内容介绍
1 http协议
2 request请求对象
http协议
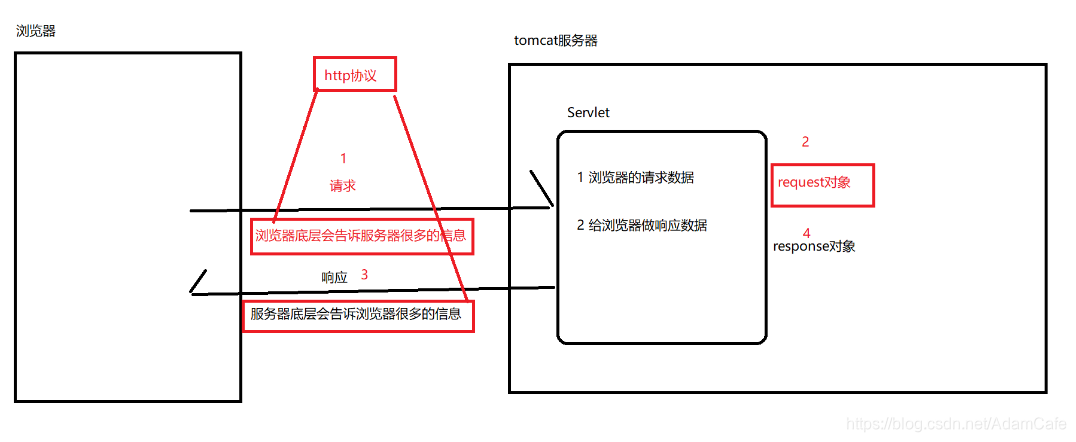
概述
协议:规定了被约束对象都需要去遵守的规则
http协议:是互联网上运用最为广泛的一种浏览器和服务器之间的协议(合同)
这份合同规定了浏览器访问服务器要遵循的内容以及服务器响应浏览器要遵循的内容
作用
强制规定了只要浏览器访问服务器就要传递哪些内容以及这些内容传递时的格式
强制规定 了只要服务器响应浏览器要响应哪些内容以及这些内容响应时的格式
协议规定的内容(抓包工具)
请求内容:浏览器发送给服务器的数据(今天)
响应内容:服务器响应给浏览器的数据 (明天)
浏览器上使用 F12键,然后在地址栏输入要访问的网址.
请求内容
请求内容:
请求行(第一行) 请求头(key:value) 请求体(表单的的内容)
注意:对于请求内容
get提交没有请求体 所有的表单的数据都在请求行中(地址栏中)
post提交有请求体 所有的表单数据都在请求体中(不在地址栏中)
面试题 get提交和post提交的区别?
get提交没有请求体 所有的页面数据都在请求行中 会在地址栏中暴露 不安全
post提交有请求体 所有的页面数据都在请求体中 不会地址栏中暴露 安全
get提交有着大小的限制 post没有大小的限制
什么情况下访问服务器是get提交? 什么情况下访问服务器时post提交?
浏览器只要和服务器交互 只有将表单的method设置成post才属于post提交,其它的一律是get提交
http请求协议的组成内容
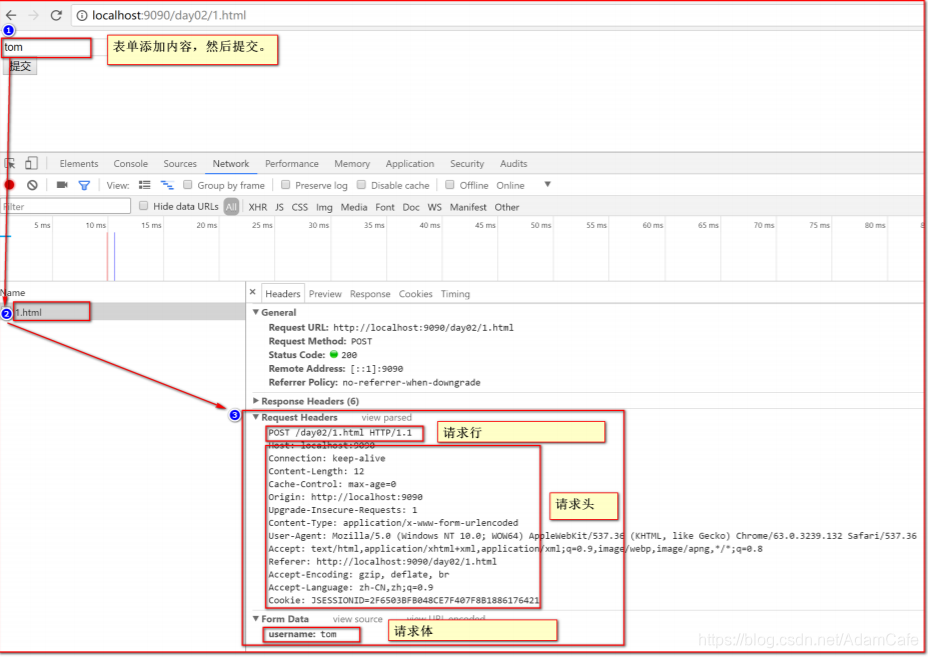
请求行 请求头 请求体
请求行
请求方式 请求资源 协议版本 POST /day_02/sd1 HTTP/1.1
请求头
数据的格式:键值对的数据
掌握的头数据:Referer User-Agent
Referer:当前页面的来源地址 防盗链
User-Agent:用户的浏览器版本信息
请求体
只有post提交才有 是页面表单的数据要传递给服务器的内容
问:请求行 请求头 请求体的数据最终都要传递给服务器 服务器如何获取到这些数据?
