BinTree.h
#pragma once
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BTNode
{
struct BTNode* _pLeft;
struct BTNode* _pRight;
BTDataType _data;
}BTNode;
// 二叉树的创建
BTNode* CreateBinTree(BTDataType* array, int size, BTDataType invalid);
// 二叉树的拷贝
BTNode* CopyBinTree(BTNode* pRoot);
// 二叉树的销毁
void DestroyBinTree(BTNode** pRoot);
// 递归:前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* pRoot);
// 递归:中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* pRoot);
// 递归:后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* pRoot);
// 层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* pRoot);
// 获取二叉树中节点个数
int GetBinTreeSize(BTNode* pRoot);
// 获取二叉树中第K层节点个数
int GetKLevelNodeCount(BTNode* pRoot, int K);
// 获取二叉树中叶子节点个数
int GetLeafCount(BTNode* pRoot);
// 获取二叉树深度(高度)
int GetBinTreeHeight(BTNode* pRoot);
// 检测值为x的元素是否在二叉树中,在返回该节点的地址,否则返回NULL
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);
// 二叉树的镜像
void Mirror(BTNode* pRoot);
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root);
BinTree.c
#include "BinTree.h"
#include "queue.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType data)
{
BTNode* pNewNode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (pNewNode == NULL)
{
assert(0);
}
pNewNode->_data = data;
pNewNode->_pLeft = NULL;
pNewNode->_pRight = NULL;
return pNewNode;
}
void swap(BTDataType* a, BTDataType* b)
{
BTDataType tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
思路:根据概念,先创建根节点,在创建根的左子树,根的右子树
注意:
<1>传的索引是临时变量,函数运行结束后被销毁,所以需要传地址,将索引数值的变化带出递归
<2>将函数封装起来,便于使用
<3>传入的标记使用invalid,防止换标记二叉树创建不了
// 二叉树的创建
BTNode* _CreateBinTree(BTDataType* array, int size, int* index, BTDataType invalid)
{
BTNode* pRoot = NULL;
if (*index<size && array[*index]!='#')
{
pRoot = BuyNode(array[*index]);
(*index)++;
pRoot->_pLeft = _CreateBinTree(array, size, index, invalid);
(*index)++;
pRoot->_pRight = _CreateBinTree(array, size, index, invalid);
}
return pRoot;
}
BTNode* CreateBinTree(BTDataType* array, int size, BTDataType invalid)
{
int index = 0;
return _CreateBinTree(array, size, &index, invalid);
}
思路:根据二叉树的概念,同创建一样操作
<1>空树不拷贝
<2>子树不为空就递归拷贝子树,为空就用创建的新子树节点接收
<3>最后把拷贝好的左右子树用新的根节点接收
// 二叉树的拷贝
BTNode* CopyBinTree(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
BTNode* newLeft = NULL;
BTNode* newRight = NULL;
BTNode* newNode = BuyNode(pRoot->_data);
if (pRoot->_pLeft != NULL)
{
newLeft=CopyBinTree(pRoot->_pLeft);
}
else
{
newLeft = NULL;
}
if (pRoot->_pRight != NULL)
{
newRight = CopyBinTree(pRoot->_pRight);
}
else
{
newRight = NULL;
}
newNode->_pLeft = newLeft;
newNode->_pRight = newRight;
return newNode;
}
注意:
<1>最后才可以销毁根节点,所以采用后序遍历规则-----销毁完所有的节点之后要把Root节点置空
<2>函数体内部修改形参的值,要传形参的地址,所以销毁函数中传Root的地址!!!
