一、项目介绍
本文基于深度学习目标检测算法YOLOv11,设计并实现了一套轴承缺陷智能识别系统。针对工业场景中轴承表面常见的凹槽(aocao)、凹线(aoxian)、擦伤(cashang)和划痕(huahen)四类缺陷,构建了包含1,085张图像的数据集(训练集759张、验证集326张),通过数据增强和迁移学习优化模型性能。系统采用PyTorch框架开发,集成用户友好的UI界面与登录注册功能,支持实时检测与结果可视化。实验表明,YOLOv11在验证集上达到平均精度(mAP@0.5)99.5%,显著提高了缺陷检测效率。本研究为工业质检自动化提供了可落地的解决方案。
引言
轴承作为机械设备的核心部件,其表面缺陷直接影响设备寿命与运行安全。传统人工检测存在效率低、主观性强等问题,而基于深度学习的视觉检测技术为解决这一难题提供了新思路。YOLO系列算法因其实时性与高精度在工业检测中广受关注,但现有研究多集中于通用场景,针对轴承多类缺陷的定制化检测系统仍待探索。
目录
基于深度学习YOLOv11的轴承缺陷识别检测系统(YOLOv11+YOLO数据集+UI界面+登录注册界面+Python项目源码+模型)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
基于深度学习YOLOv11的轴承缺陷识别检测系统(YOLOv11+YOLO数据集+UI界面+登录注册界面+Python项目源码+模型)
二、项目功能展示
✅ 用户登录注册:支持密码检测和安全性验证。
✅ 三种检测模式:基于YOLOv11模型,支持图片、视频和实时摄像头三种检测,精准识别目标。
✅ 双画面对比:同屏显示原始画面与检测结果。
✅ 数据可视化:实时表格展示检测目标的类别、置信度及坐标。
✅智能参数调节:提供置信度滑块,动态优化检测精度,适应不同场景需求。
✅科幻风交互界面:深色主题搭配动态光效,减少视觉疲劳,提升操作体验。
✅多线程高性能架构:独立检测线程保障流畅运行,实时状态提示,响应迅速无卡顿。

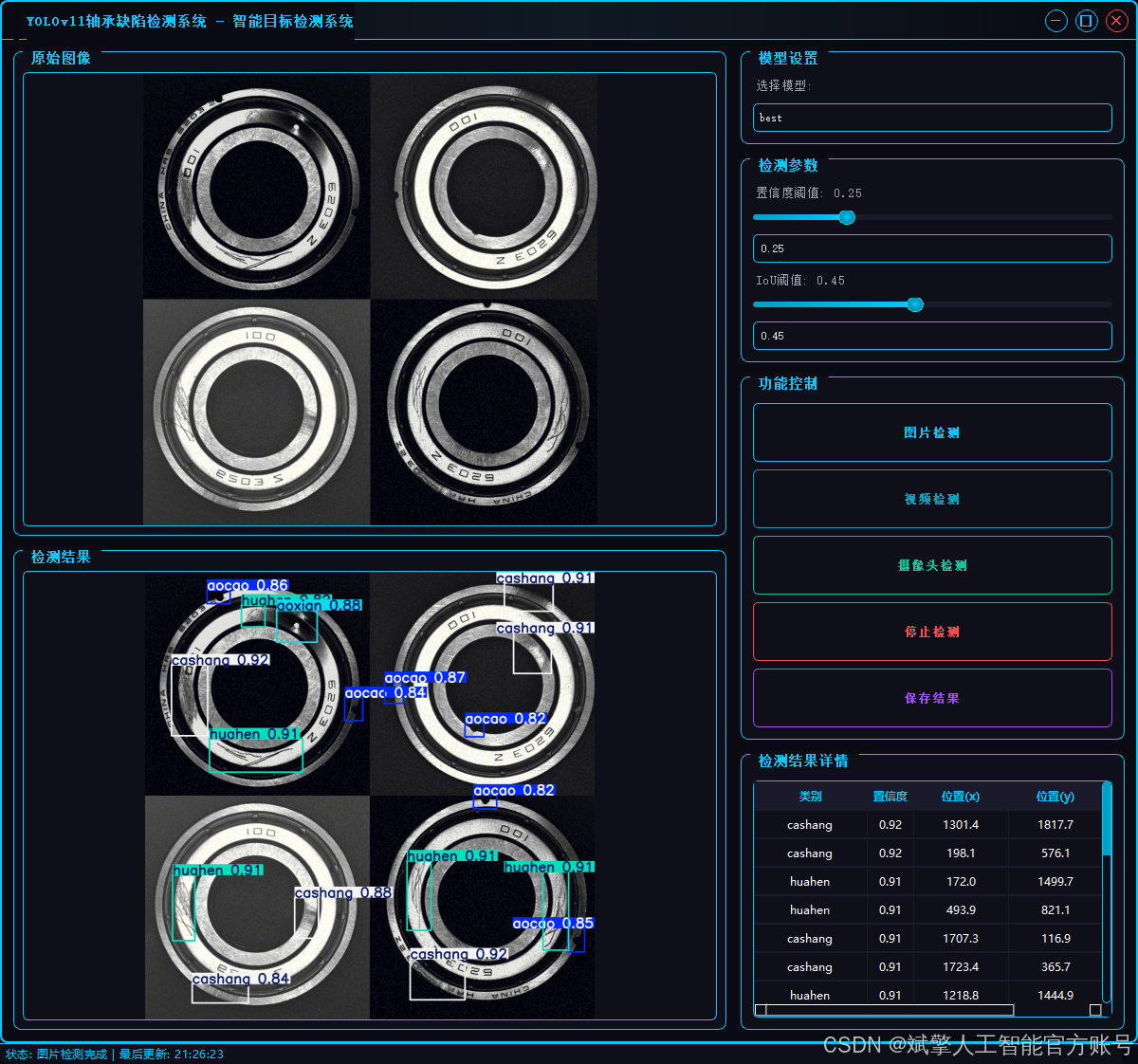
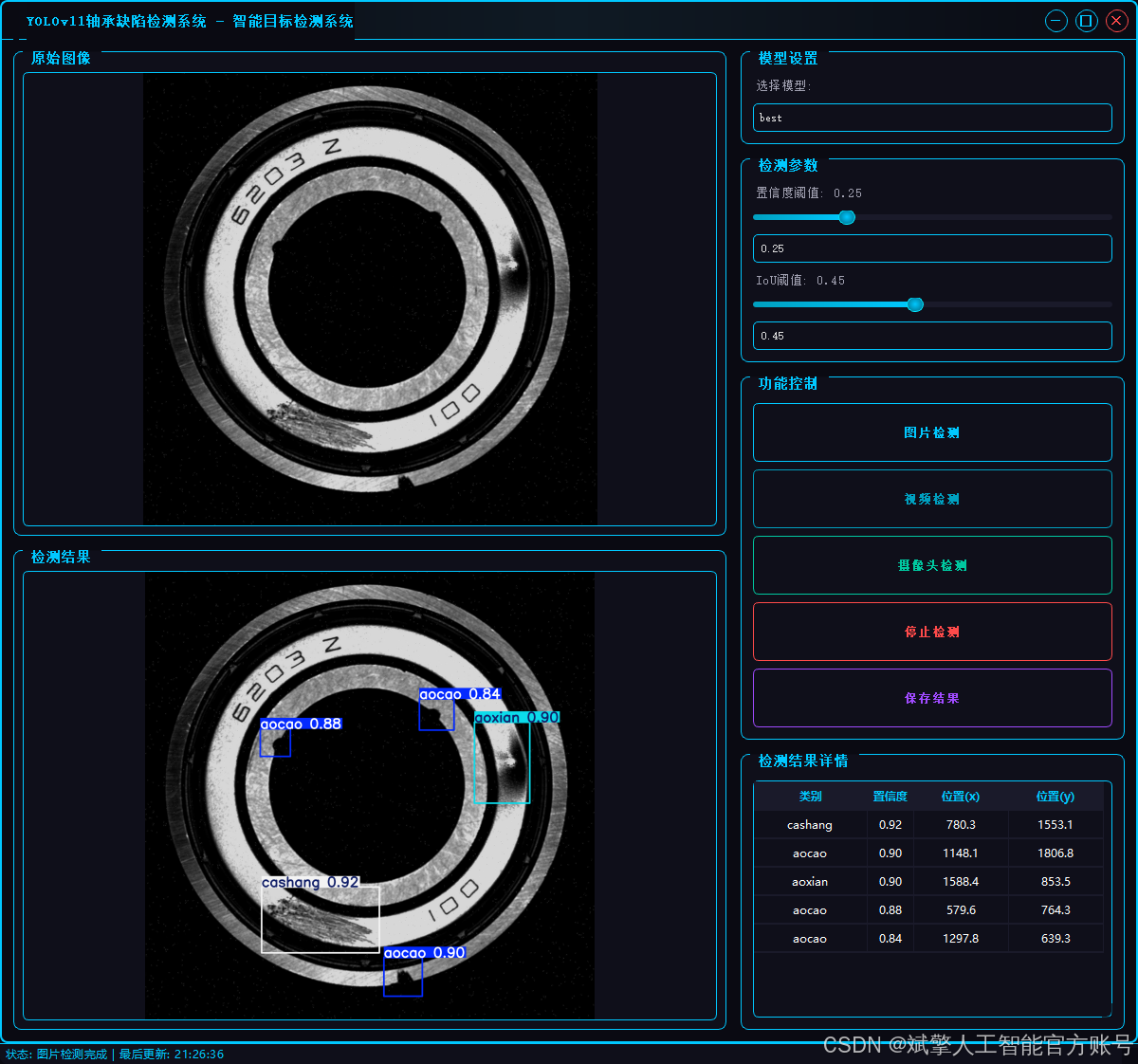
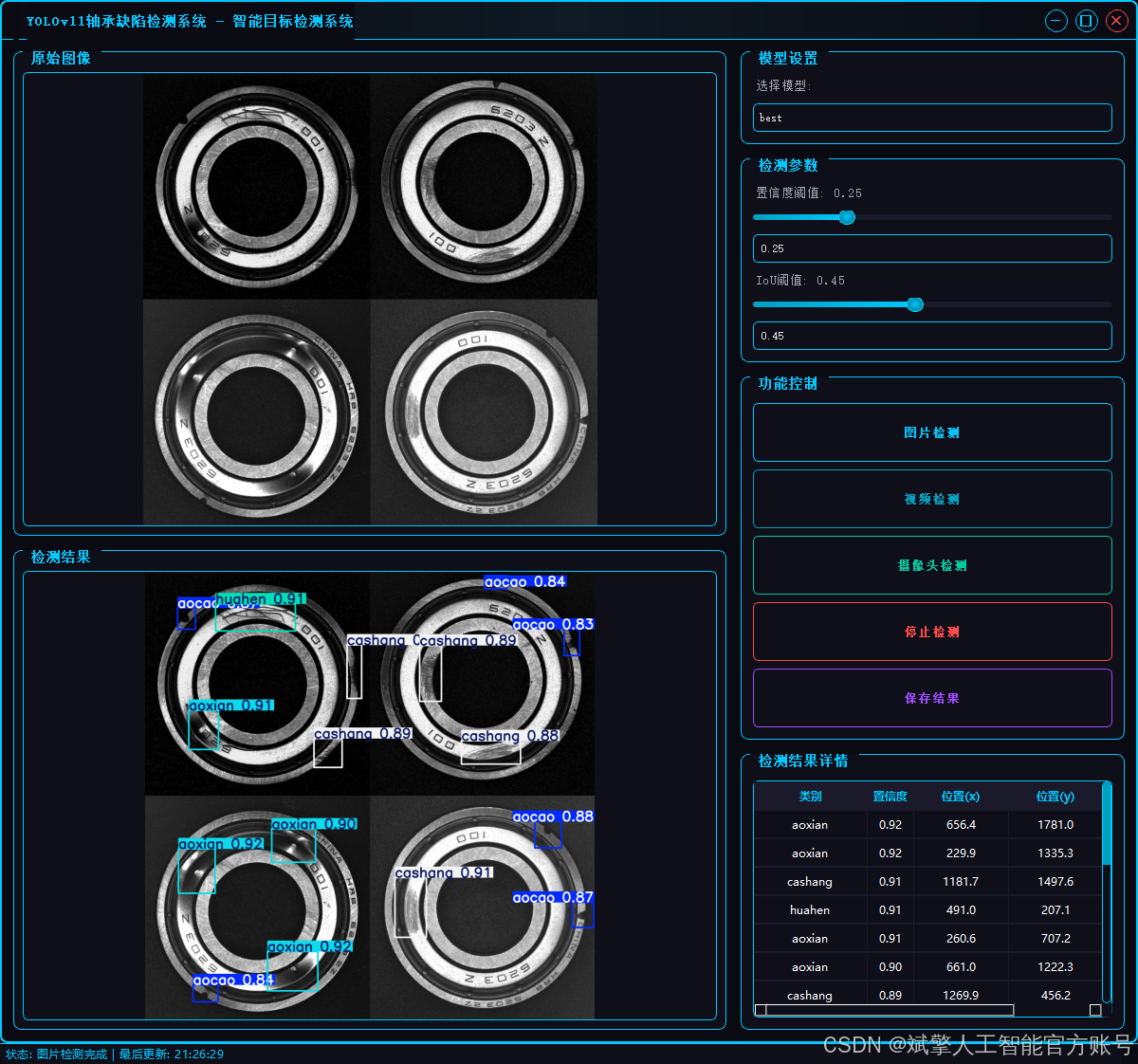
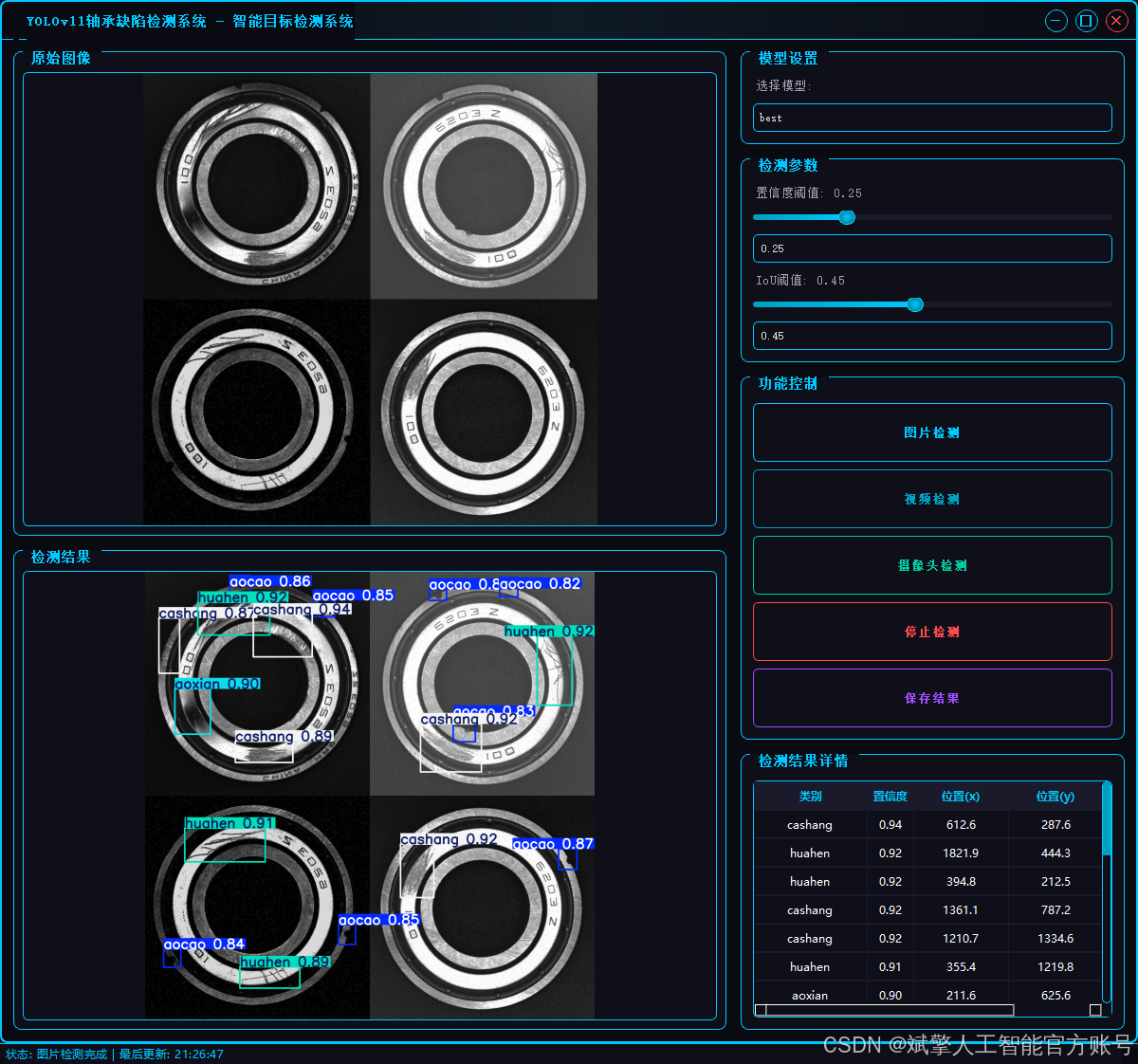
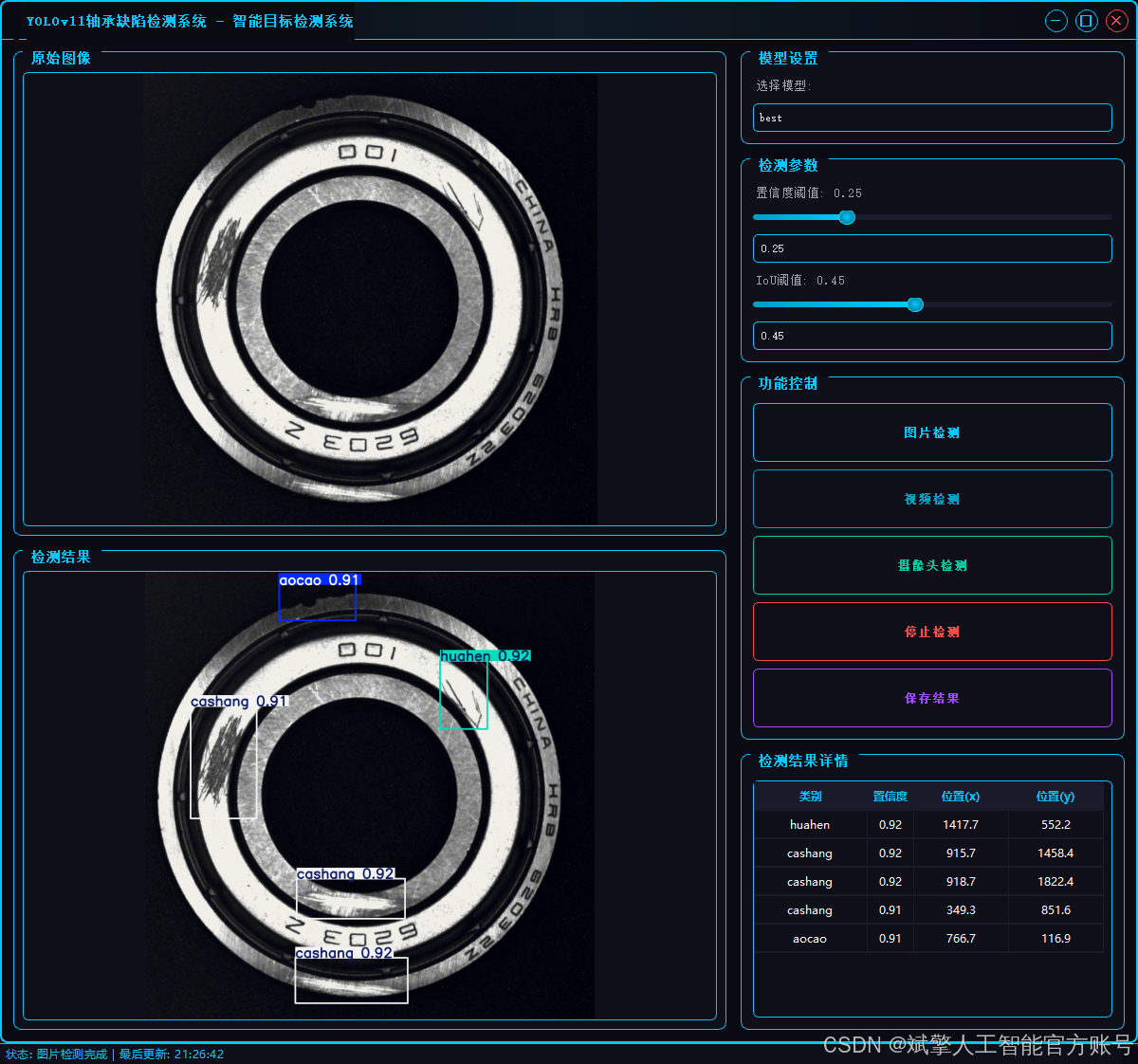
2.1 用户登录系统
-
提供用户登录和注册功能
-
用户名和密码验证
-
账户信息本地存储(accounts.json)
-
密码长度至少6位的安全要求
2.2 检测功能
-
图片检测:支持JPG/JPEG/PNG/BMP格式图片的火焰烟雾检测
-
视频检测:支持MP4/AVI/MOV格式视频的逐帧检测
-
摄像头检测:实时摄像头流检测(默认摄像头0)
-
检测结果保存到"results"目录
2.3 检测结果显示
-
显示原始图像和检测结果图像
-
检测结果表格展示,包含:
-
检测到的类别
-
置信度分数
-
物体位置坐标(x,y)、
-
2.4 参数配置
-
模型选择
-
置信度阈值调节(0-1.0)
-
IoU(交并比)阈值调节(0-1.0)
-
实时同步滑块和数值输入框
2.5 其他功能
-
检测结果保存功能
-
视频检测时自动保存结果视频
-
状态栏显示系统状态和最后更新时间
-
无边框窗口设计,可拖动和调整大小
3. 技术特点
-
采用多线程处理检测任务,避免界面卡顿
-
精美的UI设计,具有科技感的视觉效果:
-
发光边框和按钮
-
悬停和按下状态效果
