predictably slower with a large modulus.
Factorise the 150-bit number 510143758735509025530880200653196460532653147into its two constituent primes. Give the smaller one as your answer.
Resources:
方式1:质因数分解网站:http://factordb.com/
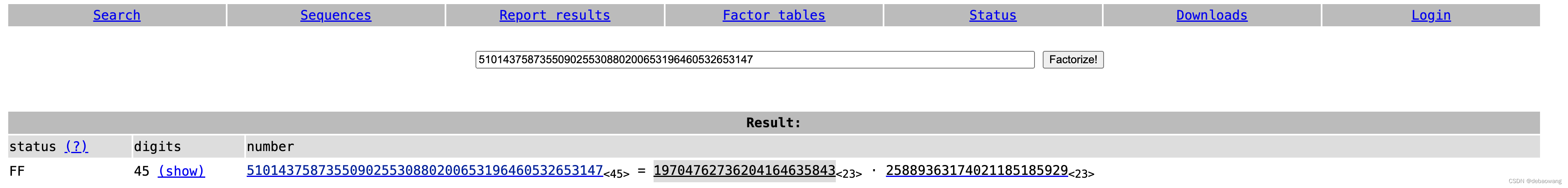
方式2:Using sagemath
# in SageMath
factor(510143758735509025530880200653196460532653147 )
# 19704762736204164635843 * 25889363174021185185929
相关视频:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SmJRKo4XL18&ab_channel=JohnHammond
这个视频内容是有关RSA整数分解的一道题,作用使用python的pwntools模块来维持一个http session 通过该session完成提交整数分解的结果。质因数分解用的是python primefac module。
summary:
现有的整数分解算法可以快速分解“小整数”。因此RSA中小模数N是不安全的。
Monoprime
Why is everyone so obsessed with multiplying two primes for RSA. Why not just use one?
Challenge files:
Resources:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util import number
n = 171731371218065444125482536302245915415603318380280392385291836472299752747934607246477508507827284075763910264995326010251268493630501989810855418416643352631102434317900028697993224868629935657273062472544675693365930943308086634291936846505861203914449338007760990051788980485462592823446469606824421932591
e = 65537
ct = 161367550346730604451454756189028938964941280347662098798775466019463375610700074840105776873791605070092554650190486030367121011578171525759600774739890458414593857709994072516290998135846956596662071379067305011746842247628316996977338024343628757374524136260758515864509435302781735938531030576289086798942
if number.isPrime(n):
phi_n = n - 1
d = number.inverse(e, phi_n)
pt = pow(ct, d, n)
pt = number.long_to_bytes(pt).decode()
print(pt)
Manyprime
题目描述
Using one prime factor was definitely a bad idea so I’ll try using over 30 instead.
If it’s taking forever to factorise, read up on factorisation algorithms and make sure you’re using one that’s optimised for this scenario.
Challenge files:
Resources:
首先对N进行素因子分解
# in sagemath
n = 580642391898843192929563856870897799650883152718761762932292482252152591279871421569162037190419036435041797739880389529593674485555792234900969402019055601781662044515999210032698275981631376651117318677368742867687180140048715627160641771118040372573575479330830092989800730105573700557717146251860588802509310534792310748898504394966263819959963273509119791037525504422606634640173277598774814099540555569257179715908642917355365791447508751401889724095964924513196281345665480688029639999472649549163147599540142367575413885729653166517595719991872223011969856259344396899748662101941230745601719730556631637
e = 65537
ct = 320721490534624434149993723527322977960556510750628354856260732098109692581338409999983376131354918370047625150454728718467998870322344980985635149656977787964380651868131740312053755501594999166365821315043312308622388016666802478485476059625888033017198083472976011719998333985531756978678758897472845358167730221506573817798467100023754709109274265835201757369829744113233607359526441007577850111228850004361838028842815813724076511058179239339760639518034583306154826603816927757236549096339501503316601078891287408682099750164720032975016814187899399273719181407940397071512493967454225665490162619270814464
ecm.factor(n)
得到素分解之后,
- 计算
N的Euler totient - 求e的逆元,得到d
- 执行RSA解密算法
- 将数字转换为字符串,得到flag
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util import number
n = 580642391898843192929563856870897799650883152718761762932292482252152591279871421569162037190419036435041797739880389529593674485555792234900969402019055601781662044515999210032698275981631376651117318677368742867687180140048715627160641771118040372573575479330830092989800730105573700557717146251860588802509310534792310748898504394966263819959963273509119791037525504422606634640173277598774814099540555569257179715908642917355365791447508751401889724095964924513196281345665480688029639999472649549163147599540142367575413885729653166517595719991872223011969856259344396899748662101941230745601719730556631637
e = 65537
ct = 320721490534624434149993723527322977960556510750628354856260732098109692581338409999983376131354918370047625150454728718467998870322344980985635149656977787964380651868131740312053755501594999166365821315043312308622388016666802478485476059625888033017198083472976011719998333985531756978678758897472845358167730221506573817798467100023754709109274265835201757369829744113233607359526441007577850111228850004361838028842815813724076511058179239339760639518034583306154826603816927757236549096339501503316601078891287408682099750164720032975016814187899399273719181407940397071512493967454225665490162619270814464
