1. PageBean
分页三要素
page 页码 视图层传递过来
rows 页大小 视图层传递过来
total 总记录数 后台查出来
pagination 是否分页 视图层传递过来
getStartIndex() 基于MySql数据库分页,获取分页开始标记
package com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util;
/**
* 分页工具类
*
*/
public class PageBean {
private int page = 1;// 页码
private int rows = 10;// 页大小
private int total = 0;// 总记录数
private boolean pagination = true;// 是否分页
public PageBean() {
super();
}
public int getPage() {
return page;
}
public void setPage(int page) {
this.page = page;
}
public int getRows() {
return rows;
}
public void setRows(int rows) {
this.rows = rows;
}
public int getTotal() {
return total;
}
public void setTotal(int total) {
this.total = total;
}
public void setTotal(String total) {
this.total = Integer.parseInt(total);
}
public boolean isPagination() {
return pagination;
}
public void setPagination(boolean pagination) {
this.pagination = pagination;
}
/**
* 获得起始记录的下标
*
* @return
*/
public int getStartIndex() {
return (this.page - 1) * this.rows;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PageBean [page=" + page + ", rows=" + rows + ", total=" + total + ", pagination=" + pagination + "]";
}
}
2. 后台
2.1 entity
package com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.entity;
public class Book {
private int id;
private String bookname;
private float price;
private String booktype;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBookname() {
return bookname;
}
public void setBookname(String bookname) {