-
自定义滑块、表格和下拉框样式
-
-
检测结果保存机制
-
响应式布局,适应不同窗口大小
4. 系统流程
-
用户登录/注册
-
选择检测模式(图片/视频/摄像头)
-
调整检测参数(可选)
-
开始检测并查看结果
-
可选择保存检测结果
-
停止检测或切换其他模式
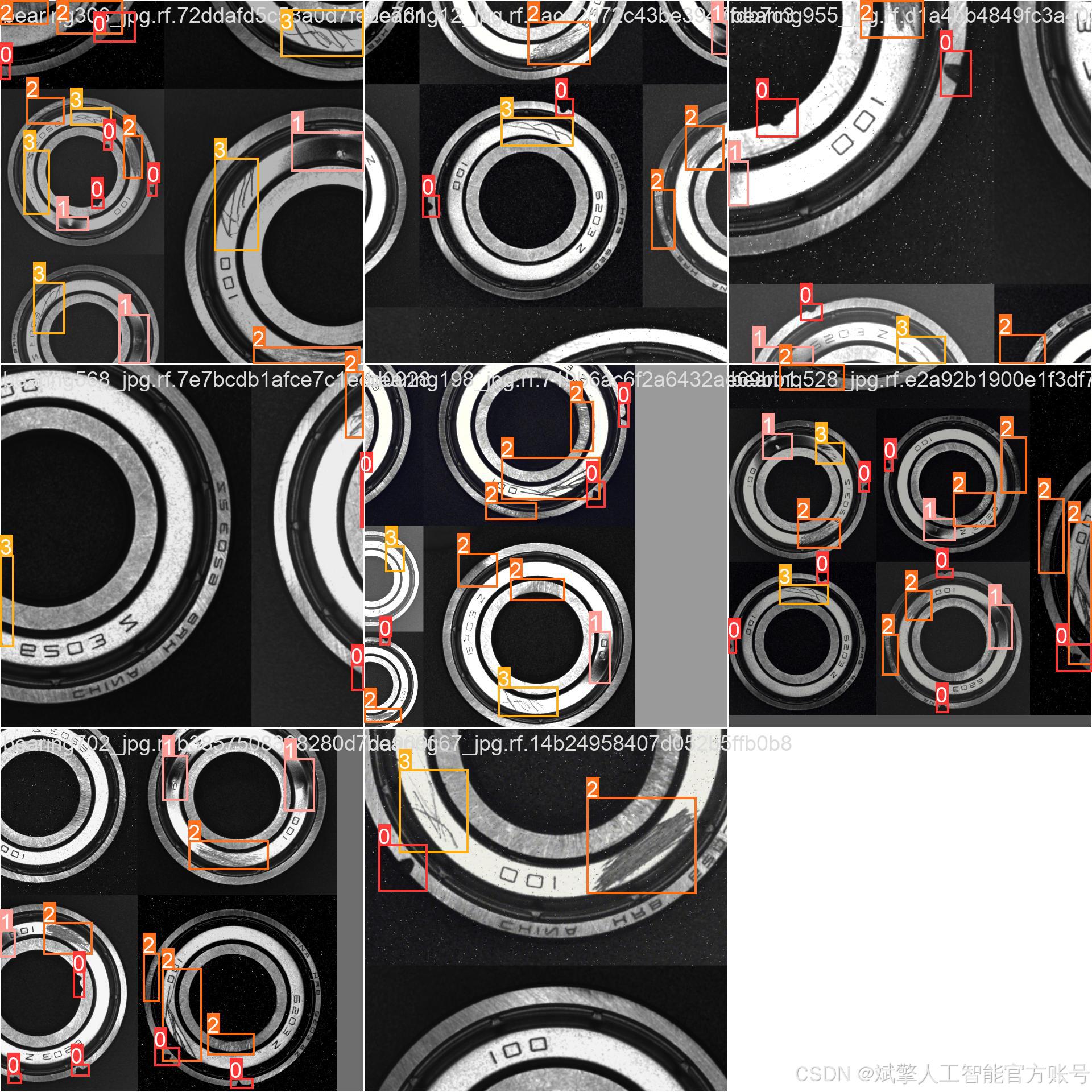
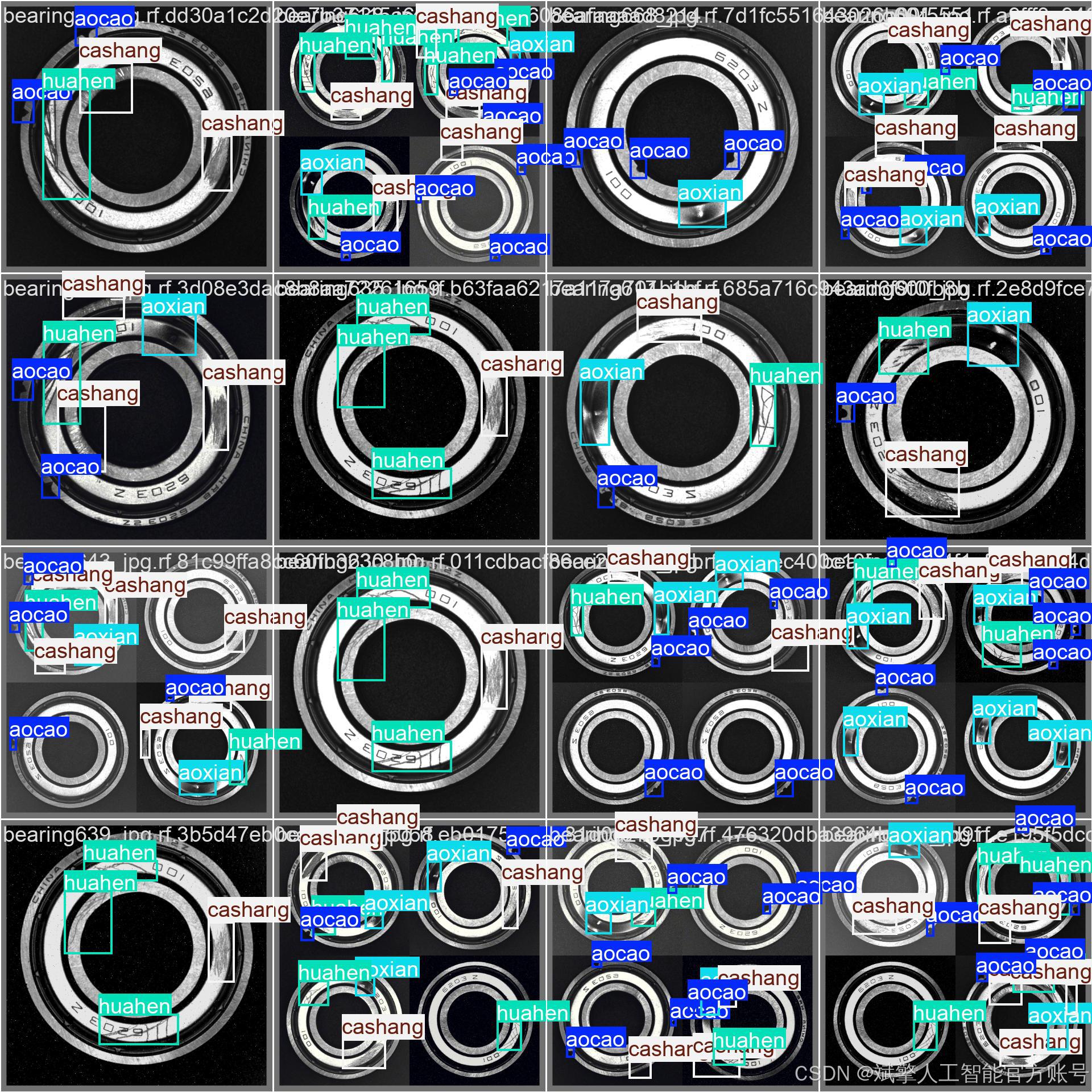
三、数据集介绍
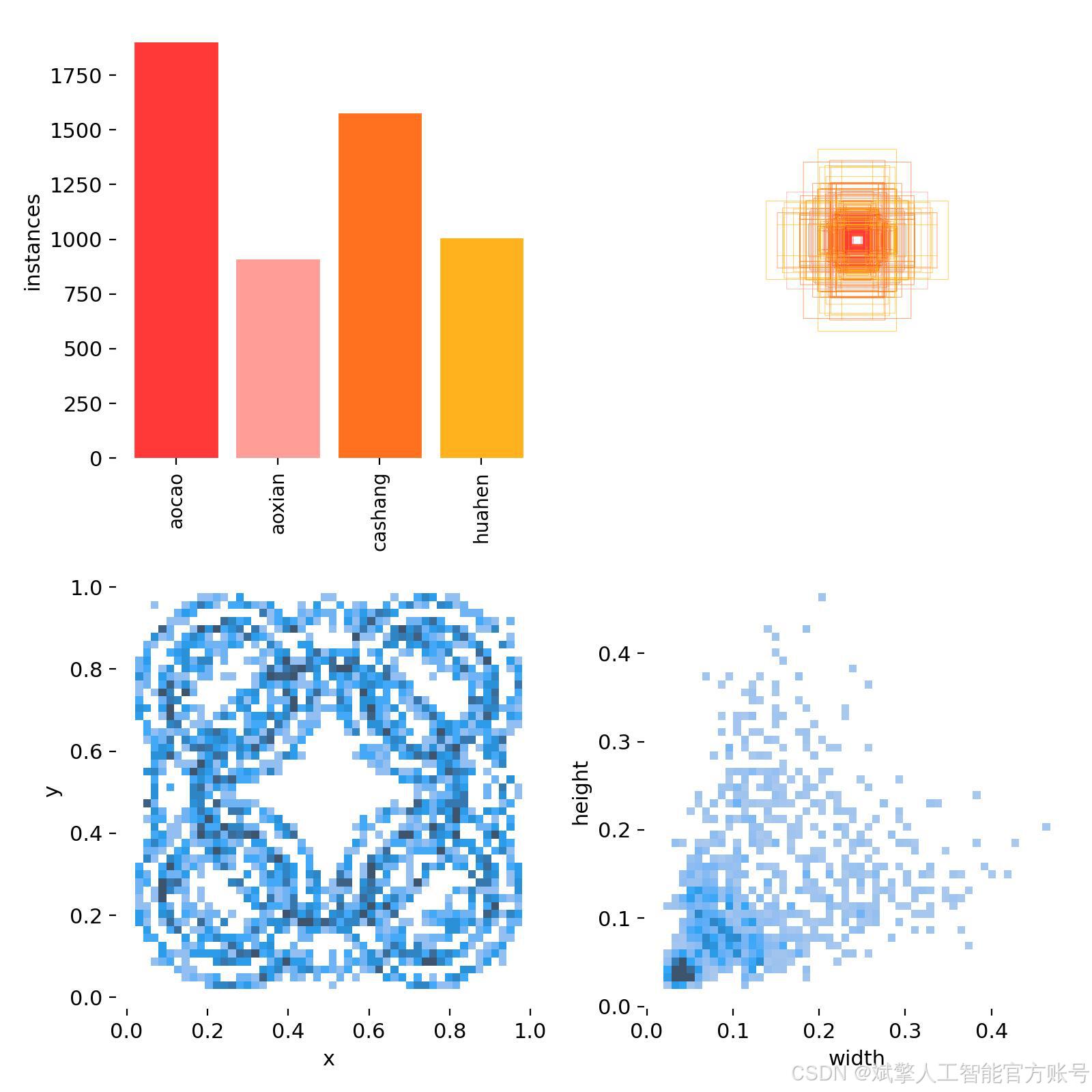
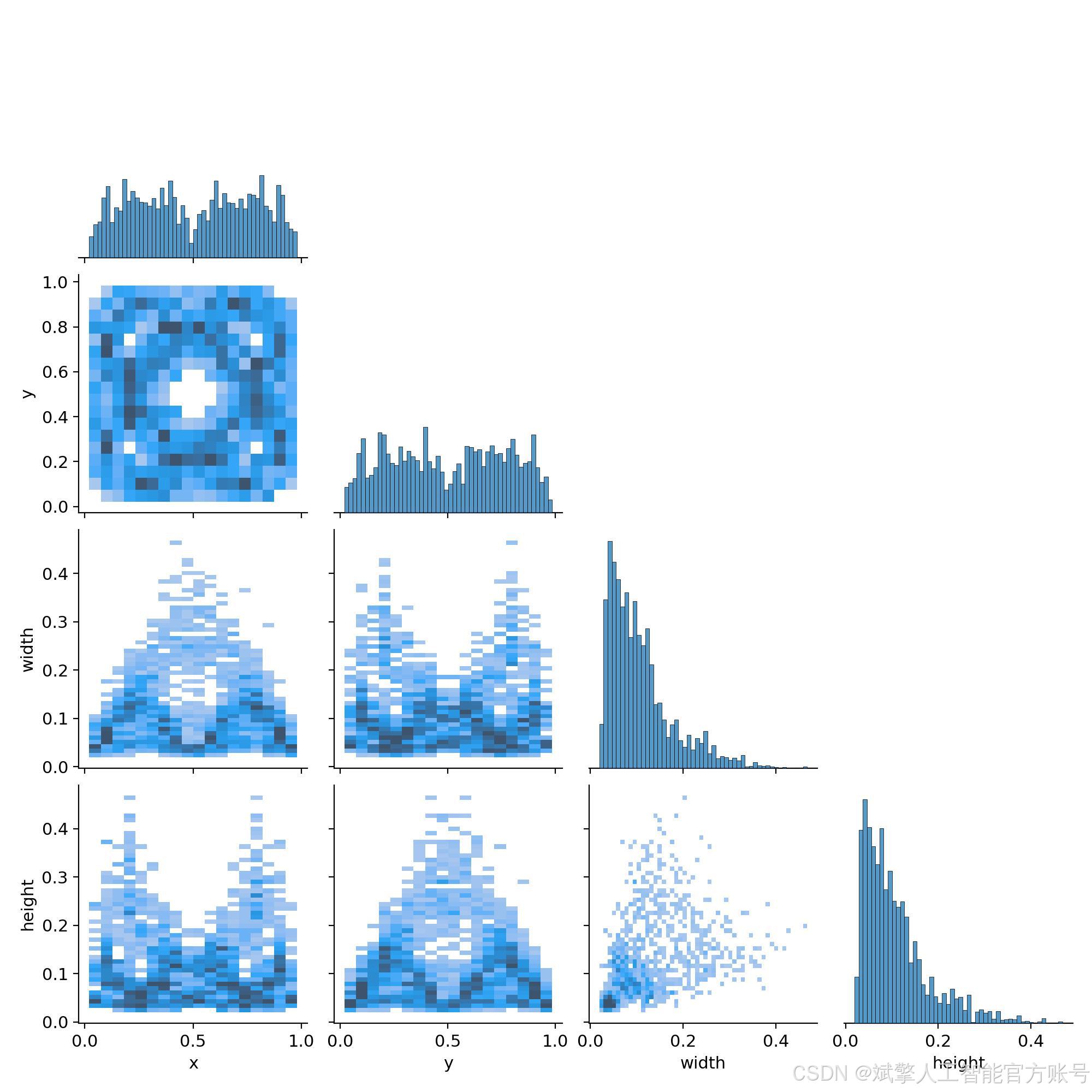
本研究所使用的轴承缺陷数据集共包含 1,085 张 高分辨率工业图像,涵盖轴承表面常见的 4 类缺陷:凹槽(aocao)、凹线(aoxian)、擦伤(cashang)和划痕(huahen)。数据集按照 8:2 的比例 划分为 训练集(759 张) 和 验证集(326 张),以确保模型训练和评估的可靠性。
数据集配置文件
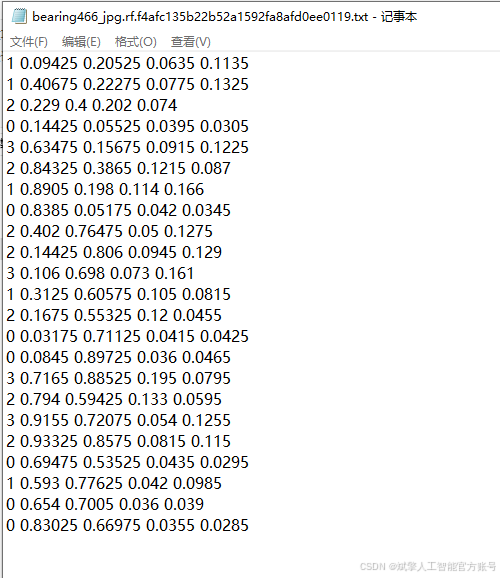
数据集采用标准化YOLO格式组织:
train: F:\轴承缺陷检测数据集\images\train
val: F:\轴承缺陷检测数据集\images\val
nc: 4
names: ['aocao', 'aoxian', 'cashang', 'huahen']


四、项目环境配置
创建虚拟环境
首先新建一个Anaconda环境,每个项目用不同的环境,这样项目中所用的依赖包互不干扰。
终端输入
conda create -n yolov11 python==3.9
激活虚拟环境
conda activate yolov11
安装cpu版本pytorch
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
安装所需要库
pip install -r requirements.txt
pycharm中配置anaconda
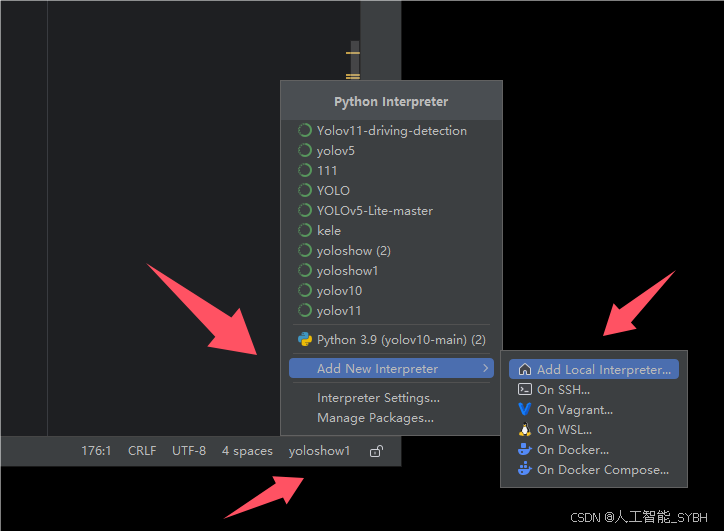
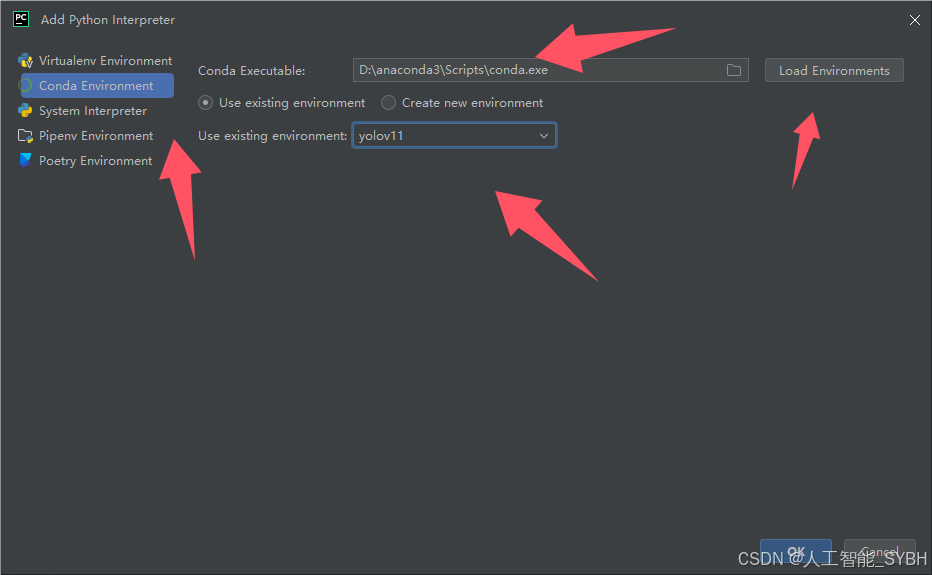
五、模型训练
训练代码
from ultralytics import YOLO
model_path = 'yolo11s.pt'
data_path = 'data.yaml'
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLO(model_path)
results = model.train(data=data_path,
epochs=100,
batch=8,
device='0',
workers=0,
project='runs',
name='exp',
)根据实际情况更换模型 # yolov11n.yaml (nano):轻量化模型,适合嵌入式设备,速度快但精度略低。 # yolov11s.yaml (small):小模型,适合实时任务。 # yolov11m.yaml (medium):中等大小模型,兼顾速度和精度。 # yolov11b.yaml (base):基本版模型,适合大部分应用场景。 # yolov11l.yaml (large):大型模型,适合对精度要求高的任务。
--batch 8:每批次8张图像。--epochs 100:训练100轮。--datasets/data.yaml:数据集配置文件。--weights yolov11s.pt:初始化模型权重,yolov11s.pt是预训练的轻量级YOLO模型。
