void Creat (int a[][5], int m ){
int i=0,j=0;
a[0][0]=m;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
for(j=0;j<5;j++){
a[i][j]=m+i+j;
}
}
}
void Output( int a[][5] ){
int i=0,j=0;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
for(j=0;j<5;j++){
printf("%5d",a[i][j]);
}
if(i!=4)printf("\n");
}
}
oh~.





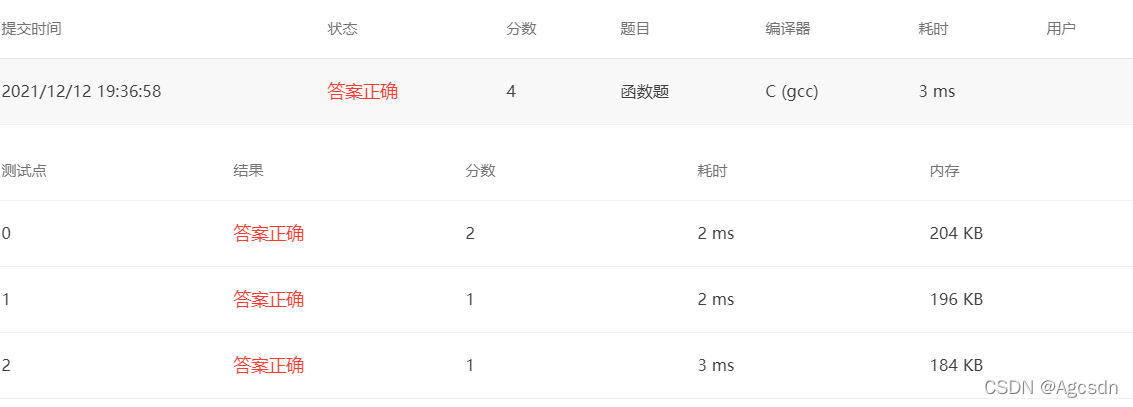
 该代码段展示了如何使用C语言初始化一个5x5的矩阵,并填充指定数值。之后,它会打印出整个矩阵。这个过程对于理解数组操作和矩阵处理基础至关重要。
该代码段展示了如何使用C语言初始化一个5x5的矩阵,并填充指定数值。之后,它会打印出整个矩阵。这个过程对于理解数组操作和矩阵处理基础至关重要。
















 1985
1985

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








