文章目录
1.python的安装
在rhel8中自带python3

在rhel7中安装(rhel7中自带python2)
注意:源码编译安装可以定制化安装

yum install -y gcc
yum install -y zlib-devel.x86_64

./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python3

make && make install


ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/* /usr/local/bin/

2.python的用法
2.1 python2与python3的语法对比
在python2中:



在python3中:


2.2 python中的注释
注释可以放在代码前对代码进行描述。
对于重点代码行可以在尾行注释。
print('hello world')
# this is a comment
print('hello 2020') #this also a comment
"""
they are all
comment
"""
print('hello python')

2.3 python中的输入输出
在python2中


在python3中

2.3 python的格式化输出(占位符)
| %s | str字符串 |
|---|---|
| %d | int整型 |
| %f | float浮点型 |
| %% | %百分号 |
可能考虑到是python国内网络的问题,这时我们用国内的镜像源来加速。
pip install ipython -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com

注意:在rhel8中可以直接用 pip3 install ipython

ipython
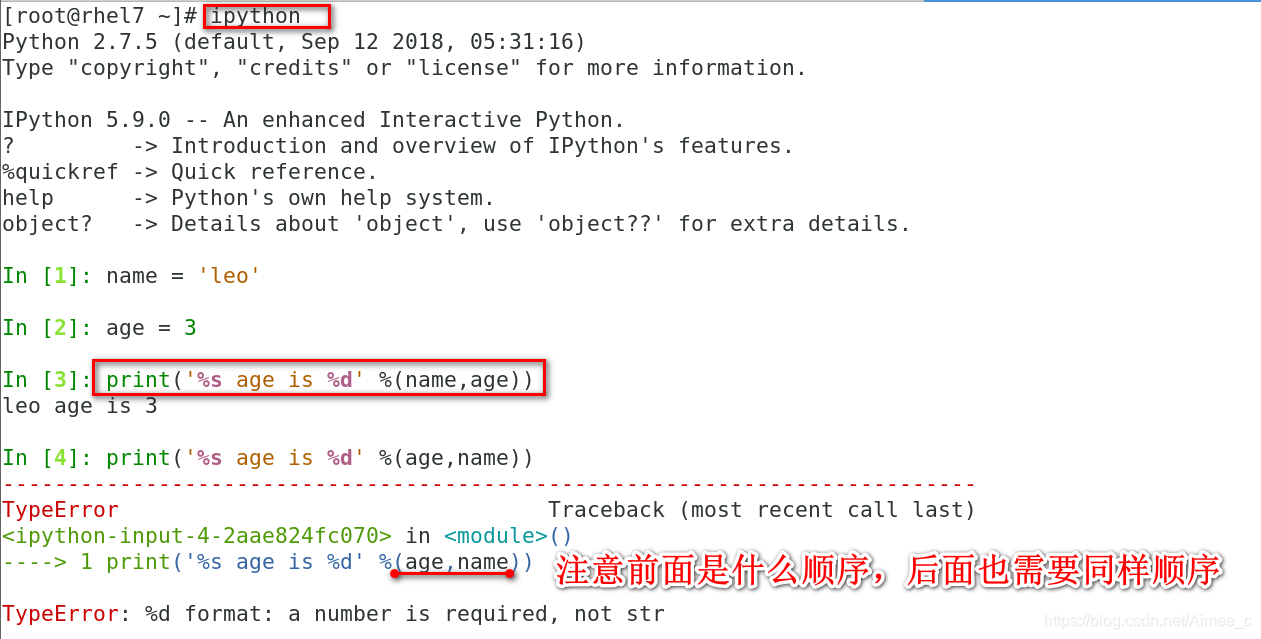
In [1]: name = 'leo'
In [2]: age = 3
In [3]: print('%s age is %d' %(name,age))
leo age is 3
In [4]: print('%s age is %d' %(age,name))
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-4-2aae824fc070> in <module>()
----> 1 print('%s age is %d' %(age,name))
TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str
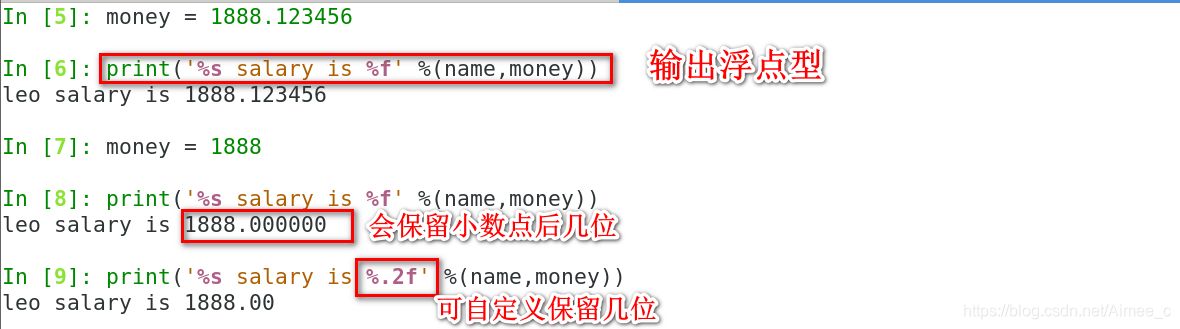
In [5]: money = 1888.123456
In [6]: print('%s salary is %f' %(name,money))
leo salary is 1888.123456##输出浮点型
In [7]: money = 1888
In [8]: print('%s salary is %f' %(name,money))
leo salary is 1888.000000
In [9]: print('%s salary is %.2f' %(name,money))
leo salary is 1888.00 ##小数点后保留2位
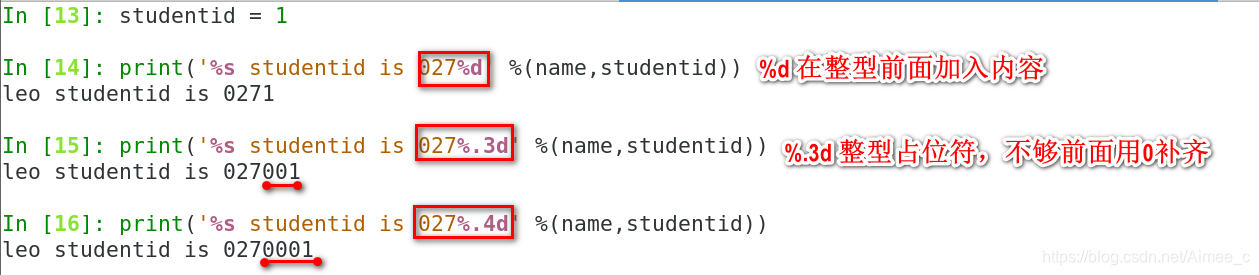
In [13]: studentid = 1
In [14]: print('%s studentid is 027%d' %(name,studentid))
leo studentid is 0271 #%d 在整型前面加入内容
In [15]: print('%s studentid is 027%.3d' %(name,studentid))
leo studentid is 027001 #%.3d 整型占位符,不够前面用0补齐
In [16]: print('%s studentid is 027%.4d' %(name,studentid))
leo studentid is 0270001
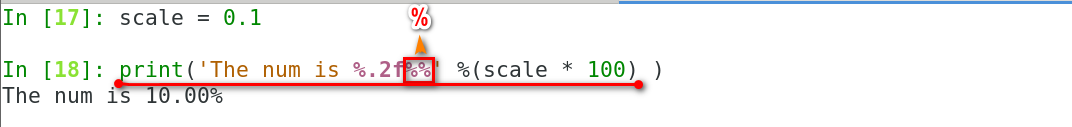
In [17]: scale = 0.1
In [18]: print('The num is %.2f%%' %(scale * 100) )
The num is 10.00% #输出%
3.Python中的变量
3.1 python中变量的命名方式
要求:
1.以字母、数字和下划线组成
2.不能以数字开头
3.不能和系统中的变量冲突
命名方式:
(1)大头峰命名法:每个单词的首字母大写
如:FirstName、LastName
(2)小头峰命名法:第一个单词以小写字母开头,后续的单词以大写字母开头
如:firstName、lastName
3.2 python中变量的类型
1.变量类型
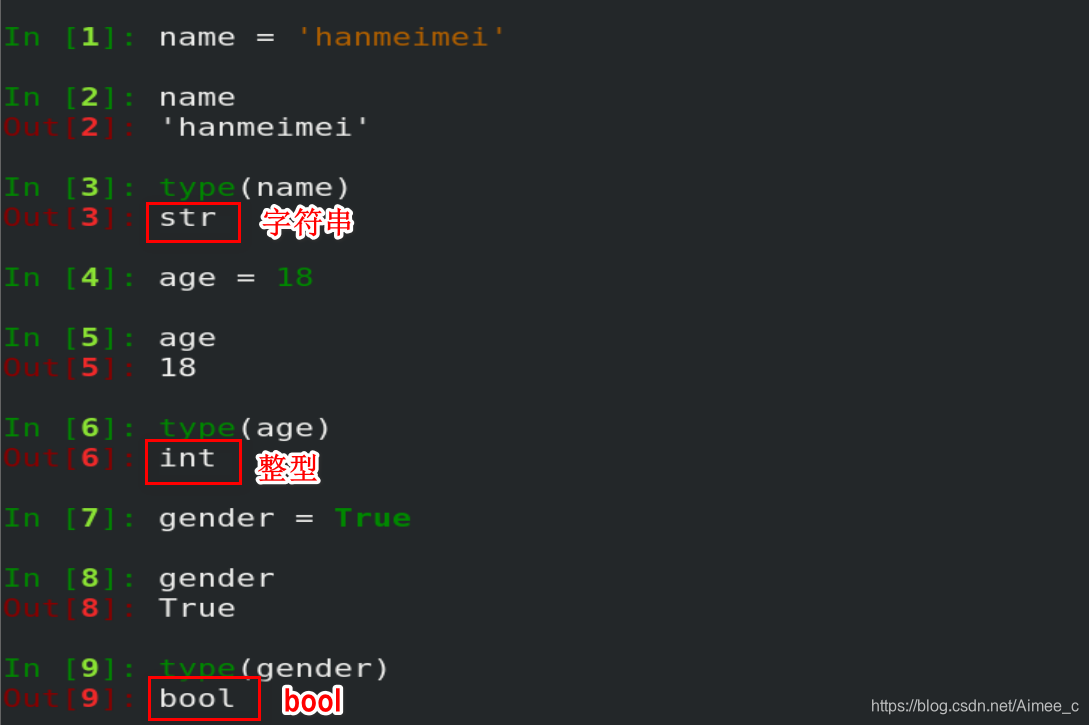