训练结果
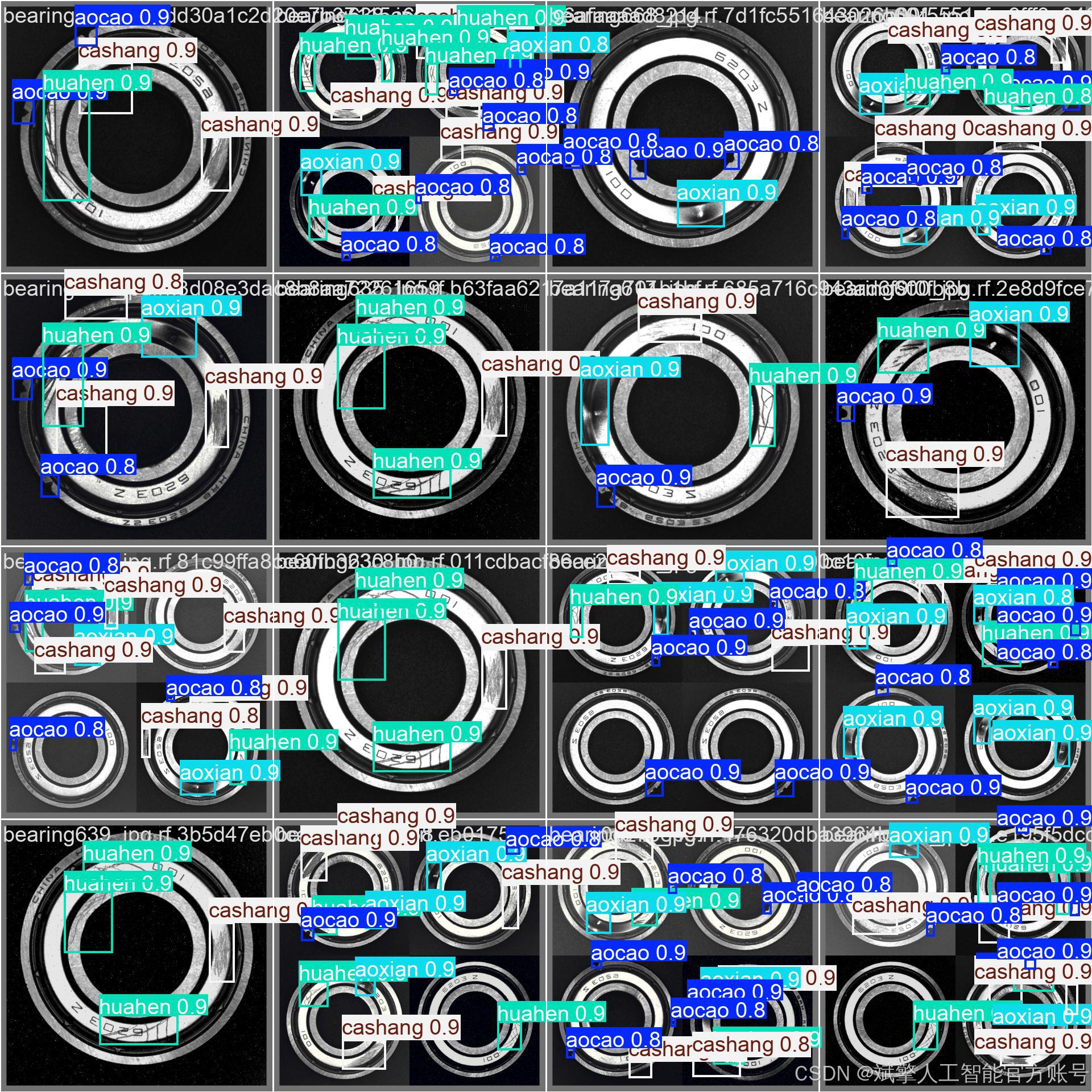
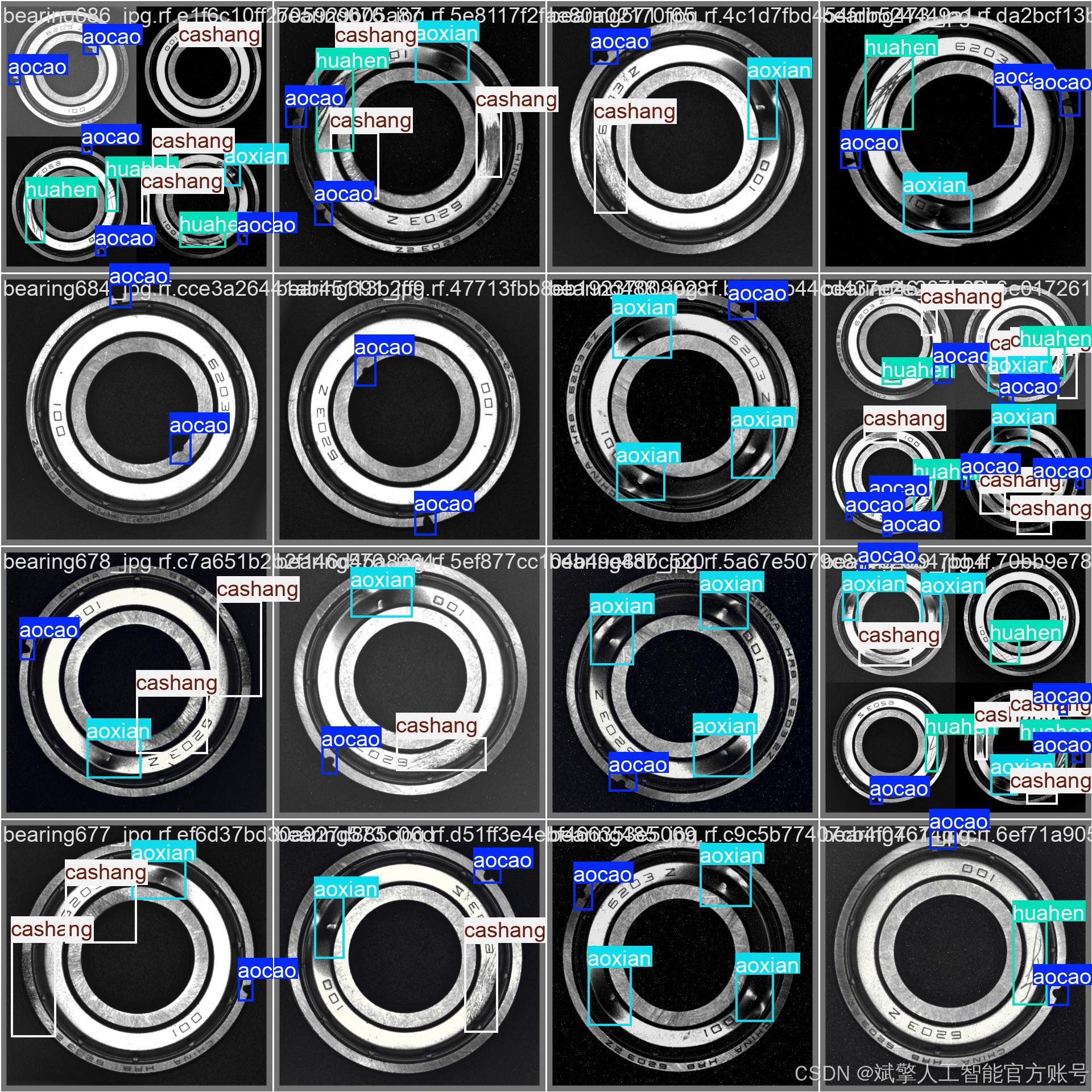
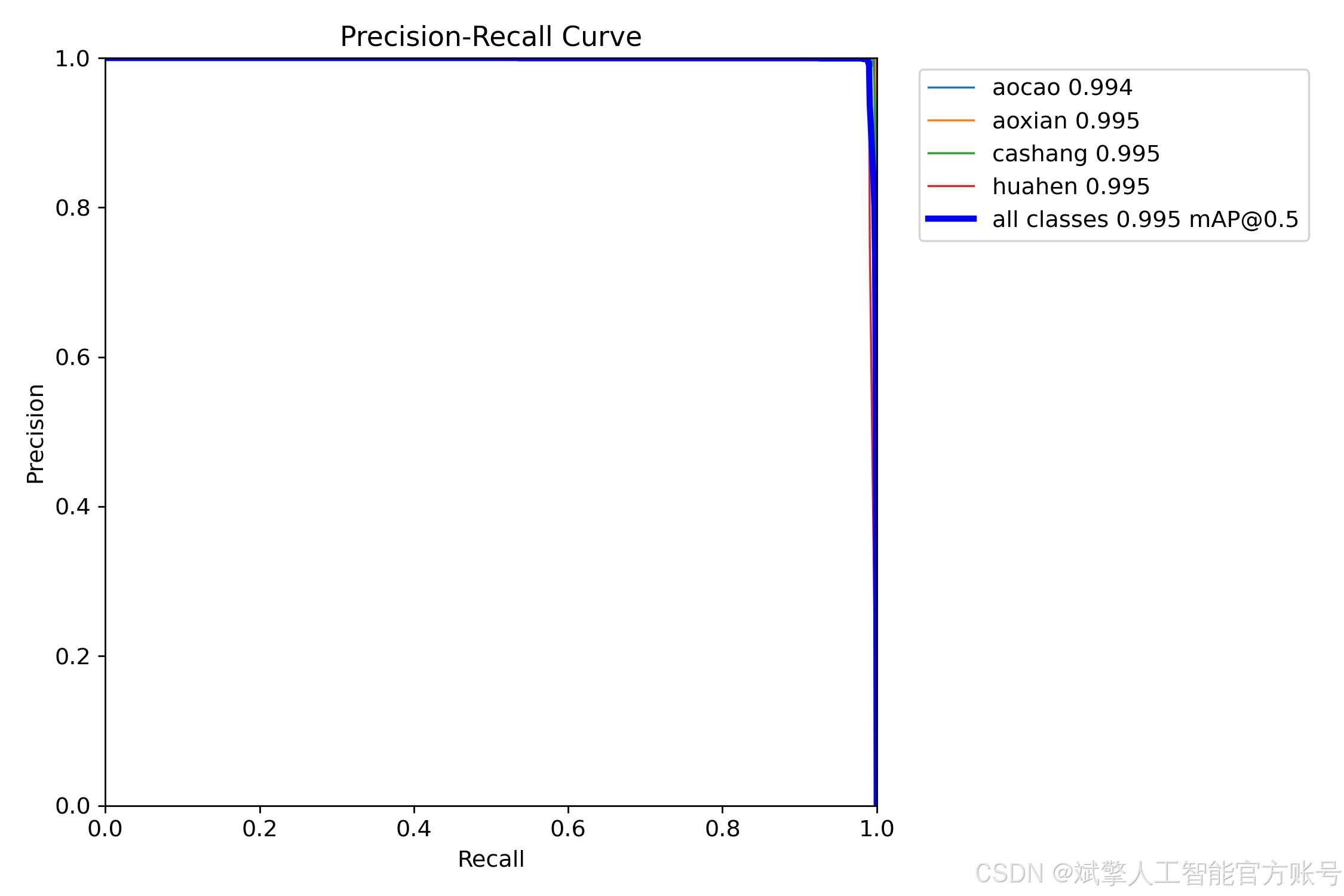
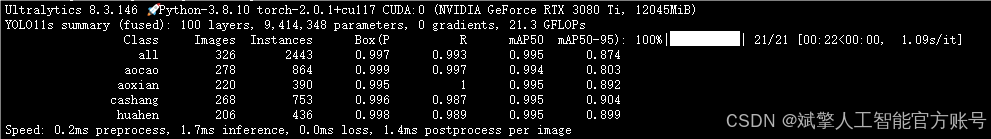
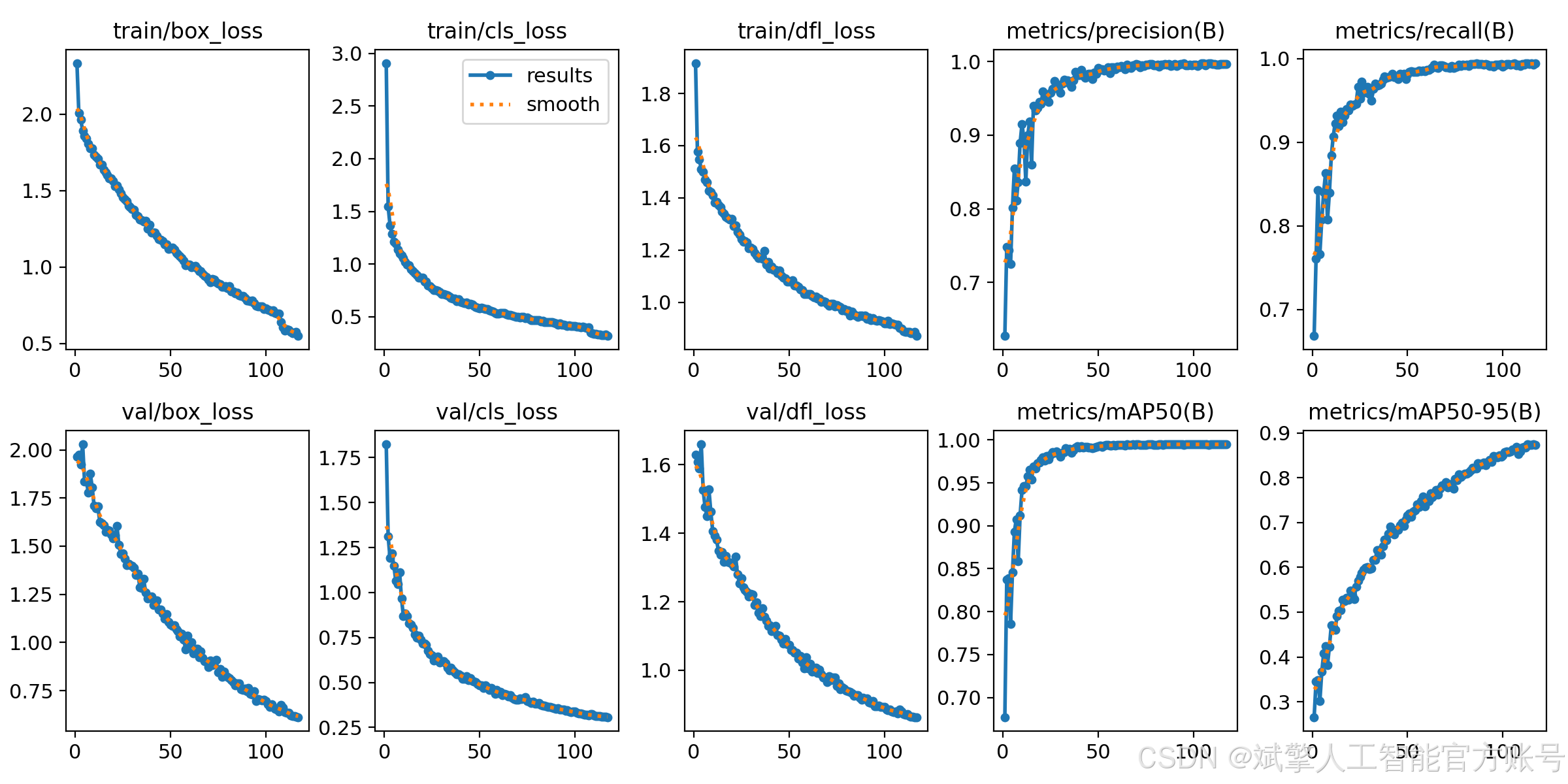

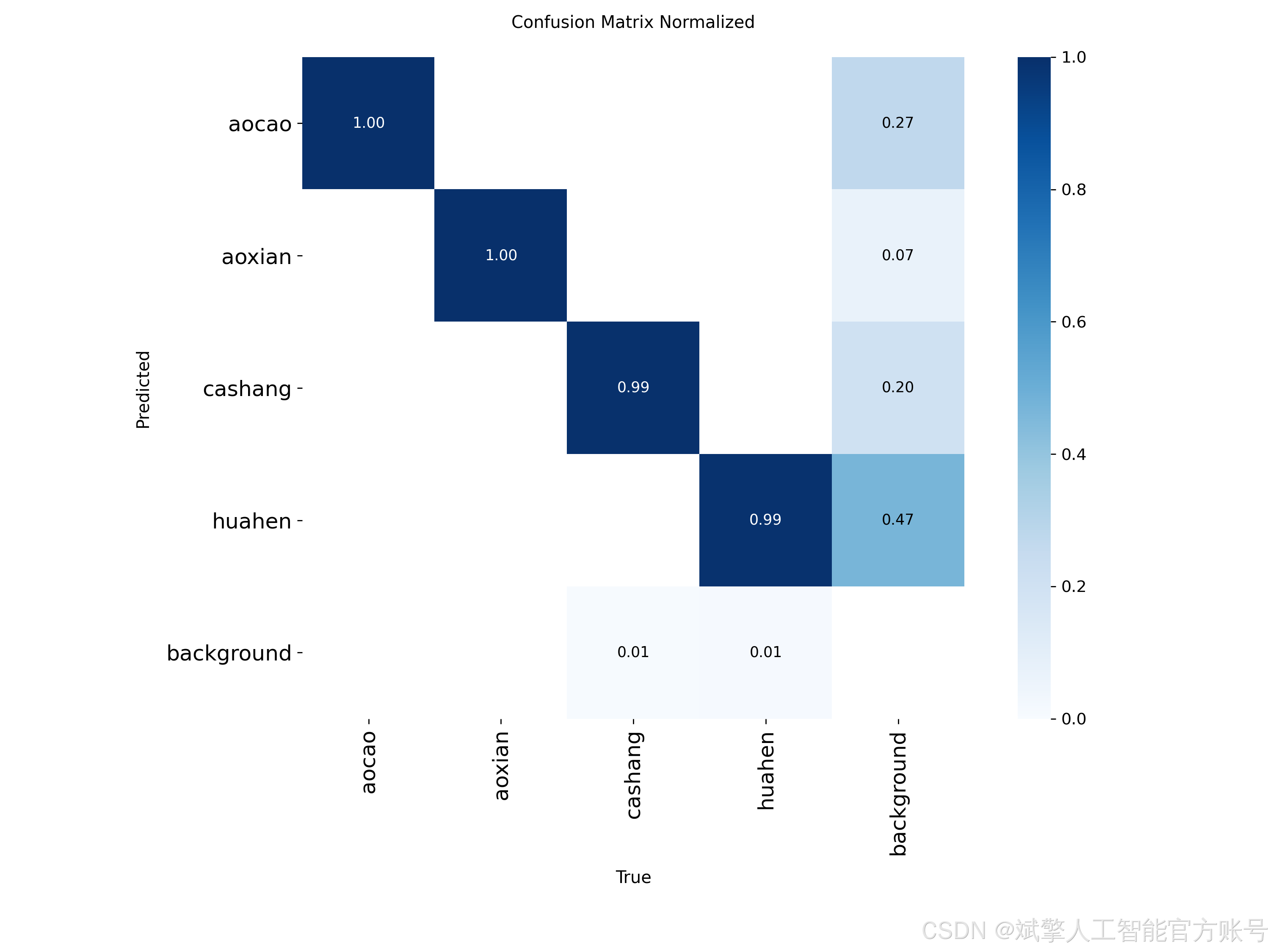
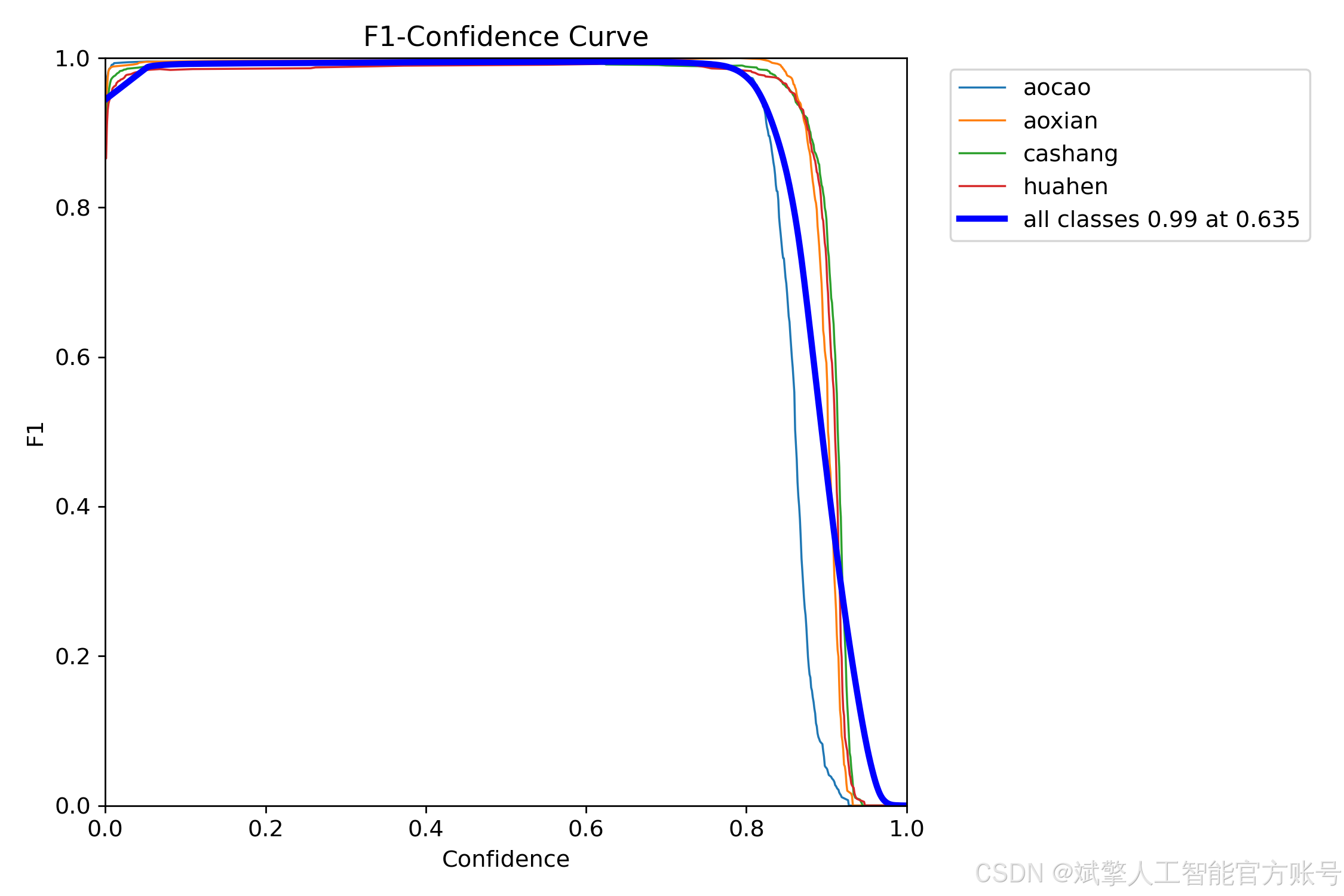
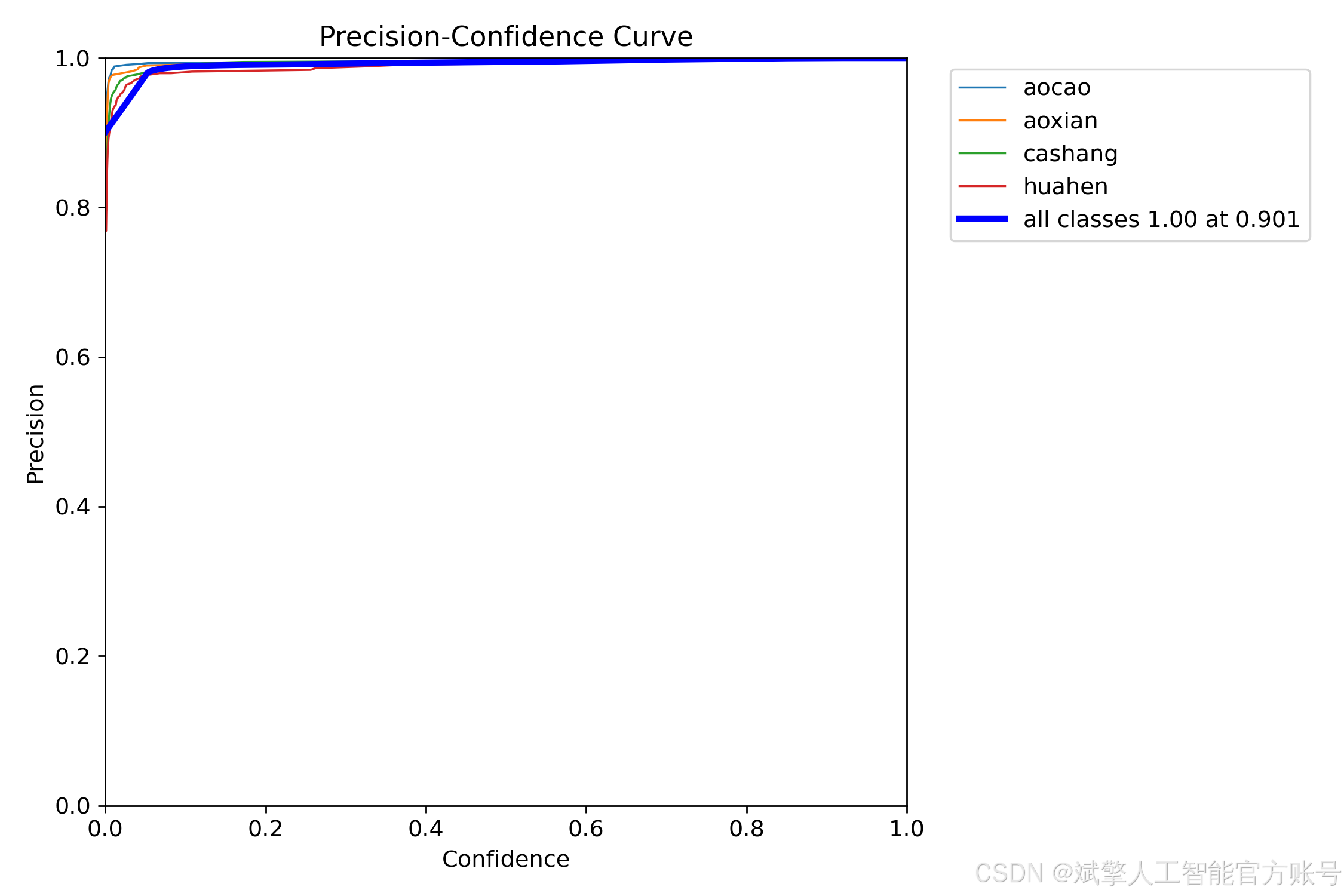
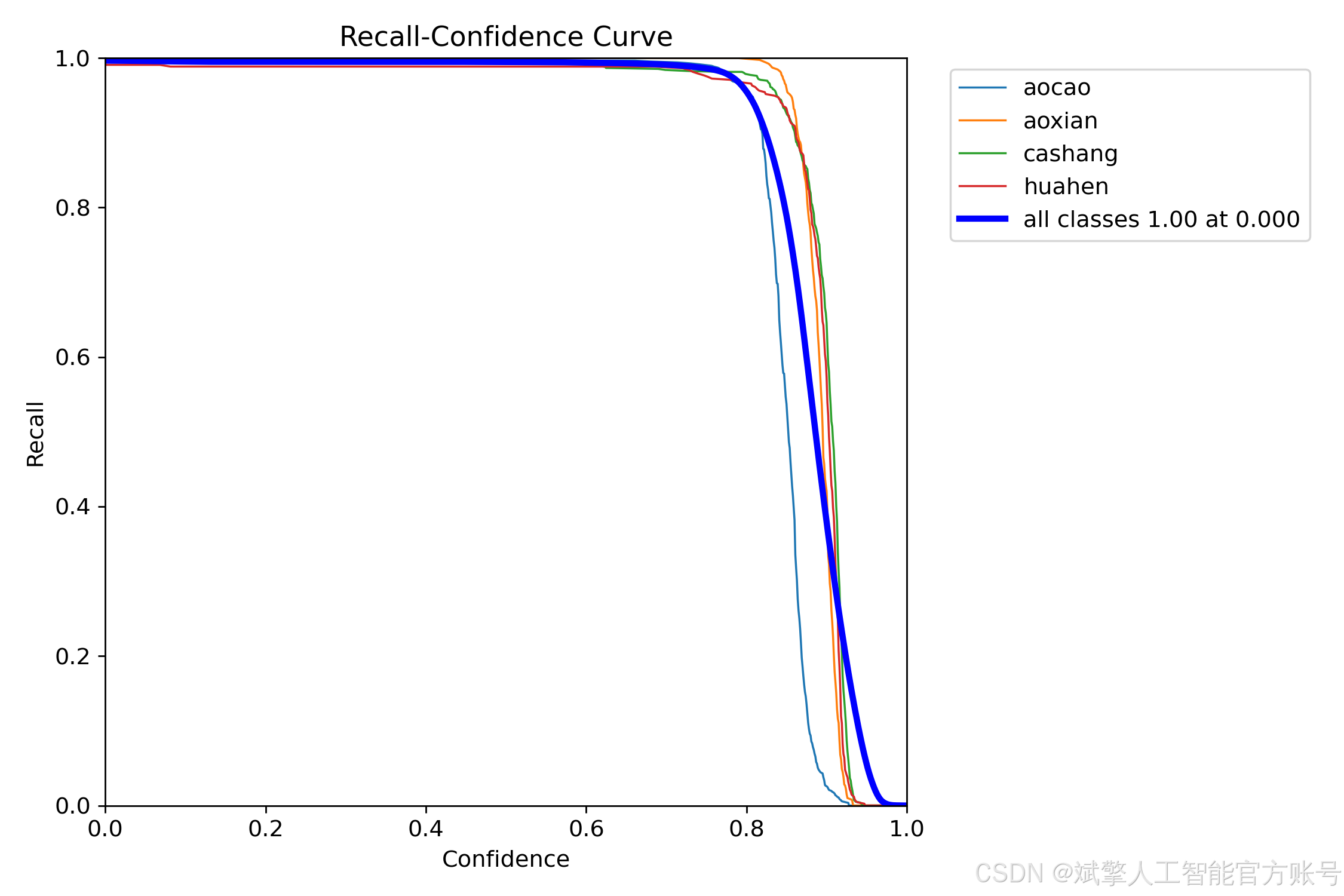




六、核心代码

import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMessageBox, QFileDialog
from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, pyqtSignal
from ultralytics import YOLO
from UiMain import UiMainWindow
import time
import os
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QDialog
from LoginWindow import LoginWindow
class DetectionThread(QThread):
frame_received = pyqtSignal(np.ndarray, np.ndarray, list) # 原始帧, 检测帧, 检测结果
finished_signal = pyqtSignal() # 线程完成信号
def __init__(self, model, source, conf, iou, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
self.model = model
self.source = source
self.conf = conf
self.iou = iou
self.running = True
def run(self):
try:
if isinstance(self.source, int) or self.source.endswith(('.mp4', '.avi', '.mov')): # 视频或摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(self.source)
while self.running and cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 保存原始帧
original_frame = frame.copy()
# 检测
results = self.model(frame, conf=self.conf, iou=self.iou)
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# 提取检测结果
detections = []
for result in results:
for box in result.boxes:
