作业
手动实现一个循环顺序队列

#include <iostream>
#define MAX 1024
using namespace std;
class pooper_queue
{
private:
char *arr; //指向数组的指针
int size_len; //队列容量
int front; //对头指针
int tail; //队尾指针
int number1; //队列当前元素个数
public:
//无参构造函数
pooper_queue()
{
arr = new char[size_len];
}
//有参构造函数
pooper_queue(int m):size_len(m),front(0),tail(0),number1(0)
{
arr = new char[size_len];
}
//析构函数
~pooper_queue(){
delete []arr;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
pooper_queue& operator=(const pooper_queue &other)
{
if(this!=&other)
{
delete []arr;
size_len = other.size_len;
front = other.front;
tail = other.tail;
number1 = other.number1;
arr = new char[size_len];
for(int i = 0;i<size_len;i++)
{
arr[i] = other.arr[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
//判空函数
bool empty() const
{
return number1 == 0;
}
//判满函数
bool full() const
{
return size_len == number1;
}
//第一个元素访问
char front_one()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"访问失败"<<endl;
}
return arr[front];
}
//访问最后一个元素
char tail_one()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"访问失败"<<endl;
}
return arr[(tail-1+size_len)%size_len]; //顺序表访问最后一个元素
}
//返回容纳的元素数
int getsize() const
{
return number1;
}
//队尾插入元素
void tail_interposition(const char& s) //s为插入的元素
{
if(full())
{
cout<<"队列已满,插入失败"<<endl;
}
arr[tail] = s;
tail = (tail+1)%size_len;
number1++;
}
//于尾部原位构造元素
//删除首个元素
void front_delete()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"队列为空,删除失败"<<endl;
}
front = (front+1)%size_len;
number1--;
}
};
int main()
{
pooper_queue s1(5);
s1.tail_interposition(6);
s1.tail_interposition(7);
s1.tail_interposition(9);
s1.tail_interposition(0);
cout << "队头元素" <<s1.front_one()<< endl; // 输出队头元素
cout << "队尾元素 " <<s1.tail_one()<< endl; // 输出队尾元素
cout << "元素个数" << s1.getsize() << endl; // 输出队列元素个数
s1.front_delete();
cout << "输出删除后的元素个数"<<s1.getsize()<<endl; //删除后的元素个数
return 0;
}
课堂代码1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义一个父类
class Father
{
public:
string name;
protected:
int pwd;
private:
int money;
public:
Father() {cout<<"Father::无参构造"<<endl;}
Father(string n, int p, int m):name(n), pwd(p), money(m) {cout<<"Father::有参构造"<<endl;}
~Father() {cout<<"Father::析构函数"<<endl;}
void show()
{
cout<<"Father::name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"Father::pwd = "<<pwd<<endl;
cout<<"Father::money = "<<money<<endl;
}
};
//定义一个子类
class Son:public Father
{
public:
int name; //子类中可以定义与父类中同名的成员
};
//再定义一个类
class Test
{
public:
Father f;
public:
// Test():f("张三",111111,100000000){cout<<"Test::无参构造"<<endl;}
};
int main()
{
cout << sizeof (Father)<< " "<< sizeof (Son) << endl;
Father f1; //Father 的无参构造
Son s1; //构造
Test t1;
cout<<"***************************************"<<endl;
//验证子类中包含一个父类,并且出现同名情况时,使用子类成员和父类成员
cout<<"&s1 = "<<&s1<<" &s1.name = "<<&s1.name<<" &Father::name = "<<&s1.Father::name<<endl; //对象的地址 第一个成员的地址
cout<<"&t1 = "<<&t1<<" &t1.f = "<<&t1.f<<endl;
return 0;
}
课堂代码2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义一个父类
class Father
{
public:
string name;
protected:
int pwd;
private:
int money;
public:
Father() {cout<<"Father::无参构造"<<endl;}
Father(string n, int p, int m):name(n), pwd(p), money(m) {cout<<"Father::有参构造"<<endl;}
~Father() {cout<<"Father::析构函数"<<endl;}
Father(const Father &other):name(other.name),pwd(other.pwd), money(other.money)
{cout<<"Father::拷贝构造函数"<<endl;}
Father &operator=(const Father&other)
{
if(this!=&other)
{
this->name = other.name;
this->pwd = other.pwd;
this->money = other.money;
}
cout<<"Father::拷贝赋值函数"<<endl;
return *this;
}
void show()
{
cout<<"Father::name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"Father::pwd = "<<pwd<<endl;
cout<<"Father::money = "<<money<<endl;
}
};
//定义一个子类
class Son:public Father
{
private:
string toy; //玩具
public:
Son(){cout<<"Son::无参构造"<<endl;}
Son(string n, int p, int m, string t): Father(n, p, m), toy(t)
{
cout<<"Son::有参构造"<<endl;
}
~Son(){cout<<"Son::析构函数"<<endl;}
//定义拷贝构造函数
Son(const Son& other):Father(other),toy(other.toy)
{
cout<<"Son::拷贝构造函数"<<endl;
}
//定义子类的拷贝赋值函数
Son &operator=(const Son &other)
{
if(this != &other)
{
// this->name = other.name;
// this->pwd = other.pwd;
// this->money = other.money; //?