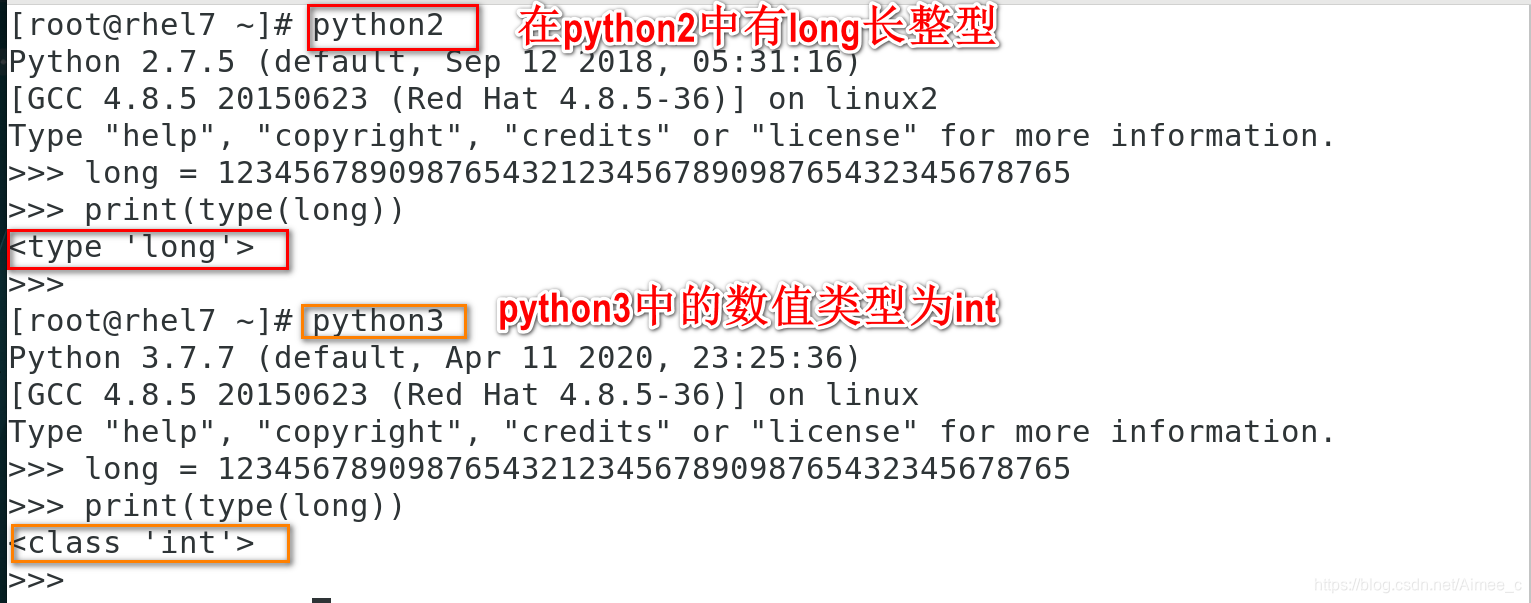
注意:在python2中有long(长整型),python3中无long
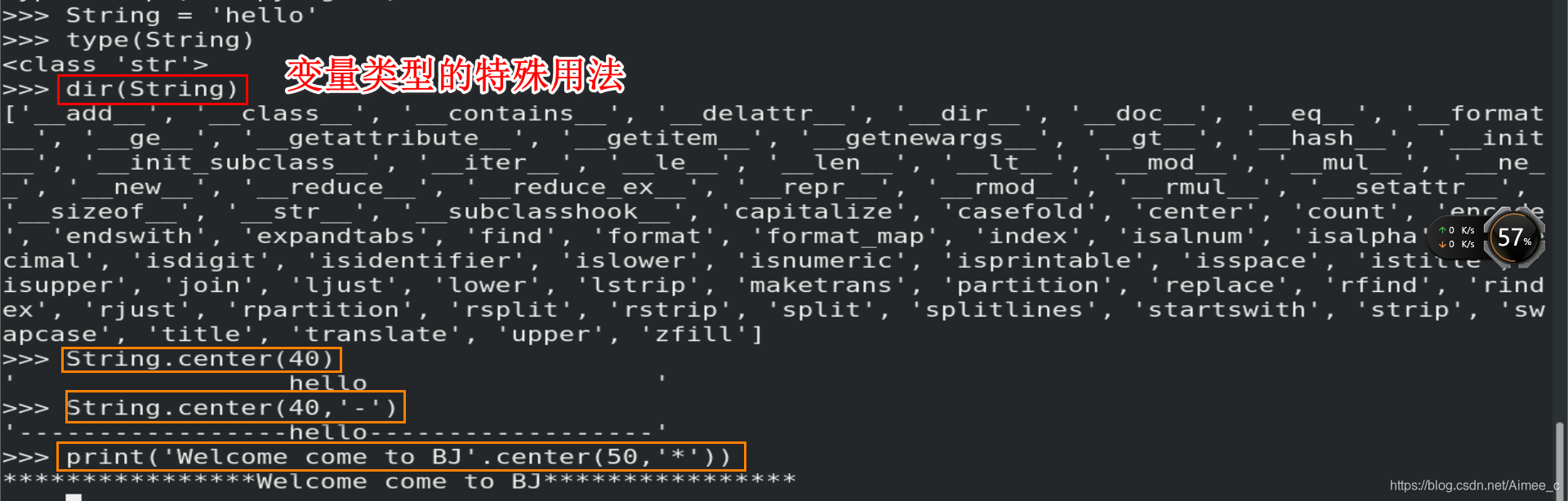
2.变量类型的特殊用法
>>> String = 'hello'
>>> type(String)
<class 'str'>
>>> dir(String) ###变量类型的特殊用法查询
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
>>> String.center(40)
' hello '
>>> String.center(40,'-')
'-----------------hello------------------'