// 二叉树的销毁
void DestroyBinTree(BTNode** pRoot)
{
if (*pRoot != NULL)
{
DestroyBinTree((*pRoot)->_pLeft);
DestroyBinTree((*pRoot)->_pRight);
free(pRoot);
*pRoot = NULL;
}
}
对二叉树的遍历操作:
// 递归:前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot != NULL)
{
printf("%c ", pRoot->_data);
PreOrder(pRoot->_pLeft);
PreOrder(pRoot->_pRight);
}
}
// 递归:中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot != NULL)
{
InOrder(pRoot->_pLeft);
printf("%c ", pRoot->_data);
InOrder(pRoot->_pRight);
}
}
// 递归:后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot != NULL)
{
PostOrder(pRoot->_pLeft);
PostOrder(pRoot->_pRight);
printf("%c ", pRoot->_data);
}
}
注意:需要借助之前的队列辅助,队列中存放的是二叉树节点的指针
// 层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* pRoot)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q,pRoot);
while (QueueEmpty(&q) != 0)
{
//取队头元素
BTNode* p=QueueFront(&q);
//遍历该元素
printf("%c ", p->_data);
//如果左孩子存在,保存
if (p->_pLeft != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, p->_pLeft);
}
//如果右孩子存在,保存
if (p->_pRight != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, p->_pRight);
}
//删除队头
QueuePop(&q);
}
}
注意:空树节点为0,非空递归求解左右子树节点个数,最后还要加上根节点的1才能返回
// 获取二叉树中节点个数
int GetBinTreeSize(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return GetBinTreeSize(pRoot->_pLeft) + GetBinTreeSize(pRoot->_pRight) + 1;
