AJAX 的基石是 XMLHttpRequest 对象。
1.创建一个 XMLHttpRequest 对象
2.定义回调函数
3.打开 XMLHttpRequest 对象
4.向服务器发送请求
所有现代浏览器都支持 XMLHttpRequest 对象。
XMLHttpRequest 对象可用于在后台与 Web 服务器交换数据。这意味着可以更新网页的部分内容,而无需重新加载整个页面。
所有现代浏览器(Chrome、Firefox、IE、Edge、Safari、Opera)都有一个内置的 XMLHttpRequest 对象。
创建 XMLHttpRequest 对象的语法:
variable = new XMLHttpRequest();
定义回调函数
回调函数是作为参数传递给另一个函数的函数。
在这种情况下,回调函数应包含响应准备就绪时要执行的代码。
xhttp.onload = function() {
// What to do when the response is ready
}
发送请求
要向服务器发送请求,可以使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 open() 和 send() 方法:
xhttp.open("GET", "ajax_info.txt");
xhttp.send();
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>The XMLHttpRequest Object</h2>
<div id="demo">
<p>Let AJAX change this text.</p>
<button type="button" onclick="loadDoc()">Change Content</button>
</div>
<script>
function loadDoc() {
const xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onload = function() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = this.responseText;
}
xhttp.open("GET", "ajax_info.txt");
xhttp.send();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>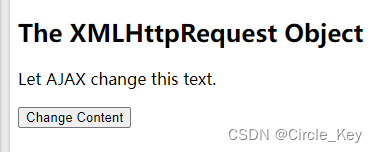

跨域访问
出于安全原因,现代浏览器不允许跨域访问。
这意味着网页和它尝试加载的 XML 文件必须位于同一台服务器上。
W3Schools 上的示例都打开位于 W3Schools 域中的 XML 文件。
如果您想在您自己的网页之一上使用上面的示例,您加载的 XML 文件必须位于您自己的服务器上。
XMLHttpRequest Object Methods XMLHttpRequest 对象方法
方法 | 描述 |
| new XMLHttpRequest() | 创建一个新的XMLHttpRequest对象 |
| abort() | •取消当前请求 |
| getAllResponseHeaders() | 返回报头信息 |
| getResponseHeader() | •返回特定的标头信息 |
| open(method, url, async, user, psw) | 。指定请求。 method: the request type GET or POST |
| send() | 将请求发送到用于GET请求的服务器 |
| send(string) | 将请求发送到服务器。用于POST请求 |
| setRequestHeader() | 将标签/值对添加到要发送的报头中 |
XMLHttpRequest Object Properties XMLHttpRequest 对象属性
属性 | 描述 |
| onload | 定义接收(加载)请求时要调用的函数。 |
| onreadystatechange | 定义readyState属性更改时要调用的函数 |
| readyState | 保存XMLHttpRequest的状态。 0:请求未初始化 1:服务器连接建立 2:请求收到 3:处理请求 4:请求完成,响应就绪 |
| responseText | 将响应数据作为字符串返回 |
| responseXML | 将响应数据作为XML数据返回 |
| status | 返回请求的状态号 200:“OK 403: "禁止" ”404:“未找到”有关完整列表, 请参阅Http消息参考HTTP Messages |
| statusText | •返回状态文本(例如:“正常”或“未找到”) |
The onload Property onload 属性
使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象,您可以定义一个回调函数,以便在请求收到答复时执行。
该函数在
XMLHttpRequest对象的onload属性中定义:<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id="demo"> <h2>The XMLHttpRequest Object</h2> <button type="button" onclick="loadDoc()">Change Content</button> </div> <script> function loadDoc() { const xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhttp.onload = function() { document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = this.responseText; } xhttp.open("GET", "ajax_info.txt"); xhttp.send(); } </script> </body> </html>
Multiple Callback Functions 多个回调函数
如果网站中有多个 AJAX 任务,则应创建一个函数来执行 XMLHttpRequest 对象,并为每个 AJAX 任务创建一个回调函数。
函数调用应包含 URL 以及响应准备就绪时要调用的函数。
loadDoc("url-1", myFunction1);
loadDoc("url-2", myFunction2);
function loadDoc(url, cFunction) {
const xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onload = function() {cFunction(this);}
xhttp.open("GET", url);
xhttp.send();
}
function myFunction1(xhttp) {
// action goes here
}
function myFunction2(xhttp) {
// action goes here
}The onreadystatechange Property onreadystatechange 属性
readyState 属性保存 XMLHttpRequest 的状态。
onreadystatechange 属性定义了一个回调函数,当 readyState 改变时执行。
status 属性和 statusText 属性保存 XMLHttpRequest 对象的状态。
属性 | 描述 |
| onreadystatechange | 定义readyState属性更改时要调用的函数 |
| readyState | 保存XMLHttpRequest的状态。 0:请求未初始化 1:服务器连接建立 2:请求收到 3:处理请求 4:请求完成,响应就绪 |
| status | 返回请求的状态号 200:“OK 403: "禁止" ”404:“未找到”有关完整列表, 请参阅Http消息参考HTTP Messages |
| statusText | •返回状态文本(例如:“正常”或“未找到”) |
每次 readyState 改变时都会调用 onreadystatechange 函数。
当 readyState 为 4 且状态为 200 时,响应就绪:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="demo">
<h2>The XMLHttpRequest Object</h2>
<button type="button" onclick="loadDoc()">Change Content</button>
</div>
<script>
function loadDoc() {
const xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML =
this.responseText;
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "ajax_info.txt");
xhttp.send();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>注意
onreadystatechange事件被触发四次 (1-4),每次 readyState 发生变化一次。




 AJAX的核心是XMLHttpRequest对象,用于与服务器异步交换数据。创建XMLHttpRequest对象后,定义回调函数,通过open()和send()方法向服务器发送请求。现代浏览器均内置此对象。AJAX请求需同源策略,否则受限于跨域访问。onload和onreadystatechange属性用于处理响应,当readyState为4且状态为200时,表示响应完成。
AJAX的核心是XMLHttpRequest对象,用于与服务器异步交换数据。创建XMLHttpRequest对象后,定义回调函数,通过open()和send()方法向服务器发送请求。现代浏览器均内置此对象。AJAX请求需同源策略,否则受限于跨域访问。onload和onreadystatechange属性用于处理响应,当readyState为4且状态为200时,表示响应完成。
















 1324
1324

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