>>> print('Welcome come to BJ'.center(50,'*'))
****************Welcome come to BJ****************
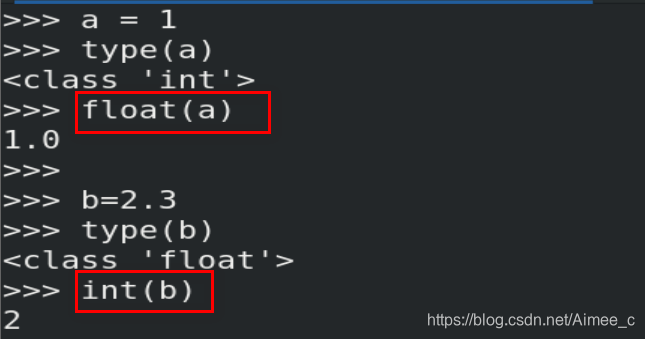
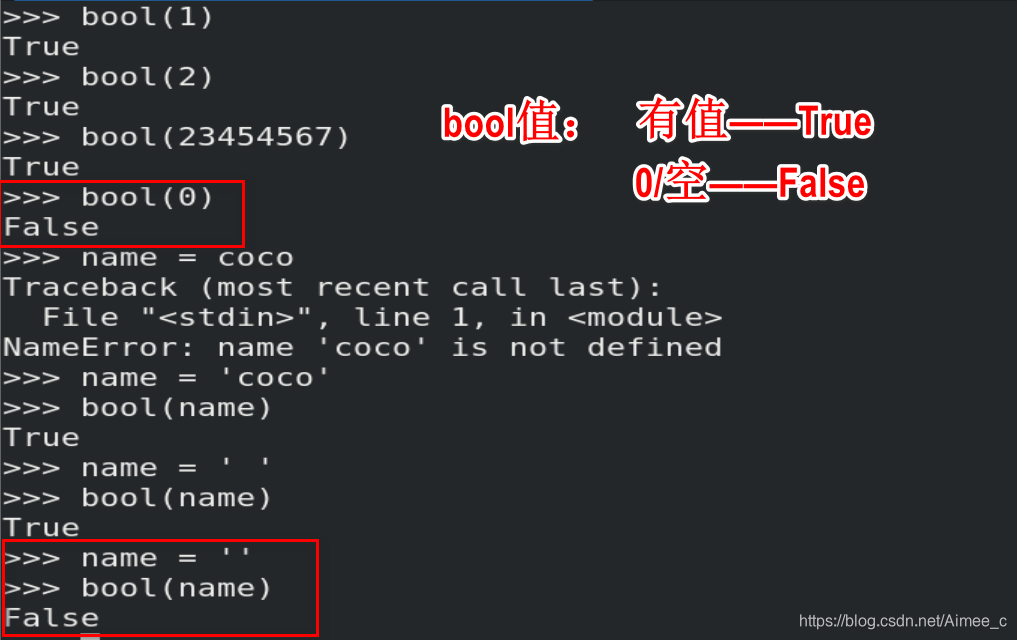
3.数值类型的转换
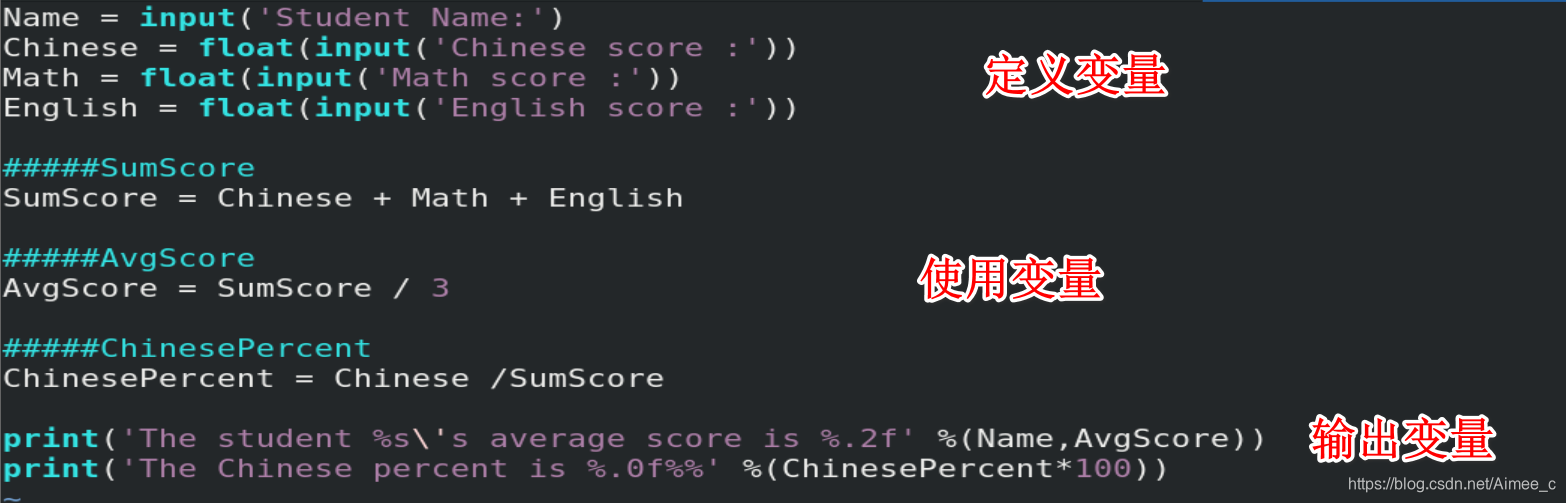
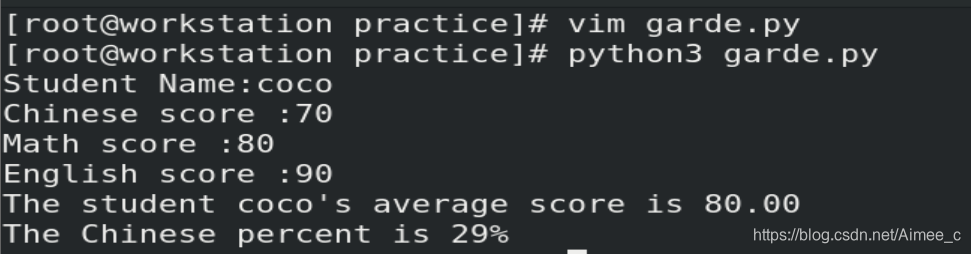
3.3 变量的练习
- 输入学生姓名;
- 依次输入学生的三门科目成绩;
- 计算该学生的平均成绩, 并打印;