}
}
思路:将复杂的问题转换为子问题,k层的节点就是k-1层节点的左子树节点和右子树节点的和
// 获取二叉树中第K层节点个数
int GetKLevelNodeCount(BTNode* pRoot, int K)
{
if (pRoot == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (pRoot->_pLeft == NULL && pRoot->_pRight == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return GetKLevelNodeCount(pRoot->_pLeft, K - 1) + GetKLevelNodeCount(pRoot->_pRight, K - 1);
}
}
// 获取二叉树中叶子节点个数
int GetLeafCount(BTNode* pRoot)
{
//叶子节点没有子节点
if (pRoot == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (pRoot->_pLeft == NULL && pRoot->_pRight == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return GetLeafCount(pRoot->_pLeft) + GetLeafCount(pRoot->_pRight);
}
}
// 获取二叉树深度(高度)
int GetBinTreeHeight(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (pRoot->_pLeft == NULL && pRoot->_pRight == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
int t1 = GetBinTreeHeight(pRoot->_pLeft);
int t2 = GetBinTreeHeight(pRoot->_pRight);
if (t1 < t2)
{
return t2 + 1;
}
else
{
return t1 + 1;
}
}
}
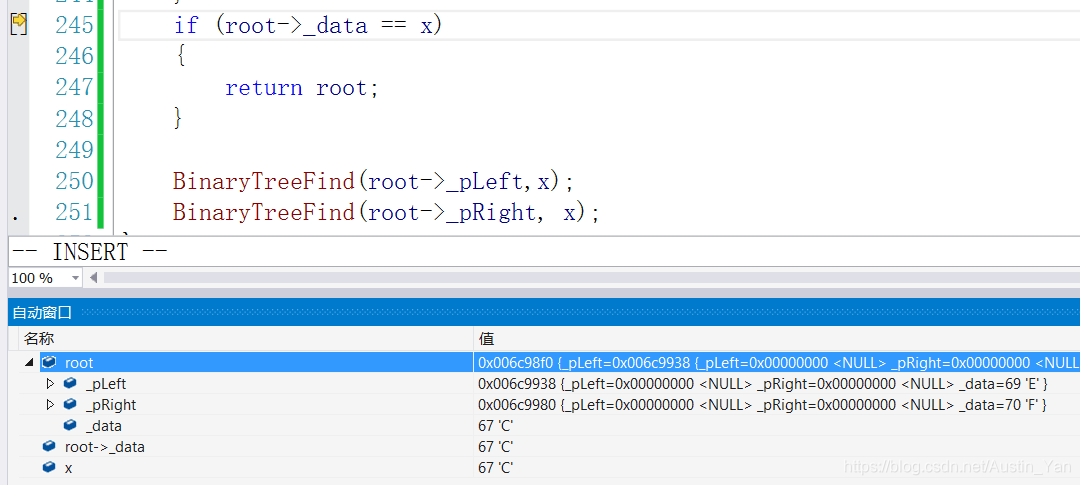
// 检测值为x的元素是否在二叉树中,在返回该节点的地址,否则返回NULL
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->_data == x)
{
return root;
}
BinaryTreeFind(root->_pLeft,x);
BinaryTreeFind(root->_pRight, x);
}
// 二叉树的镜像
void Mirror(BTNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot != NULL)
