1.什么是Struts2
Struts2是一个基于MVC设计模式的Web应用框架,它本质相当于一个servlet,在MVC设计模式中,Struts2作为控制器来建立模型与视图的交互。
Struts2的优点有:
- Result方式页面导航,通过Result标签的配置很方便的实现页面重定向和跳转
- 通过配置来调度业务类,使得配置和修改都比较容易
- 自定义拦截器、结果类型、标签等
- 等等
2.下载Struts2
下载指定版本的Struts(我这里用的是2.3.24):https://archive.apache.org/dist/struts/
下载解压后的目录结构如下:
将apps/struts2-blank.war文件放到apache-tomcat下的webapps后启动tomcat,tomcat会在webapps下自动将war文件解压成一个struts2-blank项目,该项目中有使用struts2基本的jar,如下图:
3.Struts2的常见配置
Struts2的执行流程:客服端发送请求会先经过前端控制器(核心过滤器StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter),过滤器中执行一组拦截器(这一组拦截器会执行一分部代码)
了解了Struts2大概的执行流程后,应做如下配置:
- 在web.xml中配置核心过滤器,例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>struts2_day02</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<!-- 配置核心过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
- 在页面中放置要访问的action
<form action="${ pageContext.request.contextPath }/requestDemo1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
- 编写一个action,有三种方式
- Action可以是一个POJO类
- Action可以实现Action接口,重写execute()方法
- Action可以继承ActionSupport类(推荐)
/**
* 访问Servlet的API方式一:完全解耦合的方式
* 还有两种:
* 1.使用HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
* 2.让Action类实现ServletRequestAware和ServletContextAware接口,定义HttpServletRequest、ServletContext变量,
并重写setServletRequest和setServletContext
*
*/
public class RequestDemo1 extends ActionSupport{
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// 一、接收参数:
// 利用Struts2中的对象ActionContext对象.
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
// 调用ActionContext中的方法。
// 类似于Map<String,String[]> request.getParameterMap();
Map<String,Object> map = context.getParameters();
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
String[] values = (String[]) map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" "+Arrays.toString(values));
}
// 二、向域对象中存入数据
context.put("reqName", "reqValue");// 相当于request.setAttribute();
context.getSession().put("sessName", "sessValue"); // 相当于session.setAttribute();
context.getApplication().put("appName", "appValue"); // 相当于application.setAttribute();
return SUCCESS;
}
}
/**
* struts2中数据封装方式有两种:
* 1.属性驱动,在action类中提供要封装数据的属性字段以及get、set方法,页面中直接使用属性展示数据
* 2.模型驱动,在action类中提供要封装数据的对象属性以及get、set方法,页面中使用该对象访问属性方式展示数据
*/
- 在Web项目的src目录下创建struts.xml,并在其中配置action
配置action的访问有三种方式,分别是:通过method标签、通过通配符、通过动态方法访问,例如:
<!-- 通过method标签配置 -->
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="requestDemo1" class="com.itheima.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1" method="execute"></action>
</package>
<!-- 通过通配符方式配置,页面访问路径例如:${ pageContext.request.contextPath }/requestDemo1_execute.action -->
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="requestDemo1_*" class="com.itheima.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1" method="{1}"></action>
</package>
<!-- 通过动态方法方式配置,页面访问路径例如:${ pageContext.request.contextPath }/requestDemo1!execute.action -->
<constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true">
在分模块开发情况下一般将包下的struts.xml引入src目录下的status.xml中,例如:
/**
* 包下的struts_demo1.xml
*/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<!-- 全局结果页面 -->
<global-results>
<result>/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<!-- 配置action -->