class_id = int(box.cls)
class_name = self.model.names[class_id]
confidence = float(box.conf)
x, y, w, h = box.xywh[0].tolist()
detections.append((class_name, confidence, x, y))
# 发送信号
self.frame_received.emit(
cv2.cvtColor(original_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
cv2.cvtColor(annotated_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
detections
)
# 控制帧率
time.sleep(0.03) # 约30fps
cap.release()
else: # 图片
frame = cv2.imread(self.source)
if frame is not None:
original_frame = frame.copy()
results = self.model(frame, conf=self.conf, iou=self.iou)
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# 提取检测结果
detections = []
for result in results:
for box in result.boxes:
class_id = int(box.cls)
class_name = self.model.names[class_id]
confidence = float(box.conf)
x, y, w, h = box.xywh[0].tolist()
detections.append((class_name, confidence, x, y))
self.frame_received.emit(
cv2.cvtColor(original_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
cv2.cvtColor(annotated_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
detections
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Detection error: {e}")
finally:
self.finished_signal.emit()
def stop(self):
self.running = False
class MainWindow(UiMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 初始化模型
self.model = None
self.detection_thread = None
self.current_image = None
self.current_result = None
self.video_writer = None
self.is_camera_running = False
self.is_video_running = False
self.last_detection_result = None # 新增:保存最后一次检测结果