this.bookname = bookname;
}
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getBooktype() {
return booktype;
}
public void setBooktype(String booktype) {
this.booktype = booktype;
}
public Book() {
super();
}
public Book(String bookname, float price, String booktype) {
super();
this.bookname = bookname;
this.price = price;
this.booktype = booktype;
}
public Book(int id, String bookname, float price, String booktype) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.bookname = bookname;
this.price = price;
this.booktype = booktype;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [id=" + id + ", bookname=" + bookname + ", price=" + price + ", booktype=" + booktype + "]";
}
}
2.2 dao
package com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.entity.Book;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.DBAccess;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.PageBean;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.StringUtils;
public class BookDao extends BaseDao<Book>{
private Connection con=null;
private PreparedStatement ps=null;
private ResultSet rs=null;
public void addBook(Book book) {
try {
String sql="insert into book(bookname,price,booktype) values(?,?,?)";
con=DBAccess.getConnection();
ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, book.getBookname());
ps.setFloat(2, book.getPrice());
ps.setString(3, book.getBooktype());
ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBAccess.close(con, ps, null);
}
}
public List<Book> queryBookList(Book book,PageBean pageBean) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
String sql="select *from book where 1=1";
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(book.getBookname())) {
sql += " and bookname like '%"+book.getBookname()+"%' ";
}
return super.queryBookList(sql, Book.class, pageBean);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
BookDao bookDao=new BookDao();
Book book=new Book();
// book.setBookname("1");
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean();
pageBean.setPage(2);
pageBean.setRows(10);
// pageBean.setPagination(false);
int total = pageBean.getTotal();
List<Book> queryBookList = bookDao.queryBookList(book, pageBean);
for (Book book2 : queryBookList) {
System.out.println(book2);
}
}
}
BaseDao
1)匿名内部接口
2)分页查询方法,接口方法传参
(返回:总记录数+指定页码并满足条件的记录集)
3)二次查询的条件要一致
getCountSql()/getPagerSql()
package com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.dao;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.entity.Book;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.DBAccess;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.PageBean;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.StringUtils;
public class BaseDao<T> {
/**
*
* @param sql 传入的sql语句
* @param clz 传入的对象
* @param pageBean 分页
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
*/
