


- 2) SIGINT
程序终止(interrupt)信号, 在用户键入INTR字符(通常是Ctrl-C)时发出,用于通知前台进程组终止进程。
- 3) SIGQUIT
和SIGINT类似, 但由QUIT字符(通常是Ctrl-\)来控制. 进程在因收到SIGQUIT退出时会产生core文件, 在这个意义上类似于一个程序错误信号。
- 15) SIGTERM
程序结束(terminate)信号, 与SIGKILL不同的是该信号可以被阻塞和处理。通常用来要求程序自己正常退出,shell命令kill缺省产生这个信号。如果进程终止不了,我们才会尝试SIGKILL。
- 19) SIGSTOP
停止(stopped)进程的执行. 注意它和terminate以及interrupt的区别:该进程还未结束, 只是暂停执行. 本信号不能被阻塞, 处理或忽略.



代码
- 子进程运行到3的时候,会停止,父进程唤醒子进程,子进程接着运行,当子进程到4的时候,中断退出,所有的进程全部结束
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid = 0;
int ret;
int i =1;
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
perror("fork error!\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0) {
printf("children pid = %d\n", getpid());
//raise(SIGINT)
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
sleep(1);
printf("children printf %d ...\n", i);
if (i == 3) {
printf("stop!\n");
raise(SIGSTOP);//进程停止信号
}
if (i == 4) {
printf("contine\n");
raise(SIGINT);//进程中断信号
}
printf("本次id = %d\n", i);
}
printf("children exit!\n");
exit(0);
} else {
printf("children process id = %d\n", pid);
printf("father process pid = %d\n", getpid());
sleep(5);
if ((waitpid(pid, nullptr, WNOHANG)) == 0) {
ret = kill(pid, SIGCONT);
if (ret == 0)//向子进程发送 继续运行的信号
printf("信号发送成功 %d \n", pid);
else {
perror("信号发送成功 ");
}
// printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
}


- 前面是要捕捉的信号,后面是针对捕捉的信号对应的处理措施,自己写的一个函数


定义自己信号处理函数
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
void cancel(int aig){
printf("当前程序取消了ctrl+C功能\n");
}
int main() {
signal(SIGINT,cancel);
while (1){
printf("*\n");
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}


代码
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <signal.h>
#include <wait.h>
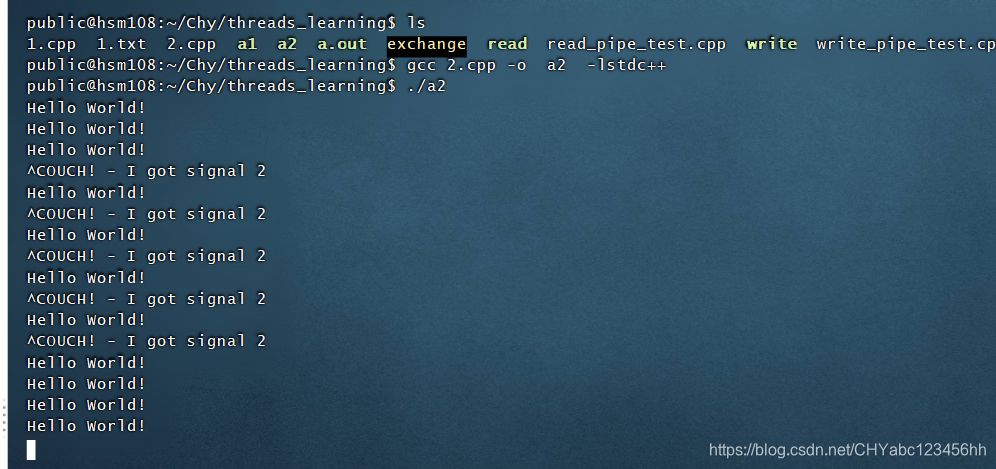
void ouch(int aig){
printf("OUCH! - I got signal %d\n",aig);
}
int main() {
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = ouch;//设置信号处理函数
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);//初始化信号集
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGINT,&act, nullptr);
while (1){
printf("Hello World!\n");
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
参考链接





















 本文介绍了C语言中处理进程控制的信号,包括SIGINT、SIGQUIT和SIGTERM,以及如何通过raise函数触发这些信号。示例代码展示了如何使子进程在接收到特定信号时进行相应操作,如停止、继续和退出。同时,还提供了两种处理信号的方法,一种是通过signal函数取消默认的CTRL+C处理,另一种是使用sigaction函数自定义SIGINT信号的处理函数。
本文介绍了C语言中处理进程控制的信号,包括SIGINT、SIGQUIT和SIGTERM,以及如何通过raise函数触发这些信号。示例代码展示了如何使子进程在接收到特定信号时进行相应操作,如停止、继续和退出。同时,还提供了两种处理信号的方法,一种是通过signal函数取消默认的CTRL+C处理,另一种是使用sigaction函数自定义SIGINT信号的处理函数。
















 931
931

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








