原题链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
1. 题目介绍
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
给出一个链表,返回环形开始的那个节点。如果这个链表中没有环,那么就返回null。
为了表示一个链表中的环形。我们使用整数pos代表链表的尾节点指向的节点。如果pos是- 1 ,说明这个链表没有环。 这个pos在函数的调用中不会被调用,也就是,pos我们不知道。
注意: 不要修改链表
Example 1:
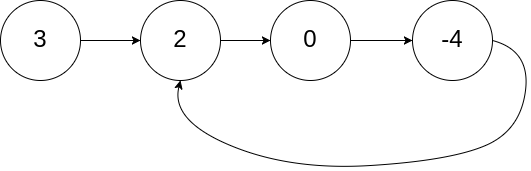
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list,
where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
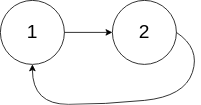
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list,
where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.

2. 解题思路
2.1 方法1:使用HashSet
使用集合HashSet。从头至尾遍历链表,每次都将经过的节点放入集合。如果当前的节点 cur 在集合中已经出现过了,那么 cur 就是环形开始的那个节点。
实现代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head ==null || head.next ==null) {
return null;
}
ListNode assist = new ListNode(0);
assist.next = head;
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = assist.next;
while(cur != null){
if (set.contains(cur) == true) {
return cur;
}else{
set.add(cur );
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
2.2 双指针法
注: 本解法和图片源自: https://www.cnblogs.com/hiddenfox/p/3408931.html
有一个快指针fast,还有一个慢指针slow。快指针每次走2步,慢指针每次走1步。
由于链表有环,那么快指针必定要超过慢指针。两个指针之间的路程差等于环的长度减去一开始两个指针的路程差。
首先我们看下面这张图:
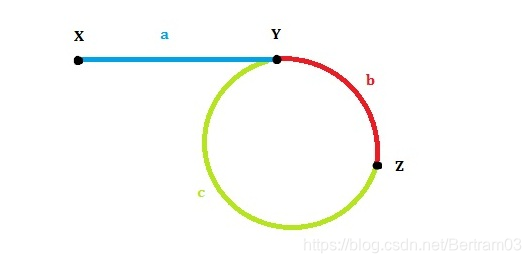
设:链表头是X,环的第一个节点是Y, slow 和 fast 第一次的交点是Z。各段的长度分别是 a , b , c,如图所示。环的长度是L。slow 和 fast 的速度分别是 1 和 2。
第一次相遇时slow走过的距离:a+b,fast走过的距离:a+b+c+b。
因为fast的速度是slow的两倍,所以fast走的距离是slow的两倍,有 2(a+b) = a+b+c+b,可以得到a=c(这个结论很重要!)。
我们发现L=b+c=a+b,也就是说,从一开始到二者第一次相遇,之间的路程就等于环的长度。
我们已经得到了结论a=c,那么让两个指针分别从X和Z开始走,每次走一步,那么正好会在Y相遇!也就是环的第一个节点。
实现代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head ==null || head.next ==null) {
return null;
}
ListNode assist = new ListNode(0);
assist.next = head;
ListNode slow = assist.next;
ListNode fast = assist.next;
//这里必须用do-while循环
//两个指针的起始位置都是一样的,要先跑起来,再判断是否相等
do{
if( fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
while(fast != slow);
//慢指针回到head处
slow = assist.next;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
3. 参考链接
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/willduan1/article/details/50938210
https://www.cnblogs.com/hiddenfox/p/3408931.html




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