public List<T> queryBookList(String sql,Class<?> clz,PageBean pageBean) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Connection con=DBAccess.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
// 如果pageBean不等于空 并且 允许分页 则执行分页代码块
if (pageBean != null && pageBean.isPagination()) {
String CountSql=getCountSql(sql);
ps=con.prepareStatement(CountSql);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
pageBean.setTotal(rs.getLong(1)+"");
}
System.out.println("总记录数:"+pageBean.getTotal());
String PagerSql=getPagerSql(sql, pageBean);
ps=con.prepareStatement(PagerSql);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
}else {
ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
}
List<T> list=new ArrayList<T>();
T t;
while (rs.next()) {
// list.add(new Book(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("bookname"), rs.getFloat("price"), rs.getString("booktype")));
// 通过反射机制实例化 并且赋值
t=(T) clz.newInstance();
Field[] fields = clz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
// getObject 因为不知道传过来是什么值 所以写个Object代替
field.set(t, rs.getObject(field.getName()));
}
list.add(t);
}
DBAccess.close(con, ps, rs);
return list;
}
// 获取总纪录数的sql语句
public String getCountSql(String sql) {
return "select count(*) from ("+sql+") t";
}
// 获取分页数据的sql语句
public String getPagerSql(String sql,PageBean pageBean) {
return sql+" limit "+pageBean.getStartIndex()+","+pageBean.getRows();
}
}
3. junit
java单元测试/白盒测试
setUp
tearDown
测试用例
Servlet中的init和destory方法只会运行一次
Junit中的setUp和tearDown方法是根据方法数量来决定的
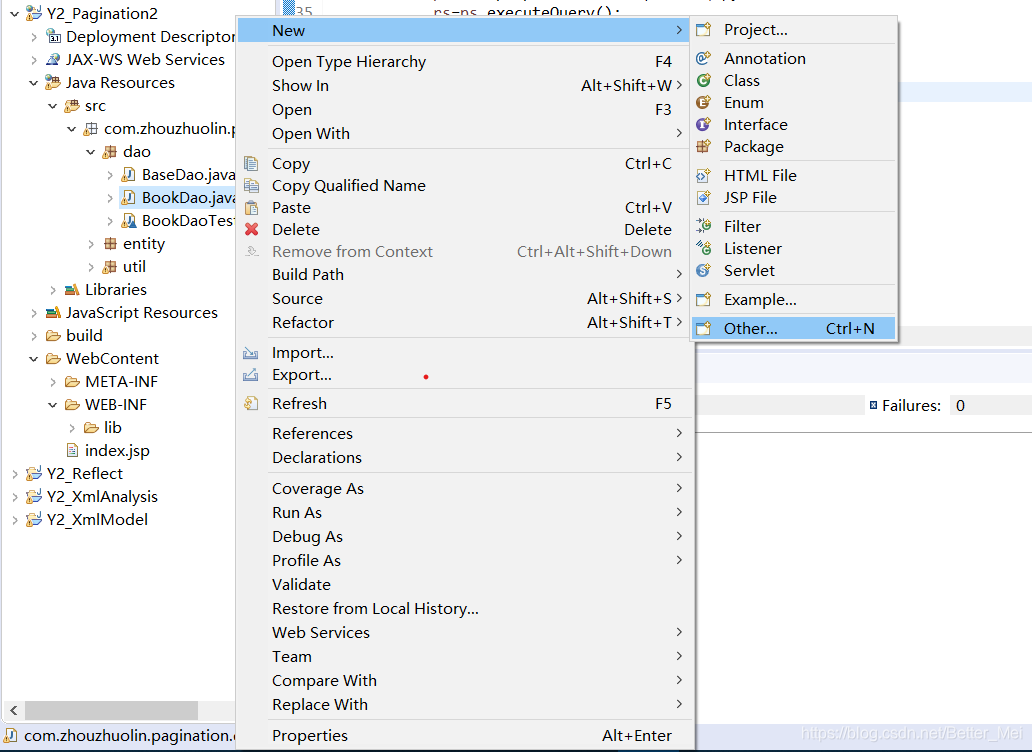