- 平均成绩保留两位小数点;
- 计算该学生语文成绩占总成绩的百分之多少?(不保留小数)并打印。eg: 78%;
Name = input('Student Name:')
Chinese = float(input('Chinese score :'))###注意:字符串不能进行运算,需要转换成浮点型
Math = float(input('Math score :'))
English = float(input('English score :'))
#####SumScore
SumScore = Chinese + Math + English
#####AvgScore
AvgScore = SumScore / 3
#####ChinesePercent
ChinesePercent = Chinese /SumScore
print('The student %s\'s average score is %.2f' %(Name,AvgScore))
print('The Chinese percent is %.0f%%' %(ChinesePercent*100))
4.Python的IDE工具
4.1 安装pycharm
下载地址:link.
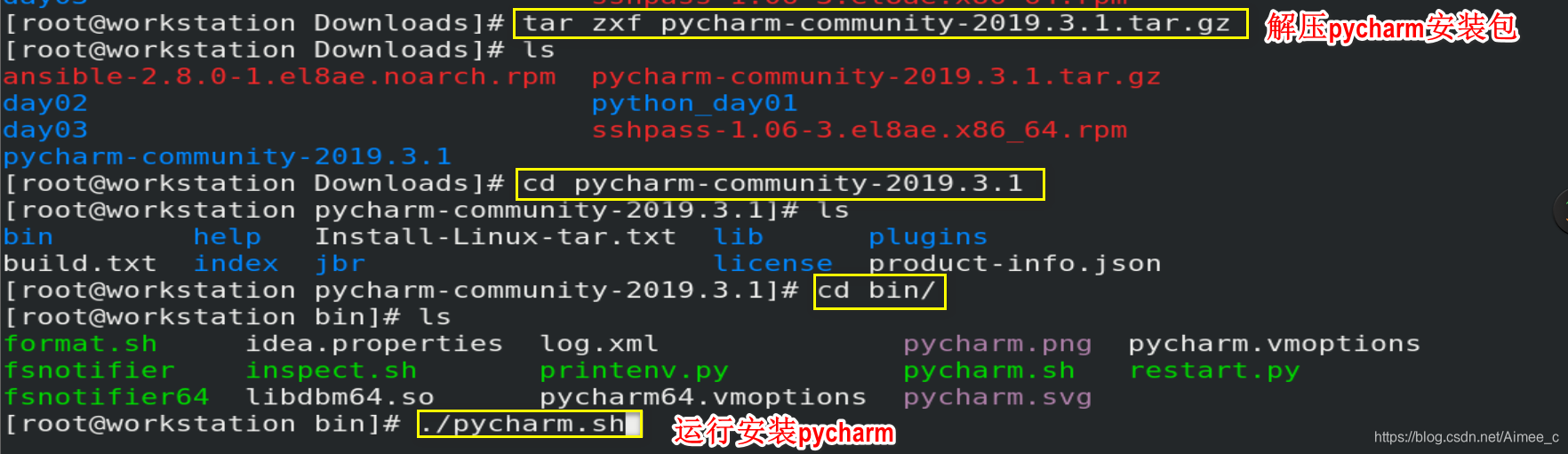
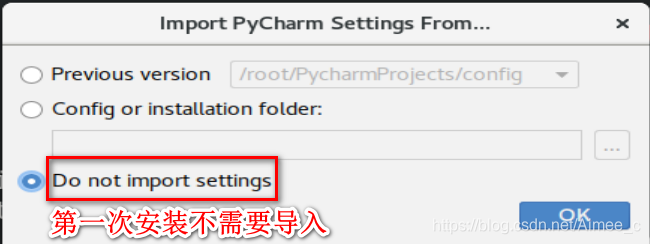
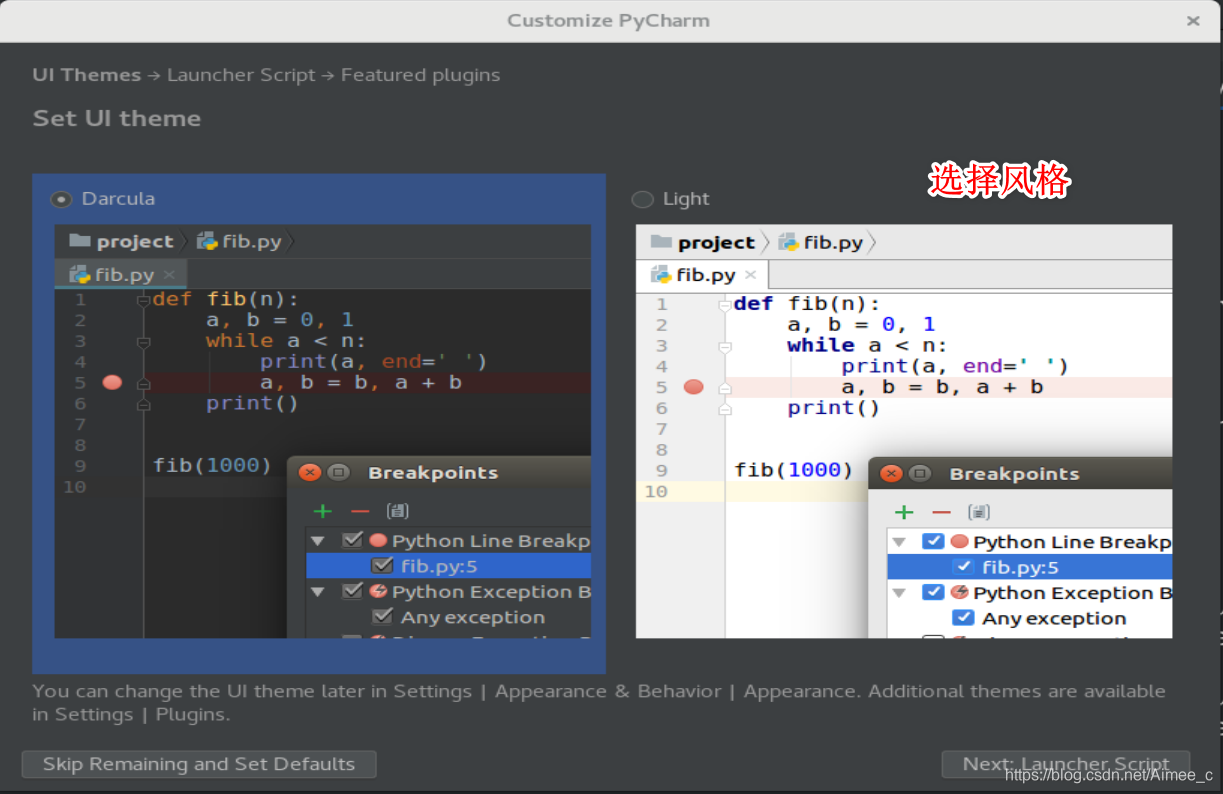
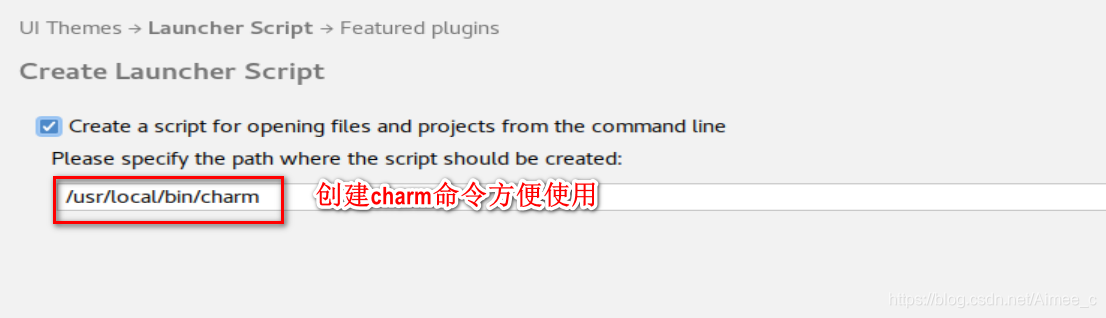