Father::operator=(other); //显性调用父类的拷贝赋值函数
this->toy = other.toy;
}
cout<<"Son::拷贝赋值han数"<<endl;
return *this;
}
//定义自己的show函数
void show()
{
// cout<<"Father::name = "<<name<<endl;
// cout<<"Father::pwd = "<<pwd<<endl;
// cout<<"Father::money = "<<money<<endl; //子类中无法访问父类的私有成员
Father::show(); //调用父类提供的show函数
cout<<"toy = "<<toy<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Son s1("zhangpp", 111111, 0, "car"); //构造
s1.show(); //调用的是继承下来的show函数
cout<<"********************************"<<endl;
Son s2(s1); //拷贝构造函数
s2.show(); //随机值
cout<<"********************************"<<endl;
s2 = s1;
s2.show();
cout<<"********************************"<<endl;
return 0;
}
课堂代码3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
private:
int perimeter;//周长
int area;//面积
public:
Shape(){}
~Shape(){}
Shape(const Shape &other):perimeter(other.perimeter),area(other.area){}
Shape &operator= (const Shape &other)
{
if(this!=&other)
{
this->perimeter = other.perimeter;
this->area = other.area;
}
return *this;
}
void show()
{
cout<<"perimeter = "<<perimeter<<endl;
cout<<"area = "<<area<<endl;
}
int get_perimeter()
{
return this->perimeter;
}
int get_area()
{
return this->area;
}
void set_perimeter(int p)
{
this->perimeter = p;
}
void set_area(int a)
{
this->area = a;
}
};
//定义一个矩形类继承
class Rectangle:public Shape
{
private:
int wide;
int high;
public:
Rectangle(){}
Rectangle(int w,int h):wide(w),high(h){}
~Rectangle(){}
Rectangle(const Rectangle &other):Shape(other),wide(other.wide),high(other.high){}
Rectangle & operator= (const Rectangle &other)
{
if(this != &other)
{
Shape::operator=(other);
this->wide = other.wide;
this->high = other.high;
}
return *this;
}
void show()
{
cout<<2*(wide+high)<<endl;
cout<<wide*high<<endl;
}
int get_perimeter()
{
this->set_perimeter( 2*(wide+high));
return Shape::get_perimeter();
}
int get_area()
{
this->set_area( wide*high);
return Shape::get_area();
}
};
//定义一个圆类
class Circle:public Shape
{
private:
int radius;
public:
Circle(){}
Circle(int r):radius(r){}
~Circle(){}
Circle(const Circle &other):Shape(other),radius(other.radius){}
Circle & operator= (const Circle &other)
{
if(this != &other)
{
Shape::operator=(other);
this->radius = other.radius;
}
return *this;
}
void show()
{
cout<<2*3.14*radius<<endl;
cout<<3.14*radius*radius<<endl;
}
int get_perimeter()
{
this->set_perimeter( 2*3.14*radius);
return Shape::get_perimeter();
}
int get_area()
{
this->set_area( 3.14*radius*radius);
return Shape::get_area();
}
};
int main()
{
Rectangle r1(6,5);
cout<<r1.get_perimeter()<< " "<<r1.get_area()<<endl;
// Circle c1(7);
// c1.show();
return 0;
}
课堂代码4
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int value_a;
public:
A() {}
A(int a):value_a(a) {cout<<"A::有参构造"<<endl;}
~A() {cout<<"A::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义一个类B
class B
{
protected:
int value_a;
int value_b;
public:
B() {}
B(int b):value_b(b) {cout<<"B::有参构造"<<endl;}
~B() {cout<<"B::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义一个子类由A和B类共同派生出来
class C: public B,public A
{
private:
int value_c;
public:
C() {}
C(int a, int b, int c): B(b), A(a),value_c(c) {cout<<"C::有参构造"<<endl;}
~C() {cout<<"C::析构函数"<<endl;}
void show()
{
cout<<"value_a = "<<A::value_a<<endl; //输出的是由类A提供的value_a
cout<<"value_a = "<<B::value_a<<endl; //输出的是由类A提供的value_a
cout<<" value_b = "<<value_b<<" value_c = "<<value_c<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