第一步选中方法类右键选择new在选择ohter
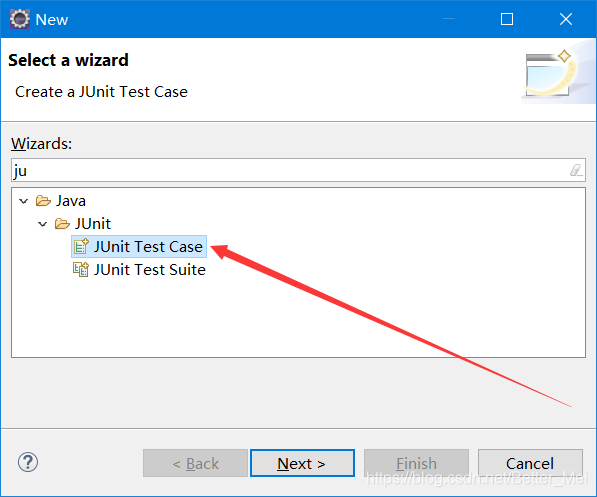
搜索junit
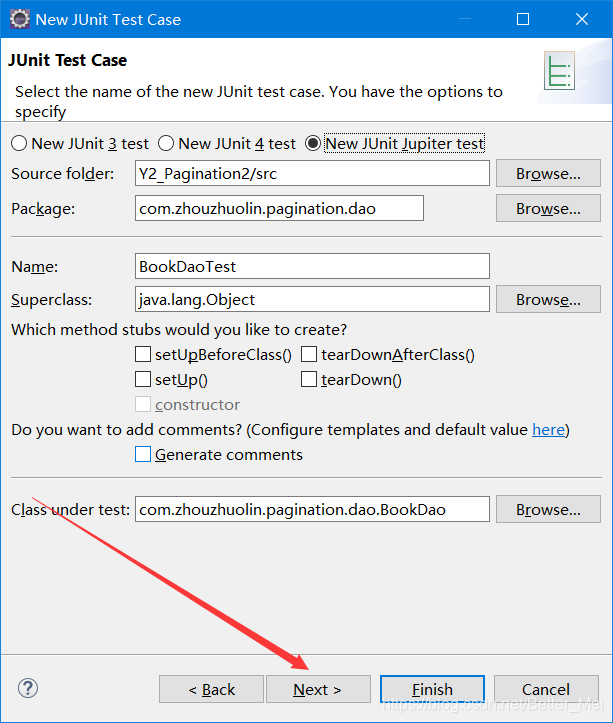
然后点next 到一下界面 继续选择next
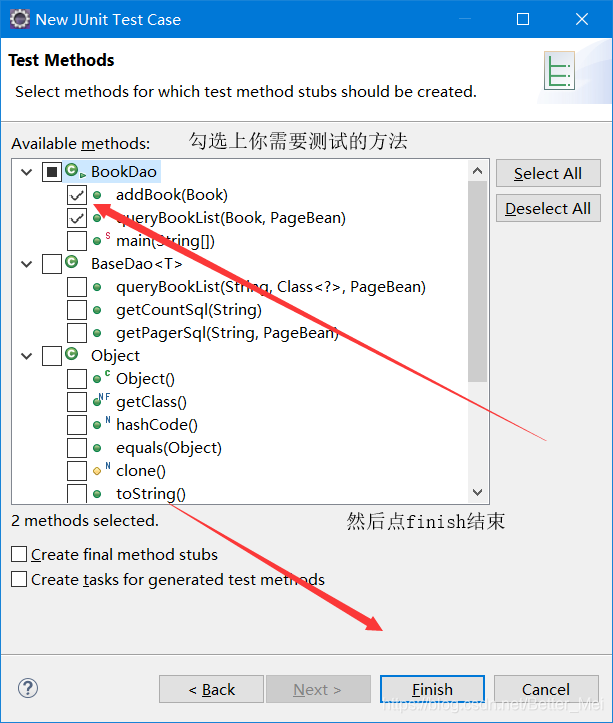
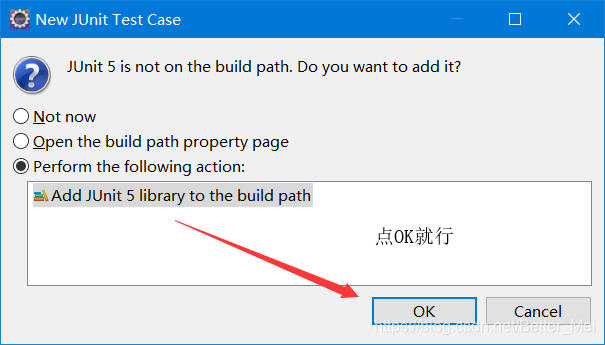
到junit界面
Servlet中的init和destory方法只会运行一次
Junit中的setUp和tearDown方法是根据方法数量来决定的
准备实体类和方法类代码如下
package com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.dao;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.entity.Book;
import com.zhouzhuolin.pagination.util.PageBean;
class BookDaoTest {
//因为我只测试分页方法 没测试添加方法 所以说不写
private BookDao bookDao=new BookDao();
private Book book=new Book();
@Test
void testAddBook() {
}
@Test
void testQueryBookListBookPageBean() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
PageBean pageBean=new PageBean();
List<Book> queryBookList = bookDao.queryBookList(book, pageBean);
for (Book book : queryBookList) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
}
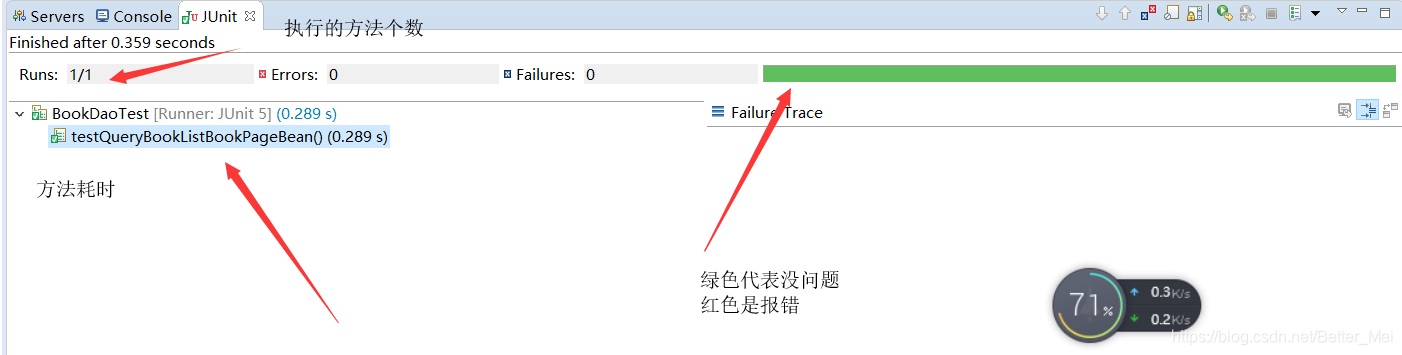
测试步骤
选中要执行的方法 点Junittest就行
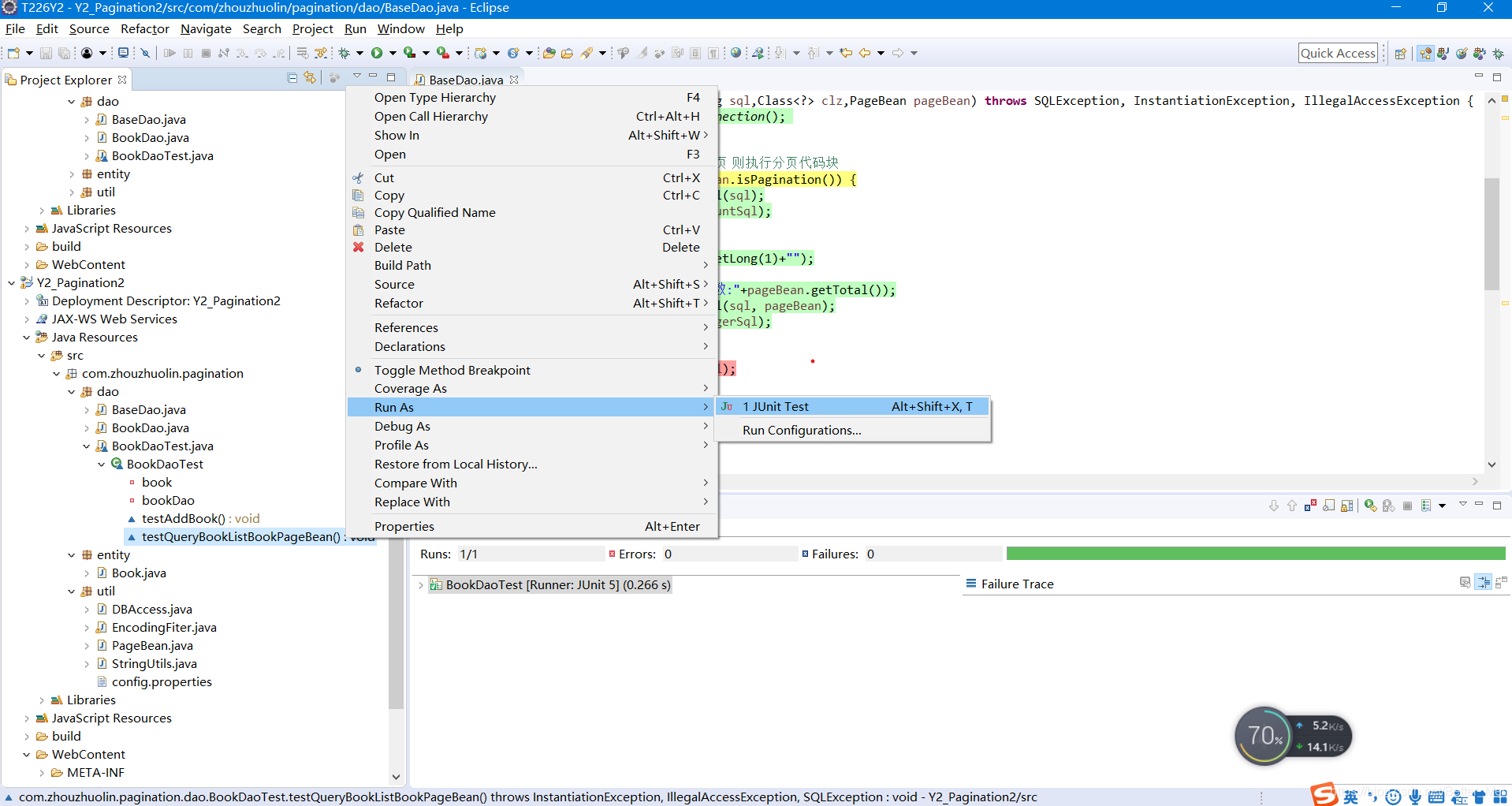
测试结果
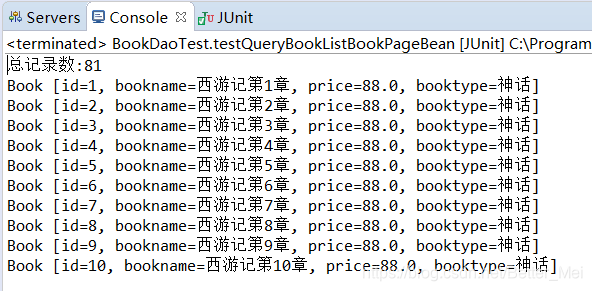
Junit面板




 本文介绍了Java中通用分页组件PageBean的关键属性,包括页码、页大小、总记录数等,并详细阐述了后台分页查询的实现,涉及entity、dao层的处理。同时,讲解了如何使用Junit进行单元测试,包括setUp和tearDown方法的使用,以及测试步骤和结果的展示。
本文介绍了Java中通用分页组件PageBean的关键属性,包括页码、页大小、总记录数等,并详细阐述了后台分页查询的实现,涉及entity、dao层的处理。同时,讲解了如何使用Junit进行单元测试,包括setUp和tearDown方法的使用,以及测试步骤和结果的展示。
















 2066
2066

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