# 连接按钮信号
self.image_btn.clicked.connect(self.detect_image)
self.video_btn.clicked.connect(self.detect_video)
self.camera_btn.clicked.connect(self.detect_camera)
self.stop_btn.clicked.connect(self.stop_detection)
self.save_btn.clicked.connect(self.save_result)
# 初始化模型
self.load_model()
def load_model(self):
try:
model_name = self.model_combo.currentText()
self.model = YOLO(f"{model_name}.pt") # 自动下载或加载本地模型
self.update_status(f"模型 {model_name} 加载成功")
except Exception as e:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "错误", f"模型加载失败: {str(e)}")
self.update_status("模型加载失败")
def detect_image(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请先停止当前检测任务")
return
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择图片", "", "图片文件 (*.jpg *.jpeg *.png *.bmp)")
if file_path:
self.clear_results()
self.current_image = cv2.imread(file_path)
self.current_image = cv2.cvtColor(self.current_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.display_image(self.original_image_label, self.current_image)
# 创建检测线程
conf = self.confidence_spinbox.value()
iou = self.iou_spinbox.value()
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, file_path, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.frame_received.connect(self.on_frame_received)
self.detection_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_detection_finished)
self.detection_thread.start()
self.update_status(f"正在检测图片: {os.path.basename(file_path)}")
def detect_video(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请先停止当前检测任务")
return
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择视频", "", "视频文件 (*.mp4 *.avi *.mov)")