请求行 请求头 请求体会随着请求封装request对象中,所以我们在服务器端只要使用提供好的request对象调用api即可获取到
request请求对象
概述
request对象代表浏览器端的请求,当浏览器端通过HTTP协议访问服务器时,HTTP请求中的所有
信息都封装在这个对象中,开发人员通过这个对象的api,可以获得客户通过浏览器传递过来的数据
作用
作用:用来封装所有页面数据(请求行 请求头 请求体)
1.获取请求行的数据
2.获取请求头的数据
3.获取请求体的数据
请求数据的封装 如下图

1.获取请求行数据的api概述(请求方式 访问的资源 协议版本)
1.(了解)String getMethod() 获取请求方式
2.(了解)String getRequestURI() 获取请求行中的资源名部分
3.(掌握)StringBuffer getRequestURL() 获取客户端请求完整URL
4.(了解)String getProtocol() 获取请求协议和版本
5.(了解)int getLocalPort() 获取端口
6.(掌握)String getRemoteAddr() 获取请求者的ip地址
Localhost:ipv6
127.0.0.1:ipv4
7.(掌握)String getContextPath() 例如:/day_02
// 服务器端获取浏览器传递获取的请求数据(请求行)
public class ServletDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求方式
System.out.println("用户的提交方式是:"+request.getMethod());
//获取请求行中的资源名部分 /day_02/sd2
System.out.println(request.getRequestURI());
// 获取请求的完整资源路径(掌握)
System.out.println(request.getRequestURL());
//获取请求协议和版本
System.out.println(request.getProtocol());
//获取请求端口
System.out.println(request.getLocalPort());
//获取请求者的ip地址(掌握)
System.out.println(request.getRemoteAddr());
// 获取当前项目的路径 /day_02
System.out.println(request.getContextPath());
// 后期
// response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/sd1");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
2.获取请求头数据的api概述 (键值对key/value的数据)
1.getHeader(String key) 根据请求头的key获取value
例如:Referer可以获取到来源地址(没有来与为null:直接访问) 防盗链
例如:User-Agent可以获取用户的浏览器版本信息 下载
2.(了解)Enumeration getHeaderNames() 返回此请求包含的所有头名称
// 服务器端获取浏览器传递获取的请求数据(请求头)
public class ServletDemo3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 演示 String value=request.getheader(“key”)
String host = request.getHeader("Connection");
System.out.println(host);
// user-agent
String value1 = request.getHeader("user-agent");
// 下载 火狐浏览器:有一套 // 其它所有的 有一套
if(value1.contains("Firefox")){
System.out.println("用户使用的是火狐浏览器...");
}
System.out.println(value1);
// referer 防盗链
String referer = request.getHeader("referer");
System.out.println(referer);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
防盗链 详见下图:
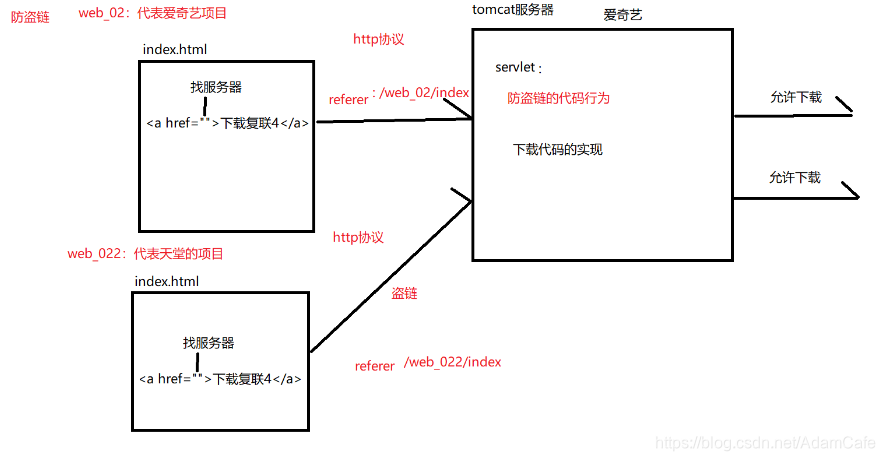
// 防盗链
public class ServletDemo4 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 做一层防盗链
String referer = request.getHeader("referer");
if(referer.contains("day_02")){
System.out.println("开始下载..");
}else{
System.out.println("你是坏人要盗我的资源,我要报警...");
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
3.获取请求体数据api概述(所有浏览器提交的表单数据)
1.String getParameter("name的属性名")
2.String[] getParameterValues("name的属性值")
3.Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap()
注意:key:对应的是表单中name属性名 **重要**
在提交表单的过程中,如果有中文 get提交没问题 但是post提交会乱码
解决方案:request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// // 服务器端获取浏览器传递获取的请求数据(请求体)
public class ServletDemo5 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取页面的数据 request.getParameter("页面的name属性")
// 只能获取单一的value
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println(username+":"+password);
String hobby = request.getParameter("hobby");