<action name="requestDemo1" class="com.itheima.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1">
<result type="redirect">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="requestDemo2" class="com.itheima.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo2">
</action>
<action name="requestDemo3" class="com.itheima.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo3">
</action>
</package>
</struts>
/**
* src目录下的struts.xml,使用include标签包含模块(包)下的struts_demo1.xml
*/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<!-- 配置Struts2的常量 -->
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action"/>
<include file="com/itheima/struts2/demo1/struts_demo1.xml"></include>
</struts>
4.关于OGNL和ValueStack
OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)是一种表达式语言,通过它简单一致的表达式语法,可以存取对象任意属性,调用对象方法,遍历整个对象结构图,实现字段类型转化等功能。
OGNL要素:
- 表达式
- 根对象(Root)
- Context对象
ValueStack是Struts的一个接口,OgnlValueStack是ValueStack的实现类,当客户端发起一个请求struts2框架会创建一个action实例的同时创建了一个OgnlValueStack值栈实例,OgnlValueStack贯穿整个action的生命周期,struts2中使用OGNL将请求action参数封装为对象存储到值栈中,并通过OGNL表达式读取值栈中的对象属性值。
操作值栈:
ValueStack vs = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
- 通过ActionContext对象获取值栈
- 通过reqeust域获取值栈
- 对Action中的属性提供get方法方式操作值栈
- 调用值栈的push和set方法操作值栈,push压入栈顶
- 从值栈中获取数据,可通过对象方式获取,可通过属性方式获取
- 使用EL访问值栈,#号获取context数据,%强制解析OGNL表达式,$在配置文件中使用OGNL
5.拦截器
拦截器,在AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)中用于某个方法或字段被访问之前进行拦截,然后在之前或之后加入某些操作。拦截是AOP的一种实现策略。
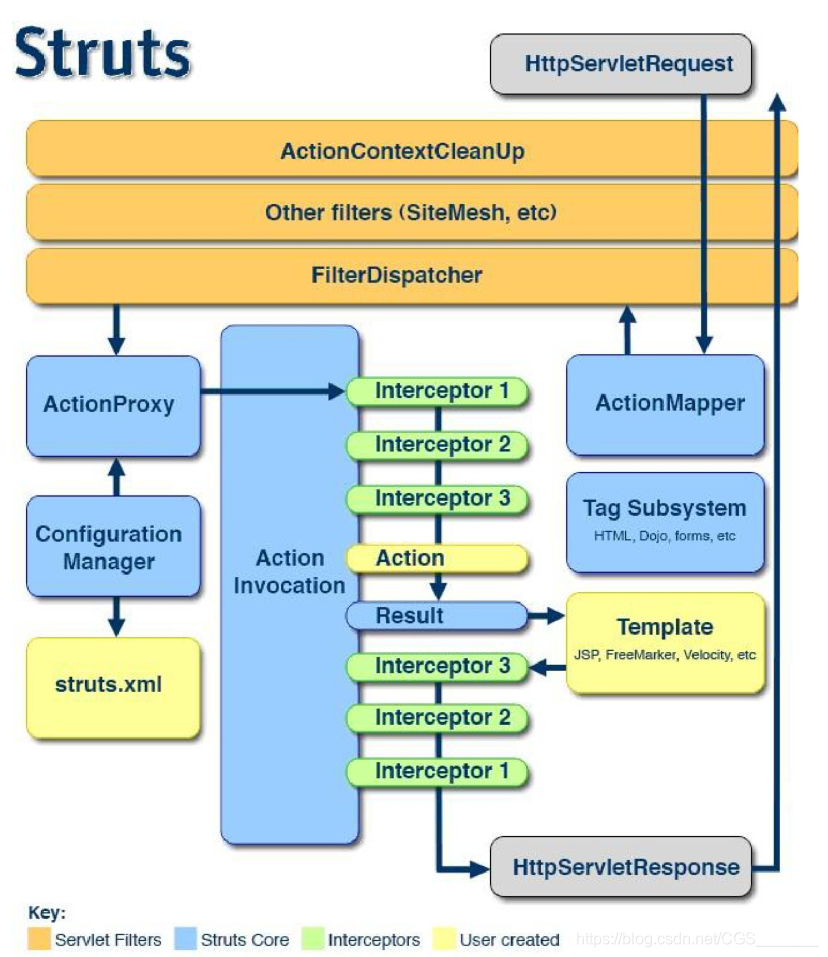
拦截器实现原理:
拦截器方法通过代理的方式来调用,当请求到达Struts2的ServletDispatcher时,Struts2会查找配置文件并根据配置实例化相对的拦截器,形成一个Stack然后一个个调用其中的拦截器。如下图:
关于拦截器的配置示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<!-- 配置Struts2的常量 -->
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action"/>
<!-- 开启静态方法访问 -->
<constant name="struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess" value="true"/>
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<!-- 定义拦截器========== -->
<!-- <interceptors>
<interceptor name="interceptorDemo1" class="com.itheima.web.interceptor.InterceptorDemo1"/>
<interceptor name="interceptorDemo2" class="com.itheima.web.interceptor.InterceptorDemo2"/>
</interceptors> -->
<interceptors>
<interceptor name="interceptorDemo1" class="com.itheima.web.interceptor.InterceptorDemo1"/>
<interceptor name="interceptorDemo2" class="com.itheima.web.interceptor.InterceptorDemo2"/>
<!-- 定义拦截器栈 -->
<interceptor-stack name="myStack">
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
<interceptor-ref name="interceptorDemo1"/>
<interceptor-ref name="interceptorDemo2"/>
</interceptor-stack>
</interceptors>
<action name="actionDemo1" class="com.itheima.web.action.ActionDemo1">
<result>/demo1/demo1.jsp</result>
<!-- 引入拦截器(一旦引入自定义拦截器,默认拦截器栈的拦截器就不执行了。)=========== -->
<interceptor-ref name="myStack"/>
<!-- <interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
<interceptor-ref name="interceptorDemo1"/>
<interceptor-ref name="interceptorDemo2"/> -->
</action>
<action name="uiAction" class="com.itheima.web.action.UIAction">
<result name="input">/demo2/demo3.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>























 987
987

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