if file_path:
self.clear_results()
self.is_video_running = True
# 初始化视频写入器
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(file_path)
frame_width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
frame_height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
cap.release()
# 创建保存路径
save_dir = "results"
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
timestamp = time.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, f"result_{timestamp}.mp4")
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
self.video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height))
# 创建检测线程
conf = self.confidence_spinbox.value()
iou = self.iou_spinbox.value()
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, file_path, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.frame_received.connect(self.on_frame_received)
self.detection_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_detection_finished)
self.detection_thread.start()
self.update_status(f"正在检测视频: {os.path.basename(file_path)}")
def detect_camera(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请先停止当前检测任务")
return
self.clear_results()
self.is_camera_running = True
# 创建检测线程 (默认使用摄像头0)
conf = self.confidence_spinbox.value()
iou = self.iou_spinbox.value()
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, 0, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.frame_received.connect(self.on_frame_received)
self.detection_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_detection_finished)
self.detection_thread.start()
self.update_status("正在从摄像头检测...")🔐登录注册验证
对应文件:LoginWindow.py
# 账户验证核心逻辑
def handle_login(self):
username = self.username_input.text().strip()
password = self.password_input.text().strip()
if not username or not password:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "用户名和密码不能为空!")
return
if username in self.accounts and self.accounts[username] == password:
self.accept() # 验证通过
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", "用户名或密码错误!")
# 密码强度检查(注册时)
def handle_register(self):
if len(password) < 6: # 密码长度≥6位
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "密码长度至少为6位!")🎯 多重检测模式
对应文件:main.py
图片检测
def detect_image(self):
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择图片", "", "图片文件 (*.jpg *.jpeg *.png *.bmp)")
if file_path:
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, file_path, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.start() # 启动检测线程视频检测
def detect_video(self):
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择视频", "", "视频文件 (*.mp4 *.avi *.mov)")
if file_path:
self.video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter() # 初始化视频写入器
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, file_path, conf, iou)实时摄像头
def detect_camera(self):
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, 0, conf, iou) # 摄像头设备号0
self.detection_thread.start()🖼️ 沉浸式可视化
对应文件:UiMain.py
双画面显示
def display_image(self, label, image):
q_img = QImage(image.data, w, h, bytes_per_line, QImage.Format_RGB888)
pixmap = QPixmap.fromImage(q_img)
label.setPixmap(pixmap.scaled(label.size(), Qt.KeepAspectRatio)) # 自适应缩放结果表格