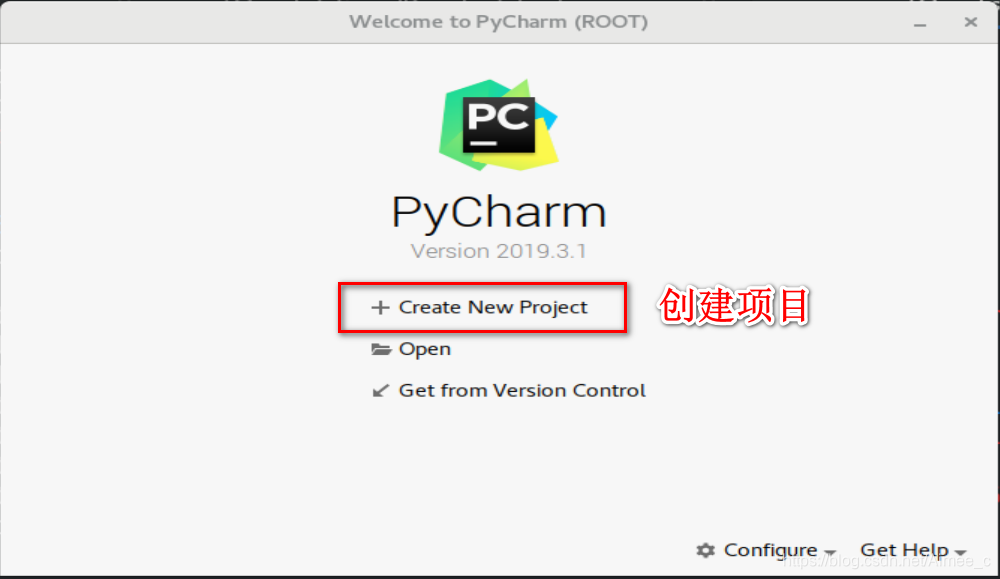
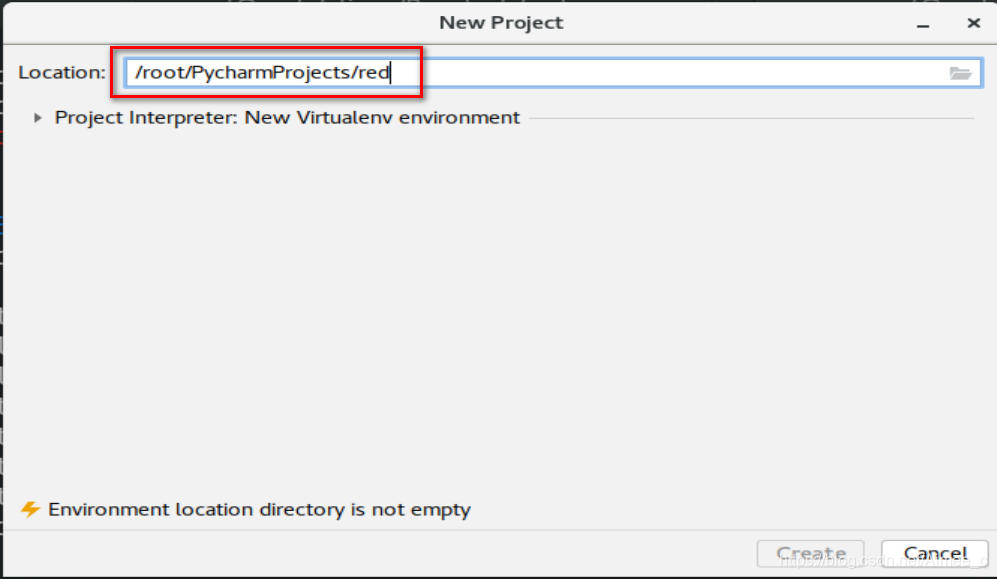
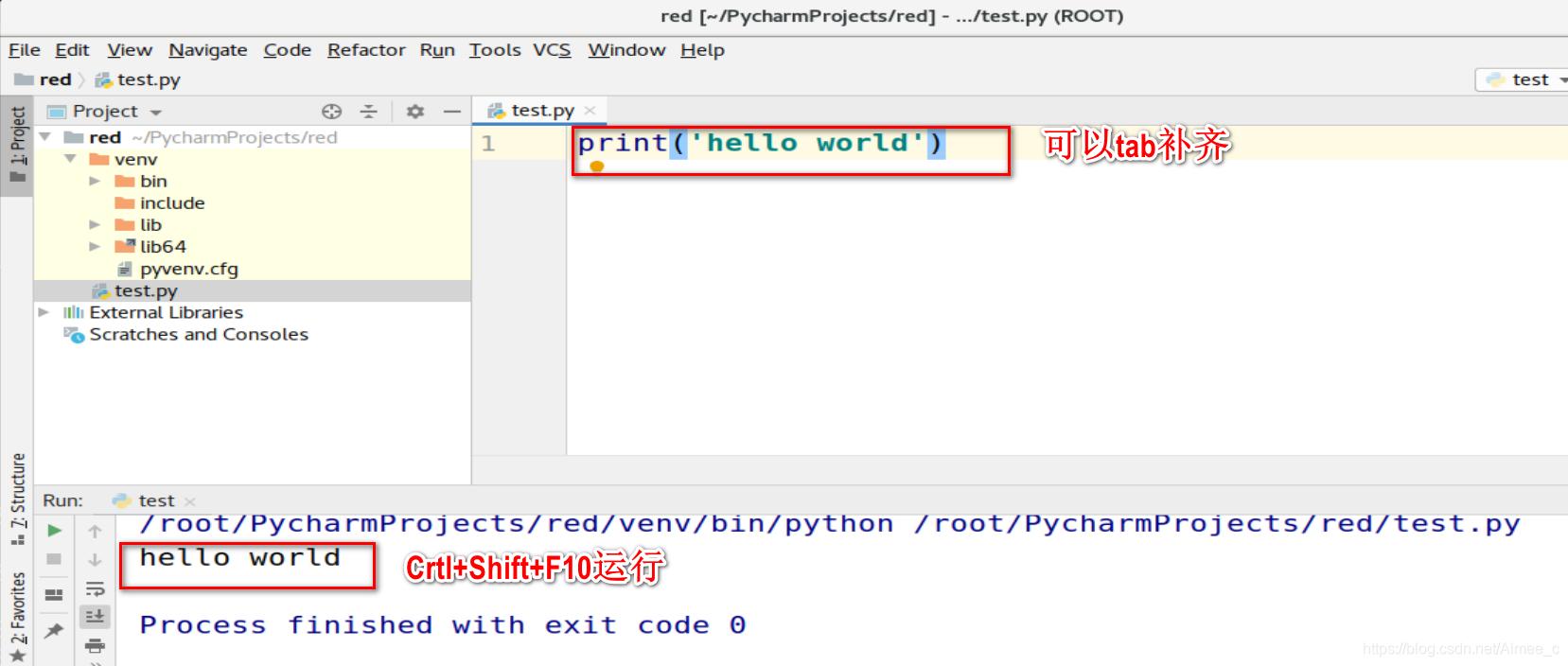
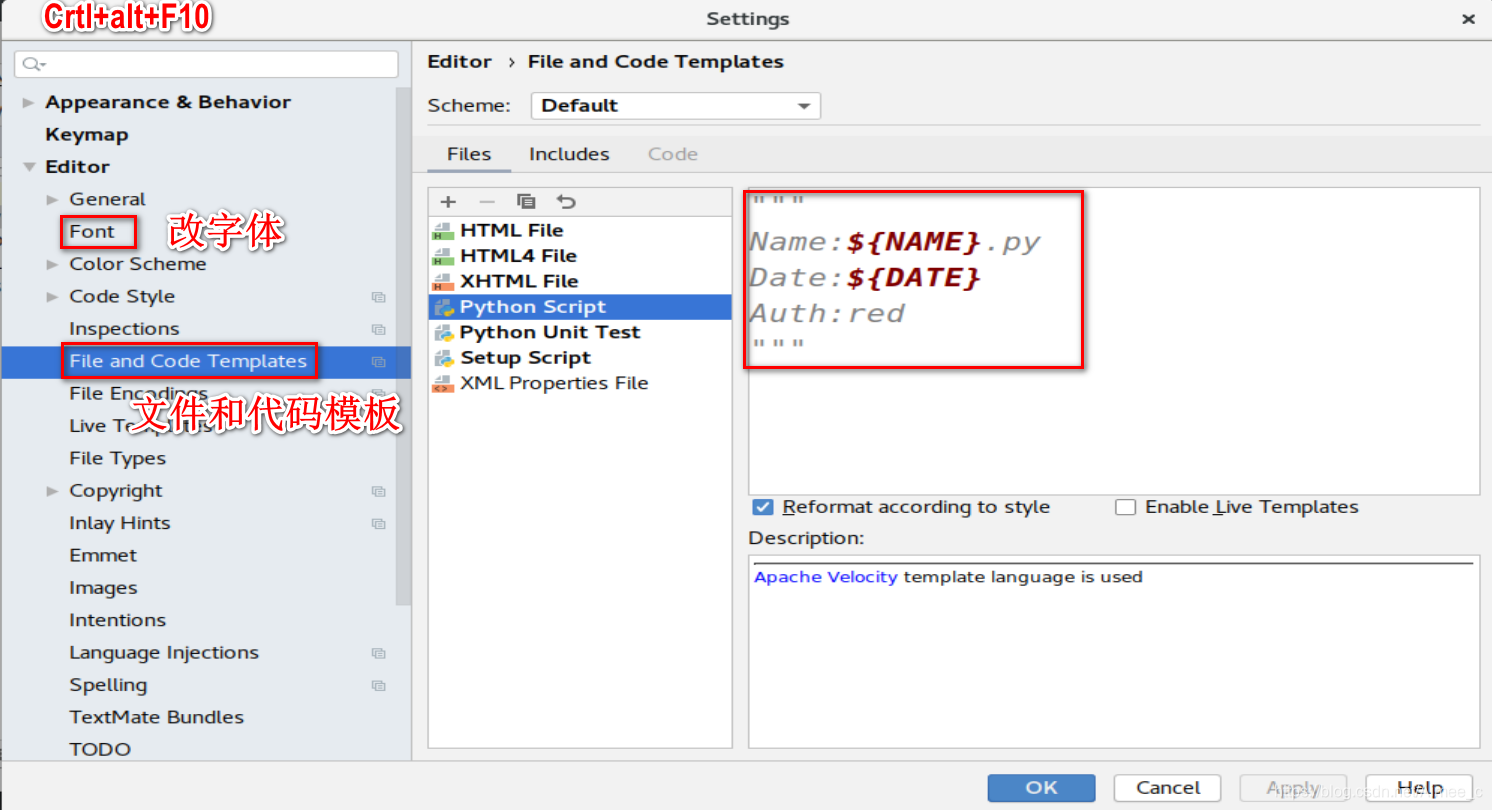
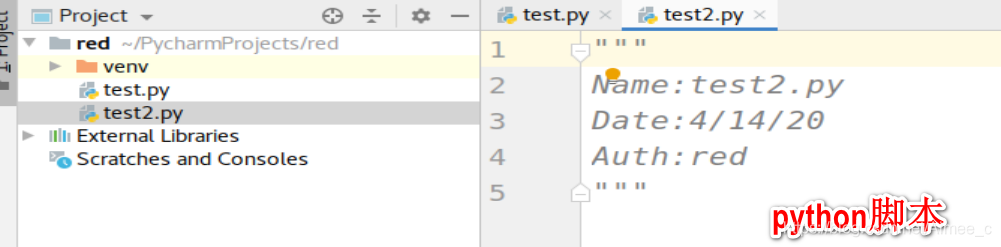
shift+F6改文件名(不能与系统冲突,如random)
 Python基础入门:变量、语法与IDE
Python基础入门:变量、语法与IDE




 本文介绍了Python的基础知识,包括在RHEL系统中的安装、Python2与Python3的语法差异、注释、输入输出以及格式化输出。强调了变量的命名规则、类型以及变量类型的特殊用法。此外,还讲解了如何在Python中进行数值类型的转换,并提供了一个计算学生平均成绩和占比的练习。最后,讨论了Python的IDE工具PyCharm的安装。
本文介绍了Python的基础知识,包括在RHEL系统中的安装、Python2与Python3的语法差异、注释、输入输出以及格式化输出。强调了变量的命名规则、类型以及变量类型的特殊用法。此外,还讲解了如何在Python中进行数值类型的转换,并提供了一个计算学生平均成绩和占比的练习。最后,讨论了Python的IDE工具PyCharm的安装。
















 939
939

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








