This post is part of a series called From Beginner To Advanced in OpenCart.
From Beginner To Advanced in OpenCart: Understanding MVC
From Beginner to Advanced in OpenCart: More Module Development
In the previous articles, we examined the MVC architecture and created our first controller, model, and view in the OpenCart application. We did this in order to help gain a better understanding of the core application.
To take things a step further, we're going to look at creating a custom module for OpenCart.
What Are OpenCart Modules?
OpenCart modules are analogous to add-ons, plugins, or extensions in other content management systems. It's through modules that OpenCart gives us the ability to extend its functionality without having to edit the application's files.
As with many other content management systems, it's generally considered to be a best practice to extend functionality of the core application through the provided APIs and OpenCart is no different. Modules allow us to introduce, remove, or modify functionality of the core application that's done in a compartmentalized and maintainable way.
OpenCart has its own Extension Market where a large number of extensions are already available. Or you can check out the wide range of OpenCart modules and extensions on Envato Market.
Our First Module
In order to get acclimated with OpenCart's module system, we can write the obligatory "Hello World" module. This will take input from the dashboard and display it on the front-end of the site.
Note that OpenCart has a number of pre-build modules. As such, we'll try to leverage those when possible when working on our own. To get started, perform the following:
- Create an Controller to Admin Path:
admin/controller/module/helloworld.php. - Create a Language File to Admin Path:
admin/language/english/module/helloworld.php. - Create a View to Admin Path:
admin/view/template/module/helloworld.twig.
1. The Language File
As discussed in our previous articles, the language file contains the static text what should be displayed in our view file. For the helloworld.php language file, the following variables contain the possible text fields what we require to display in our module:
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
|
1. The Controller
Open the "Hello World" controller file that we just created and add the class class ControllerModuleHelloworld extends Controller {} following the Class Naming Convention. Next, place the following code inside the class.
Step 1: The Default Function
| 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 050 051 052 053 054 055 056 057 058 059 060 061 062 063 064 065 066 067 068 069 070 071 072 073 074 075 076 077 078 079 080 081 082 083 084 085 086 087 088 089 090 091 092 093 094 095 096 097 098 099 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 | <?php $this->response->redirect($this->url->link('marketplace/extension', 'user_token=' . $this->session->data['user_token'] . '&type=module')); } // End If if (!isset($this->request->get['module_id'])) { $data['cancel'] = $this->url->link('marketplace/extension', 'user_token=' . $this->session->data['user_token'] . '&type=module'); if (isset($this->request->get['module_id']) && ($this->request->server['REQUEST_METHOD'] != 'POST')) { if (isset($this->request->post['module_description'])) { $data['languages'] = $this->model_localisation_language->getLanguages(); if (isset($this->request->post['status'])) { $data['header'] = $this->load->controller('common/header'); |
Step 2: Validation Method
As we tried to validate data on save in default function. So here comes the validation method.
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | /* Function that validates the data when Save Button is pressed */
//change /* Function that validates the data when Save Button is pressed */ |
Now save the file and you're done with the Admin Controller of our Hello World Module!
3. View File
As previously done in controller, you have to create some HTML for the view. For that, we'll do the following:
Step 1: Build Some Basic Controls
A form is an element that will contain elements like an text input element, a textarea, and buttons for saving or canceling input.
To create a form like this, review the code below:
