查询
除了find()之外还有:
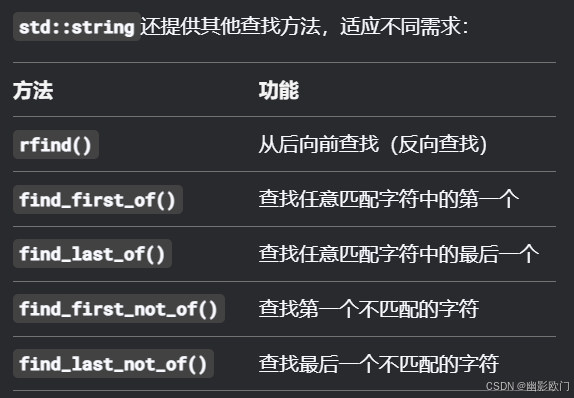
find()方法:
用于在字符串中查找子字符串或字符的位置。它返回子字符串首次出现的起始索引(从0开始),如果未找到则返回std::string::npos(一个特殊常量,通常是-1或size_t的最大值)。
size_t find(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; // 查找子字符串
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; // 查找C风格字符串
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; // 查找单个字符
条件判断:
size_t found = s.find(target);
if (found != string::npos)
-
大小写敏感:
find()区分大小写。如需不区分大小写,需自行转换字符串(如全转小写)。 -
性能:
find()的时间复杂度为O(n*m),其中n和m分别是主串和子串长度。
最值
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2};
// 使用 min_element 获取最小值的迭代器
auto min_it = min_element(v.begin(), v.end());//这里返回值是地址
// 计算最小值的下标(从 0 开始)
int min_index = distance(v.begin(), min_it);
cout << "最小值: " << *min_it << endl; // 输出: 1
cout << "位置: " << min_index << endl; // 输出: 1(第 2 个元素)
return 0;
}
删除操作
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 删除特定字符
string s = "hello world";
s.erase(remove(s.begin(), s.end(), 'l'), s.end());
cout << s << endl; // 输出: "heo word"
// 删除特定子串
s = "hello world";
size_t pos;
while ((pos = s.find("ll")) != string::npos) {
s.erase(pos, 2);
}
cout << s << endl; // 输出: "heo world"
return 0;
}
 C++字符串操作技巧之查询与删除
C++字符串操作技巧之查询与删除





















 3705
3705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