C c(1,2,3);
c.show();
return 0;
}
课堂代码5
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A //公共基类
{
protected:
int value_a;
public:
A() {cout<<"无::有参构造"<<endl;}
A(int a):value_a(a) {cout<<"A::有参构造"<<endl;}
~A() {cout<<"A::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义一个类B
class B:public A
{
protected:
int value_b;
public:
B() {cout<<"B::无参构造"<<endl;}
B(int a, int b):A(a),value_b(b) {cout<<"B::有参构造"<<endl;}
~B() {cout<<"B::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义一个子类由A和B类共同派生出来
class C: public A
{
protected:
int value_c;
public:
C() {cout<<"C::无参构造"<<endl;}
C(int a,int c): A(a),value_c(c) {cout<<"C::有参构造"<<endl;}
~C() {cout<<"C::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义汇聚子类,继承自两个中间子类
class D:public B, public C
{
private:
int value_d;
public:
D(){cout<<"D::无参构造"<<endl;}
D(int a1, int a2, int b, int c, int d):B(a1,b), C(a2,c), value_d(d)
{cout<<"D::有参构造"<<endl;}
~D(){cout<<"D::析构函数"<<endl;}
void show()
{
//对于汇聚子类中,就会拥有多份公共基类中的成员
cout<<"value_a = "<<B::value_a<<endl;
cout<<"value_a = "<<C::value_a<<endl;
cout<<"value_b = "<<value_b<<endl;
cout<<"value_c = "<<value_c<<endl;
cout<<"value_d = "<<value_d<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D d(1,2,3,4,5);
d.show();
return 0;
}
课堂代码6
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A //公共基类
{
protected:
int value_a;
public:
A() {cout<<"A::无参构造"<<endl;}
A(int a):value_a(a) {cout<<"A::有参构造"<<endl;}
~A() {cout<<"A::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义一个类B
class B: virtual public A
{
protected:
int value_b;
public:
B() {cout<<"B::无参构造"<<endl;}
B(int a, int b):A(a),value_b(b) {cout<<"B::有参构造"<<endl;}
~B() {cout<<"B::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义一个子类由A和B类共同派生出来
class C: virtual public A
{
protected:
int value_c;
public:
C() {cout<<"C::无参构造"<<endl;}
C(int a,int c): A(a),value_c(c) {cout<<"C::有参构造"<<endl;}
~C() {cout<<"C::析构函数"<<endl;}
};
//定义汇聚子类,继承自两个中间子类
class D:public B, public C
{
private:
int value_d;
public:
D(){cout<<"D::无参构造"<<endl;}
D(int a1, int a2, int b, int c, int d):A(a1), B(a1,b), C(a2,c), value_d(d)
{cout<<"D::有参构造"<<endl;}
~D(){cout<<"D::析构函数"<<endl;}
void show()
{
//对于汇聚子类中,就会拥有多份公共基类中的成员
cout<<"value_a = "<<value_a<<endl;
// cout<<"value_a = "<<C::value_a<<endl;
cout<<"value_b = "<<value_b<<endl;
cout<<"value_c = "<<value_c<<endl;
cout<<"value_d = "<<value_d<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D d(1,2,3,4,5);
d.show();
return 0;
}
课堂代码7
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义父类
class Person
{
protected:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() {}
Person(string n, int a):name(n), age(a) {}
~Person() {}
virtual void show() //该函数就是虚函数
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
}
};
//定义子类
class Stu:public Person
{
private:
double score;
public:
Stu() {}
Stu(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), score(s) {}
~Stu() {}
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<score<<endl;
}
};
//定义子类
class Worker:public Person
{
private:
double salary; //工资
public:
Worker() {}
Worker(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), salary(s) {}
~Worker() {}
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<salary<<endl;
}
};
//定义全局函数
void display(Person &s)
{
s.show();
}
int main()
{
Stu s1("张三", 18, 99);
s1.show(); //正常输出子类的show函数
cout<<"***********************************"<<endl;
Person *ptr = &s1;
ptr->show(); //?
