客官,小板凳坐好,开始啦!
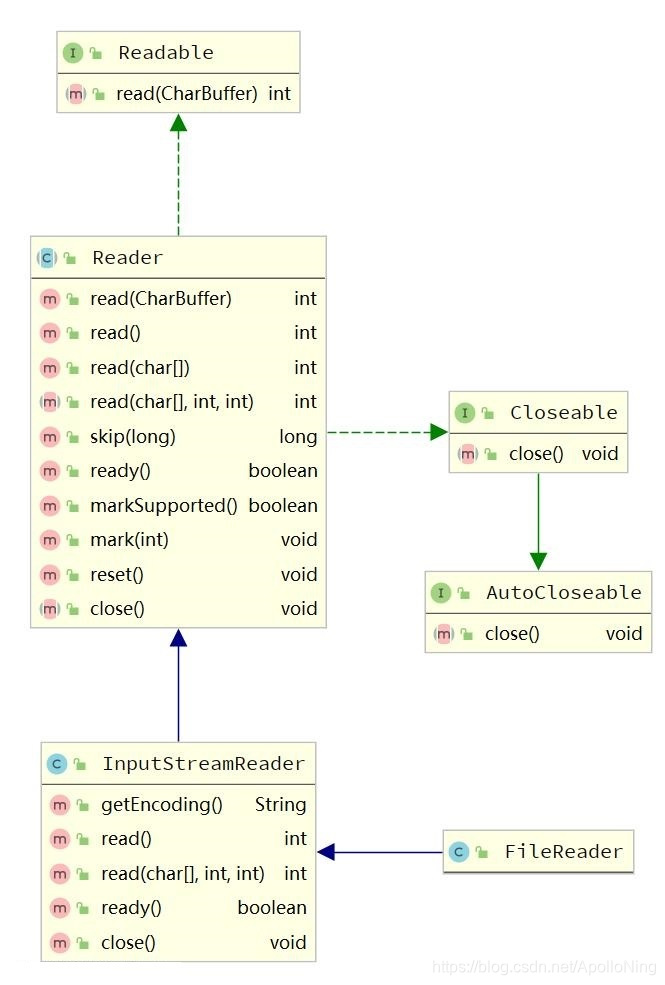
FileReader的构造方法和FileInputStream很相似,都是传入文件路径或者文件对象又或者是文件描述符。
根据继承图以及方法,来过一下常用的API吧!
- public String getEncoding() 返回编码名称
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath)) {
System.out.println("Encoding: " + fileReader.getEncoding());
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
}
}
Encoding: UTF8
- public boolean markSupported()
与FileInputStream很相似也是不支持mark的,看下源码:
public boolean markSupported() {
return false;
}
那mark和reset方法也就不说了,不支持嘛!
- public long skip(long n) throws IOException 跳过字符数,和
FileInputStream很相似!
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath)) {
long skip = fileReader.skip(1L);
System.out.println("skip = " + skip);
int data = fileReader.read();
System.out.println("data = " + data);
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
}
}
文件中的内容是:ABC。运行结果是:
skip = 1
data = 66
- public boolean ready() throws IOException
告知该流是否已准备好读取。如果输入缓冲区不是空的,或者字节可以从底层字节流中读取,那么InputStreamReader就准备好了。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath)) {
boolean ready = fileReader.ready();
System.out.println("fileReader流是否已经准备好了? " + ready);
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
}
}
运行结果:
fileReader流是否已经准备好了? true
接下来,是核心方法闪亮登场了!
FileReader一个有4个read方法:
第①个:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath)) {
int data = fileReader.read();
System.out.println("data = " + data);
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
}
}
从流中读取一个字符(2个字节),返回值一样是int类型!
原因在《聊聊FileInputStream文件输入流的二三事》一文中有作解释,可移步了解。
第②个:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath)) {
char[] chars = new char[10];
int len = fileReader.read(chars);
System.out.println("len = " + len);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars));
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
}
}
运行结果:
len = 3
[A, B, C, , , , , , , ]
可以看出,传入一个容器,返回读取字符长度。
第③个:
- public int read(java.nio.CharBuffer cb) throws IOException;
参数是 java.nio.CharBuffer
返回值 读取字符个数
第④个:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath)) {
char[] chars = new char[10];
int len = fileReader.read(chars, 4, 4);
System.out.println("len = " + len);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars));
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
}
}
len = 3
[ , , , , A, B, C, , , ]
看结果,不用再多的言语了吧!
简单聊下,FileWriter吧!
FileWriter与FileOutputStream相比,关于write方法的功能用法差不多,但是还有区别的!
public void write(int c);
public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len);
public void write(String str, int off, int len);
public void write(String str);
public void write(char cbuf[]);
最大的区别是:
FileOutputStream是立刻马上就写入到文件中!而FileWriter是要等到flush方法被调用的时候才会写入到文件中!或者close方法被调用也会写入,因为close方法会调用flush方法。
还有一个区别,就是多了append方法!





 本文探讨了Java中的FileReader文件输入流,详细介绍了getEncoding、skip、ready等方法的使用,并重点讲解了read方法的四种不同实现方式。同时,对比了FileWriter与FileOutputStream的区别,强调了FileWriter的append方法和写入时机的特点。
本文探讨了Java中的FileReader文件输入流,详细介绍了getEncoding、skip、ready等方法的使用,并重点讲解了read方法的四种不同实现方式。同时,对比了FileWriter与FileOutputStream的区别,强调了FileWriter的append方法和写入时机的特点。
















 339
339

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