{
BTNode* tmp = pRoot->_pLeft;
pRoot->_pLeft = pRoot->_pRight;
pRoot->_pRight = tmp;
Mirror(pRoot->_pLeft);
Mirror(pRoot->_pRight);
}
}
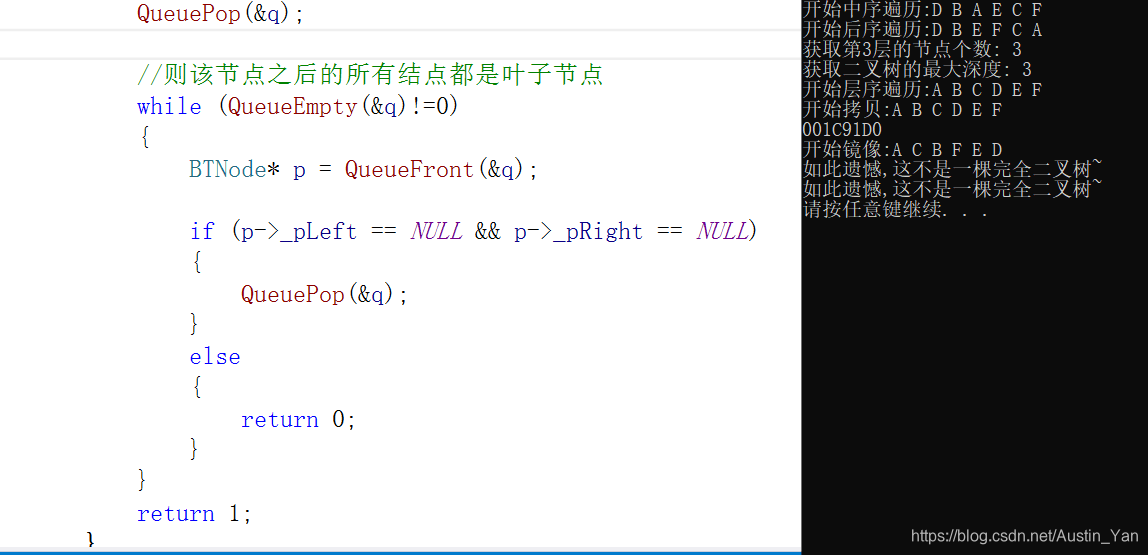
思路:层序遍历+判断
<1>空树也属于完全二叉树
<2>如果该节点有右孩子没有左孩子,肯定不是完全二叉树
<3>如果该节点只有左孩子或者其是叶子节点,那么在它之后的所有节点都要是叶子节点
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
//空树也是完全二叉树
if (root == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (QueueEmpty(&q) != 0)
{
BTNode* p=QueueFront(&q);
//只有右孩子没有左孩子,肯定不是完全二叉树
if (p->_pLeft == NULL && p->_pRight != NULL)
{
return 0;
}
//如果左右孩子都不在,或者只有左孩子,后面的节点必须都是叶子节点
if ((p->_pLeft != NULL && p->_pRight == NULL) || (p->_pLeft == NULL && p->_pRight == NULL))
{
QueuePop(&q);
//则该节点之后的所有结点都是叶子节点
while (QueueEmpty(&q)!=0)
{
BTNode* p = QueueFront(&q);
if (p->_pLeft == NULL && p->_pRight == NULL)
{
QueuePop(&q);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
if (p->_pLeft!=NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, p->_pLeft);
}
if (p->_pRight != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, p->_pRight);
}
QueuePop(&q);
}
return 1;
}
测试二叉树的基本操作:
void TestBinTree()
{
char a[] = "ABD###CE##F";
int index = 0;
BTNode* pRoot=CreateBinTree(a, strlen(a), &index, '#');
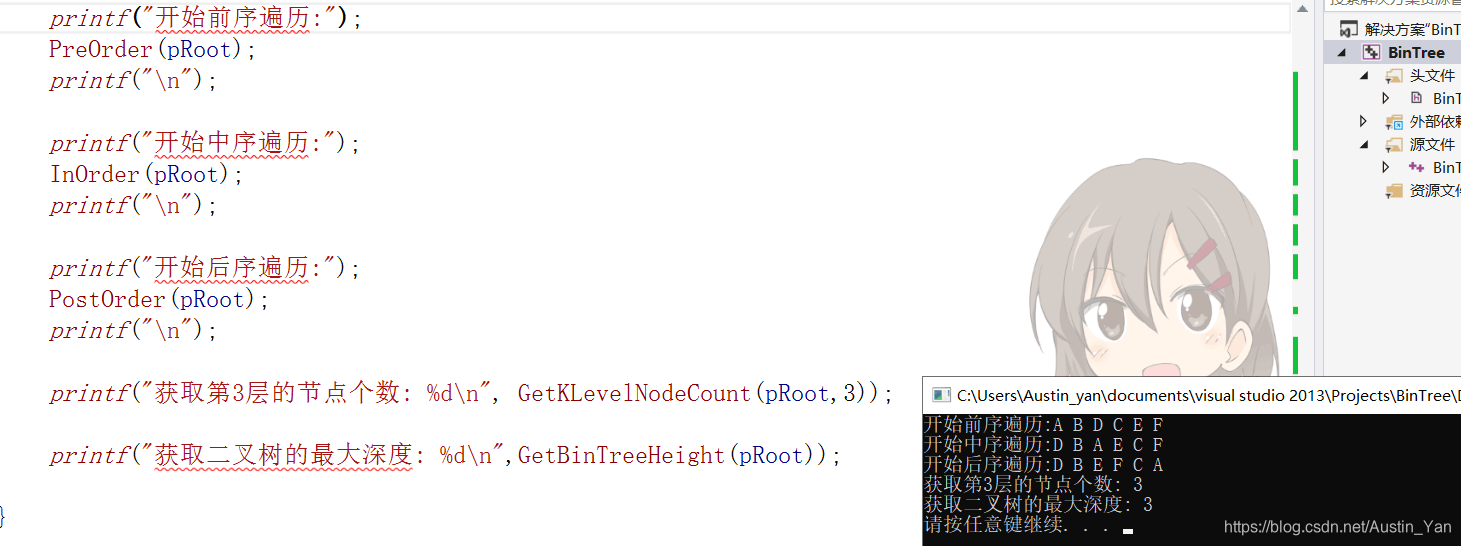
printf("开始前序遍历:");
PreOrder(pRoot);
printf("\n");