cout<<"***********************************"<<endl;
Person &ref = s1;
ref.show();
display(s1); //传递学生类对象,就会调用学生的相关函数
Worker w1("里斯", 40, 2000);
display(w1); //传递的是工人对象,调用的就是工人相关函数
return 0;
}
课堂代码8
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义父类
class Person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() {}
Person(string n, int a):name(n), age(a) {}
~Person() {}
virtual void show() = 0; //该函数就是纯虚函数 包含纯虚函数的类称为抽象类
};
//定义子类
class Stu:public Person
{
private:
double score;
public:
Stu() {}
Stu(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), score(s) {}
~Stu() {}
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<score<<endl;
}
};
//定义子类
class Worker:public Person
{
private:
double salary; //工资
public:
Worker() {}
Worker(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), salary(s) {}
~Worker() {}
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<salary<<endl;
}
};
//定义全局函数
void display(Person &s)
{
s.show();
}
int main()
{
//Person p1; //抽象类不能实例化对象
Stu s1("张三", 18, 99);
s1.show(); //正常输出子类的show函数
cout<<"***********************************"<<endl;
Person *ptr = &s1;
ptr->show(); //?
cout<<"***********************************"<<endl;
Person &ref = s1;
ref.show(); //调用的是子类重写的父类的虚函数
cout<<"***********************************"<<endl;
ref.Person::show(); //调用的就是父类提供的函数
cout<<sizeof(Stu)<<endl;
cout<<"&s1 = "<<&s1<<" &s1.name = "<<&s1.name<<endl;
return 0;
}
课堂代码9
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义父类
class Person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() {}
Person(string n, int a):name(n), age(a) {cout<<"Person::有参构造"<<endl;}
virtual ~Person() {cout<<"Person::析构函数"<<endl;}
virtual void show() = 0; //该函数就是纯虚函数 包含纯虚函数的类称为抽象类
};
//定义子类
class Stu:public Person
{
private:
double score;
public:
Stu() {}