def add_detection_result(self, class_name, confidence, x, y):
self.results_table.insertRow(row)
items = [
QTableWidgetItem(class_name), # 类别列
QTableWidgetItem(f"{confidence:.2f}"), # 置信度
QTableWidgetItem(f"{x:.1f}"), # X坐标
QTableWidgetItem(f"{y:.1f}") # Y坐标
]⚙️ 参数配置系统
对应文件:UiMain.py
双阈值联动控制
# 置信度阈值同步
def update_confidence(self, value):
confidence = value / 100.0
self.confidence_spinbox.setValue(confidence) # 滑块→数值框
self.confidence_label.setText(f"置信度阈值: {confidence:.2f}")
# IoU阈值同步
def update_iou(self, value):
iou = value / 100.0
self.iou_spinbox.setValue(iou)✨ UI美学设计
对应文件:UiMain.py
科幻风格按钮
def create_button(self, text, color):
return f"""
QPushButton {{
border: 1px solid {color};
color: {color};
border-radius: 6px;
}}
QPushButton:hover {{
background-color: {self.lighten_color(color, 10)};
box-shadow: 0 0 10px {color}; # 悬停发光效果
}}
"""动态状态栏
def update_status(self, message):
self.status_bar.showMessage(
f"状态: {message} | 最后更新: {time.strftime('%H:%M:%S')}" # 实时时间戳
)🔄 智能工作流
对应文件:main.py
线程管理
class DetectionThread(QThread):
frame_received = pyqtSignal(np.ndarray, np.ndarray, list) # 信号量通信
def run(self):
while self.running: # 多线程检测循环
results = self.model(frame, conf=self.conf, iou=self.iou)
self.frame_received.emit(original_frame, result_frame, detections)七、项目源码(视频简介)


基于深度学习YOLOv11的轴承缺陷识别检测系统(YOLOv11+YOLO数据集+UI界面+登录注册界面+Python项目源码+模型)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
基于深度学习YOLOv11的轴承缺陷识别检测系统(YOLOv11+YOLO数据集+UI界面+登录注册界面+Python项目源码+模型)




















 1084
1084

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