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | {{ header }} <div id="content"> <div class="breadcrumb"> {% for breadcrumb in breadcrumbs %} {{ breadcrumb.separator }}<a href="{{ breadcrumb.href }}">{{ breadcrumb.text }}</a> {% endfor %} </div> {% if error_warning %} <div class="warning">{{ error_warning }}</div> {% endif %} <div class="box"> <div class="heading"> <h1><img src="view/image/module.png" alt="" /> {{ heading_title }}</h1> <div class="buttons"><a οnclick="$('#form').submit();" class="button">{{ button_save }}</a><a href="{{ cancel }}" class="button">{{ button_cancel }}</a></div> </div> <div class="content"> <form action="{{ action }}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" id="form"> <table class="form"> <tr> <td><span class="required">*</span> {{ entry_code }}</td> <td><textarea name="helloworld_text_field" cols="40" rows="5">{{ helloworld_text_field }}</textarea> {% if error_code %} <span class="error">{{ error_code }}</span> {% endif %}</td> </tr> </table> |
Step 2: Adding a Table List
Under the form, a table list will appear where we can settle the module position and the page where the module to be displayed.
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | <table id="module" class="list"> </select></td> {% if module.position is 'content_bottom' %} {% if module.position is 'column_left' %} {% if module.position is 'column_right' %} </select></td> </select></td> <tfoot> |
Step 3: Adding Some JavaScript
As you can see in the previous step, there is an "Add Module" button. Specifically, we have: <a onclick="addModule();" class="button"><?php echo $button_add_module; ?></a> where user can add multiple rows to display the output of the module in different layouts on different positions.
For that, we need to write some JavaScript that will append a row to the table list. This will improve the user interface for those using our module:
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | <script type="text/javascript"><!-- var module_row = {{ module_row }}; function addModule() { html = '<tbody id="module-row' + module_row + '">'; html += ' <tr>'; html += ' <td class="left"><select name="helloworld_module[' + module_row + '][layout_id]">'; {% for layout in layouts %} html += ' <option value="{{ layout.layout_id }}">{{ addslashes(layout.name) }}</option>'; {% endfor %} html += ' </select></td>'; html += ' <td class="left"><select name="helloworld_module[' + module_row + '][position]">'; html += ' <option value="content_top">{{ text_content_top }}</option>'; html += ' <option value="content_bottom">{{ text_content_bottom }}</option>'; html += ' <option value="column_left">{{ text_column_left }}</option>'; html += ' <option value="column_right">{{ text_column_right }}</option>'; html += ' </select></td>'; html += ' <td class="left"><select name="helloworld_module[' + module_row + '][status]">'; html += ' <option value="1" selected="selected">{{ text_enabled }}</option>'; html += ' <option value="0">{{ text_disabled }}</option>'; html += ' </select></td>'; html += ' <td class="right"><input type="text" name="helloworld_module[' + module_row + '][sort_order]" value="" size="3" /></td>'; html += ' <td class="left"><a οnclick="$(\'#module-row' + module_row + '\').remove();" class="button">{{ button_remove }}</a></td>'; html += ' </tr>'; html += '</tbody>'; $('#module tfoot').before(html); module_row++; } //--></script> |
Step 4: Adding a Footer
The last thing, we need to add a child footer in the end of the view:
| 1 | {{ footer }} |
At this point, we're done preparing our first Hello World module. At this point, it's time to check whether our module is working or not.
To do that, login to dashboard and go to the Extensions > Modules page where you'll see a list of modules of OpenCart System. There will also be "Hello World" listed with an "Uninstalled" State, click on "Install" and try editing the module and you'll see a screen something like this:
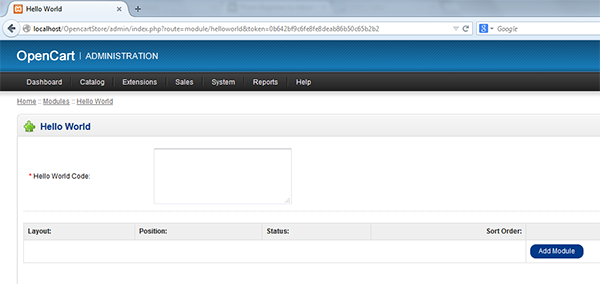
You can input some random value and try saving it, Now try editing the module again and you'll see you input entered as default.
Conclusion
In this article, we tried to build a basic OpenCart Module using MVC. It's easy to manipulate OpenCart Modules if you're familiar with the core concepts of MVC. This article gives just a basic idea how to develop a simple module following some simple steps.
In our next article, we're going to work with the frontend and will try to extend it for a store frontend. Please provide us with your feedback in the comments below!





 本文介绍如何使用MVC架构在OpenCart中创建自定义模块。通过创建一个“Hello World”模块,详细讲解了从控制器、语言文件到视图的实现过程,展示了如何扩展OpenCart功能而不修改核心文件。
本文介绍如何使用MVC架构在OpenCart中创建自定义模块。通过创建一个“Hello World”模块,详细讲解了从控制器、语言文件到视图的实现过程,展示了如何扩展OpenCart功能而不修改核心文件。
















 2493
2493

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