Stu(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), score(s) {cout<<"Stu::有参构造"<<endl;}
~Stu() {cout<<"Stu::析构函数"<<endl;} //虚析构函数,正确指引delete关键字释放空间
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<score<<endl;
}
};
//定义子类
class Worker:public Person
{
private:
double salary; //工资
public:
Worker() {}
Worker(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), salary(s) {cout<<"Worker::有参构造"<<endl;}
~Worker() {cout<<"Worker::析构函数"<<endl;}
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<salary<<endl;
}
};
//定义全局函数
void display(Person &s)
{
s.show();
}
int main()
{
Person *ptr = new Stu("张三", 18, 99); //使用父类指针指向子类空间
delete ptr;
return 0;
}
课堂代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义父类
class Person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() {}
Person(string n, int a):name(n), age(a) {cout<<"Person::有参构造"<<endl;}
virtual ~Person() {cout<<"Person::析构函数"<<endl;}
virtual void show() = 0; //该函数就是纯虚函数 包含纯虚函数的类称为抽象类
};
//定义子类
class Stu:public Person
{
private:
double score;
public:
Stu() {}
Stu(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), score(s) {cout<<"Stu::有参构造"<<endl;}
~Stu() {cout<<"Stu::析构函数"<<endl;} //虚析构函数,正确指引delete关键字释放空间
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<score<<endl;
}
};
//定义子类
class Worker:public Person
{
private:
double salary; //工资
public:
Worker() {}
Worker(string n, int a, double s):Person(n,a), salary(s) {cout<<"Worker::有参构造"<<endl;}
~Worker() {cout<<"Worker::析构函数"<<endl;}
//重写父类中提供的虚函数
void show()
{
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<salary<<endl;
}
};
//定义全局函数
void display(Person &s)
{
s.show();
}
int main()
{
Person *ptr = new Stu("张三", 18, 99); //使用父类指针指向子类空间
delete ptr;
return 0;
}
笔记
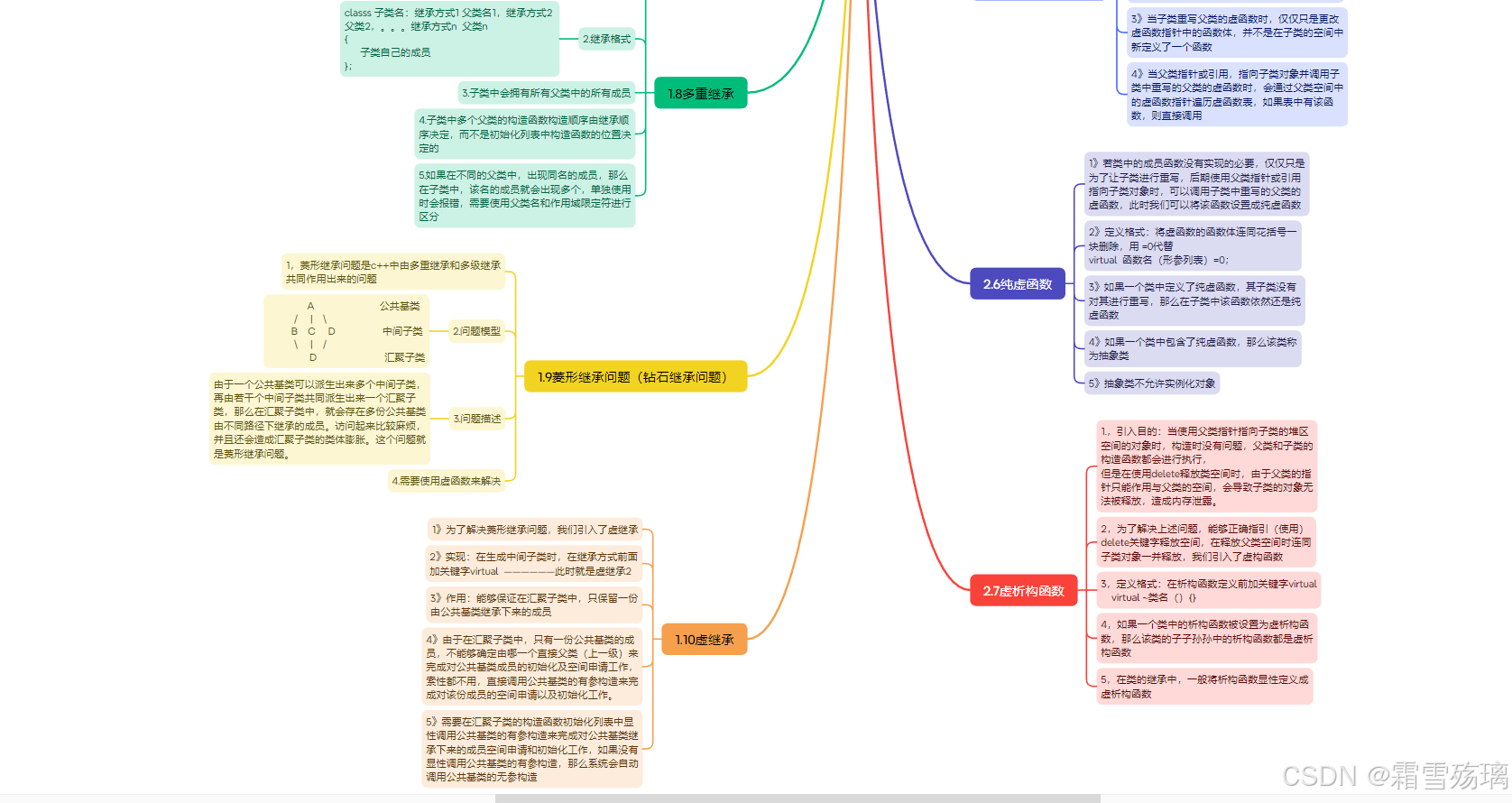
思维导图























 400
400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