# 通过sage对N进行分解得到
factors = [9282105380008121879,
9303850685953812323,
9389357739583927789,
10336650220878499841,
10638241655447339831,
11282698189561966721,
11328768673634243077,
11403460639036243901,
11473665579512371723,
11492065299277279799,
11530534813954192171,
11665347949879312361,
12132158321859677597,
12834461276877415051,
12955403765595949597,
12973972336777979701,
13099895578757581201,
13572286589428162097,
14100640260554622013,
14178869592193599187,
14278240802299816541,
14523070016044624039,
14963354250199553339,
15364597561881860737,
15669758663523555763,
15824122791679574573,
15998365463074268941,
16656402470578844539,
16898740504023346457,
17138336856793050757,
17174065872156629921,
17281246625998849649]
phi_n = 1
for i in factors:
phi_n *= i-1
d = number.inverse(e, phi_n) # get private key
pt = number.long_to_bytes(pow(ct, d, n)).decode()
print(pt)
在线的sagemath: https://sagecell.sagemath.org/
sage lesson: https://github.com/fredstro/sage-lesson-nt
sage 官方教程https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/index.html
博客教程1:https://cocalc.com/share/public_paths/embed/ee63291fa9aadeb8d5830f5c518cddb466501a70
博客教程2: https://blog.devgenius.io/sagemath-doing-math-in-python-8c34765254f7
Salty
题目描述:
Smallest exponent should be fastest, right?
Challenge files:
由于公钥 e = 1 e=1 e=1,因此无论 ϕ ( n ) \phi(n) ϕ(n)的值为多少,私钥 d d d始终为1。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util import number
n = 110581795715958566206600392161360212579669637391437097703685154237017351570464767725324182051199901920318211290404777259728923614917211291562555864753005179326101890427669819834642007924406862482343614488768256951616086287044725034412802176312273081322195866046098595306261781788276570920467840172004530873767
e = 1
ct = 44981230718212183604274785925793145442655465025264554046028251311164494127485
d = 1
pt = pow(ct, d, n)
flag = number.long_to_bytes(pt).decode()
print(flag)
这道题告诉我们,RSA的公钥采用 e = 1 e=1 e=1不安全。
Modulus Inutilis
My primes should be more than large enough now!
Challenge files:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import gmpy2
from Crypto.Util import number
"""
Because m is small, m^3 is close to n, so we can compute the 3-th root of c + k*n where k=0,1,2...
"""
n = 17258212916191948536348548470938004244269544560039009244721959293554822498047075403658429865201816363311805874117705688359853941515579440852166618074161313773416434156467811969628473425365608002907061241714688204565170146117869742910273064909154666642642308154422770994836108669814632309362483307560217924183202838588431342622551598499747369771295105890359290073146330677383341121242366368309126850094371525078749496850520075015636716490087482193603562501577348571256210991732071282478547626856068209192987351212490642903450263288650415552403935705444809043563866466823492258216747445926536608548665086042098252335883
e = 3
ct = 243251053617903760309941844835411292373350655973075480264001352919865180151222189820473358411037759381328642957324889519192337152355302808400638052620580409813222660643570085177957
def low_e_attack(ct,e,n):
i = 0
while True:
y, r = gmpy2.iroot(ct + i * n, e) # Return the integer n-th root of x and boolean value that is True iff the root is exact. x >= 0. n > 0.
if r == True:
print(f"i = {i}")
flag = number.long_to_bytes(y).decode()
print(flag)
exit()
i = i + 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
low_e_attack(ct,e,n)
Diffie-Hellman Starter 1
The set of integers modulo n, together with the operations of both addition and multiplication is a ring. This means that adding or multiplying any two elements in the set returns another element in the set.
When the modulus is prime: n = p, we are guaranteed an inverse of every element in the set, and so the ring is promoted to a field. We refer to this field as a finite field
F
p
F_p
Fp.
The Diffie-Hellman protocol works with elements of some finite field Fp, where the prime modulus is typically a large prime.
Given the prime p = 991, and the element g = 209, find the inverse element d such that g * d mod 991 = 1.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util import number
p = 991
g = 209
d = number.inverse(g, p)
print(f"d = {d}")




















 1191
1191

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








