#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1337) # for reproducibility
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 可视化模块
X = np.linspace(-1, 1, 200)
np.random.shuffle(X) # randomize the data
Y = 0.9 * X + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, (200, ))
# plot data
#plt.scatter(X, Y)
#plt.show()
X_train, Y_train = X[:160], Y[:160] # train 前 160 data points
X_test, Y_test = X[160:], Y[160:] # test 后 40 data points
#plt.plot(X_train, Y_train,'.')
#plt.show()
model = Sequential()
l1 = Dense(output_dim = 1,input_dim = 1)
model.add(l1)
model.compile(loss = 'mse',optimizer = 'sgd')
model.fit(X_train,Y_train,epochs= 3000)
print(l1.get_weights())
Xe = np.linspace(1, 2, 20)
Ye = model.predict(Xe)
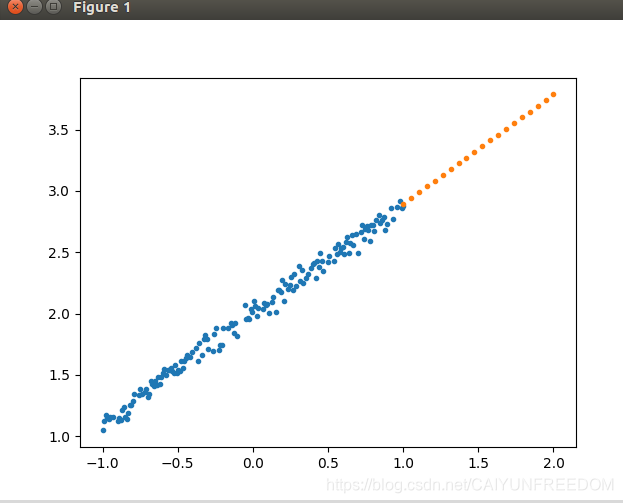
plt.plot(X_train, Y_train,'.',Xe,Ye,'.')
plt.show()
运行结果
Epoch 3000/3000
160/160 [==============================] - 0s 30us/step - loss: 0.0026
[array([[0.8913625]], dtype=float32), array([2.0040555], dtype=float32)]
训练得到的权重和偏置和理论值0.9 2 很接近了。
下图中橙色点是预测部分,蓝色点是训练数据。
代码托管在github








 本文通过使用Keras实现线性回归模型,演示了如何从数据准备到模型训练及预测的全过程。文中详细介绍了利用Python及其相关库进行数据生成、模型搭建、训练以及最终结果的可视化展示。
本文通过使用Keras实现线性回归模型,演示了如何从数据准备到模型训练及预测的全过程。文中详细介绍了利用Python及其相关库进行数据生成、模型搭建、训练以及最终结果的可视化展示。
















 1244
1244

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