printf("开始中序遍历:");
InOrder(pRoot);
printf("\n");
printf("开始后序遍历:");
PostOrder(pRoot);
printf("\n");
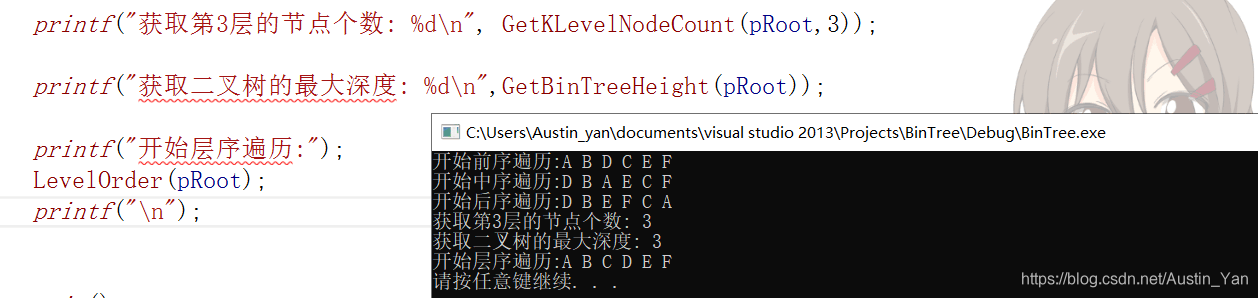
printf("获取第3层的节点个数: %d\n", GetKLevelNodeCount(pRoot,3));
printf("获取二叉树的最大深度: %d\n",GetBinTreeHeight(pRoot));
printf("开始层序遍历:");
LevelOrder(pRoot);
printf("\n");
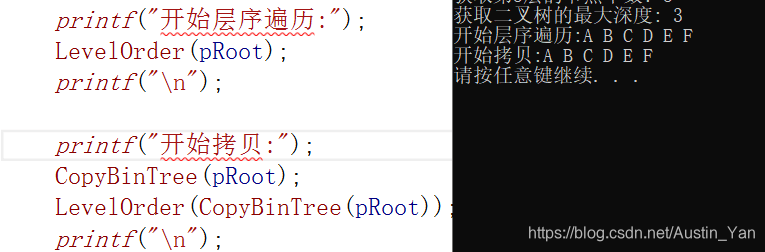
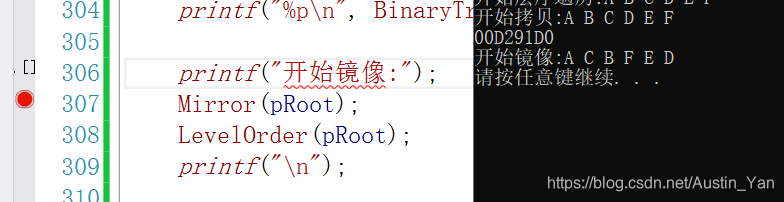
printf("开始拷贝:");
CopyBinTree(pRoot);
LevelOrder(CopyBinTree(pRoot));
printf("\n");
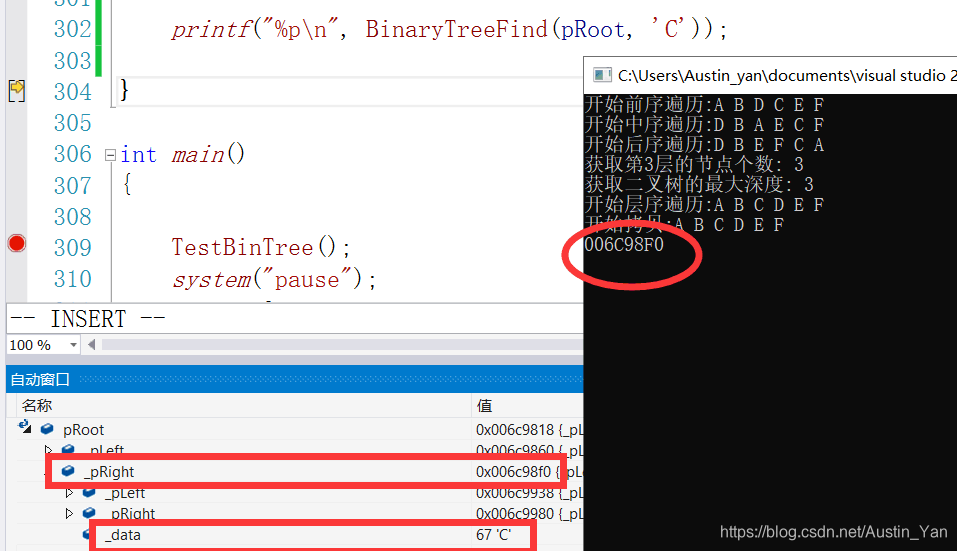
printf("%p\n", BinaryTreeFind(pRoot, 'C'));
printf("开始镜像:");
Mirror(pRoot);
LevelOrder(pRoot);
printf("\n");
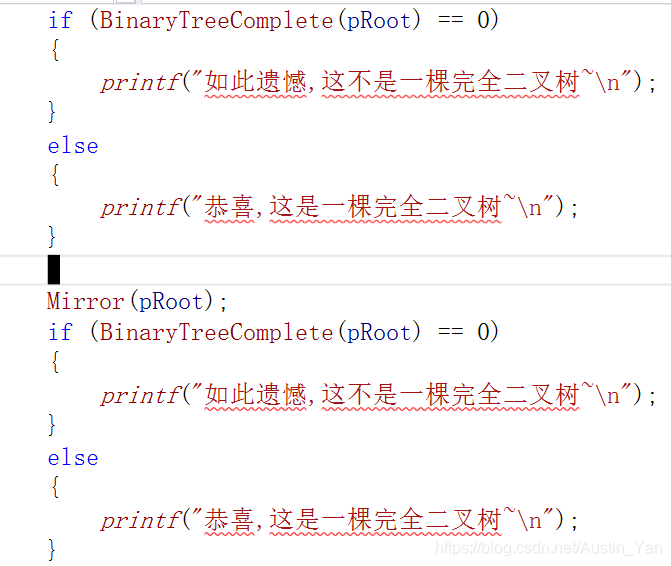
if (BinaryTreeComplete(pRoot) == 0)
{
printf("如此遗憾,这不是一棵完全二叉树~\n");
}
else
{
printf("恭喜,这是一棵完全二叉树~\n");
}
Mirror(pRoot);
if (BinaryTreeComplete(pRoot) == 0)
{
printf("如此遗憾,这不是一棵完全二叉树~\n");
}
else
{
printf("恭喜,这是一棵完全二叉树~\n");
}
}
主函数:
int main()
{
TestBinTree();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
代码运行测试图:





 博客围绕二叉树链式结构展开,介绍了BinTree.h和BinTree.c相关内容。包含二叉树的创建、拷贝、销毁、遍历等操作的思路及注意事项,如创建时传索引地址、拷贝时递归操作、销毁采用后序遍历等,还提及测试二叉树基本操作及代码运行测试图。
博客围绕二叉树链式结构展开,介绍了BinTree.h和BinTree.c相关内容。包含二叉树的创建、拷贝、销毁、遍历等操作的思路及注意事项,如创建时传索引地址、拷贝时递归操作、销毁采用后序遍历等,还提及测试二叉树基本操作及代码运行测试图。
















 1297
1297

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