System.out.println(hobby);
// 可以获取多个value值 String[] value=request.getParameterValues("页面的name属性")
String[] hobbies = request.getParameterValues("hobby");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbies));
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
// 一次性的获取页面所有带name属性的数据 Map<String,String[]> map=request.getParameterMap();
// map: key页面的name属性 value:值的数组
Map<String, String[]> map = request.getParameterMap();
for(String key:map.keySet()){
System.out.println(key+":"+Arrays.toString(map.get(key)));
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
jack:111
cy
[cy, hj, on]
+++++++++++++
username:[jack]
password:[111]
hobby:[cy, hj, on]
// 页面传递中文的问题
public class ServletDemo6 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// get提交的中文 tomcat已经解决了没有问题
// post提交的中文 有乱码
// 解决方案 request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println(username+":"+password);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
4.request请求对象的其它作用
作为容器数据存取删的方法:(request也被称为域对象)
1.void setAttribute(String name, Object o) 存储数据
2.Object getAttribute(String name) 获取数据
3.void removeAttribute(String name) 移除数据
注意:request这3个方法也可以做多个servlet之间的数据传递?
问题:当我们浏览器访问2个不同的servlet的时候,发现并不能得到我们想要的获取数据效果
原因:请求一次就创建一个request对象,响应就销毁,要想用同一个request对象,得学习请求转发
解决:使用请求转发
请求转发:可以在一个servlet中访问另外一个servlet
request.getRequestDispatcher("/servlet的地址").forward(request,response);
请求数据的转发 详见下图:
// 请求转发(内部资源)
public class ServletDemo7 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("浏览器访问到我了,但是我要跳到sd8中...");
// 跳到sd8中
/*RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("地址");
dispatcher.forward(request,response);*/
request.setAttribute("key1","aaaa"); //key1=aaa
request.setAttribute("key2","bbb"); //key2=bbb
request.getRequestDispatcher("/sd8").forward(request,response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
// 页面传递中文的问题
public class ServletDemo8 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("哈哈哈,我跳过来了...");
String key1 =(String)request.getAttribute("key1");
System.out.println("sd8:"+key1);
String key2 =(String)request.getAttribute("key2");
System.out.println("sd8:"+key2);
//删除
request.removeAttribute("key1");
// 继续跳
request.getRequestDispatcher("/sd1").forward(request,response);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
// 接受浏览器的请求数据以及给浏览器写响应数据
public class ServletDemo1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("又跳过来了我是sd1...");
String key1 =(String)request.getAttribute("key1");
System.out.println("sd1:"+key1);
String key2 =(String)request.getAttribute("key2");
System.out.println("sd1:"+key2);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
控制台输出的结果是:
控制台输出的结果是:
浏览器访问到我了,但是我要调到sd8中...
哈哈,我跳过来了....
aaa
bbb
有跳过了了我是sd1...
null
bbb
beanUtils工具包的使用
需求:在开发的过程中,我们经常性的会有需求将map的数据转给对象属性,如果自己来做转化实现的话过于麻烦,我们可以借助第三方的工具包来实现,操作简单方便
BeanUtis工具包的使用
1 导包 commons-beanutils-1.8.3 commons-logging-1.1.1
2 调用api方法 BeanUtils.populate(对象,map);
注意:只有map(key)和对象(属性)共同的内容 才会封装
登录步骤的分析 详见下图:
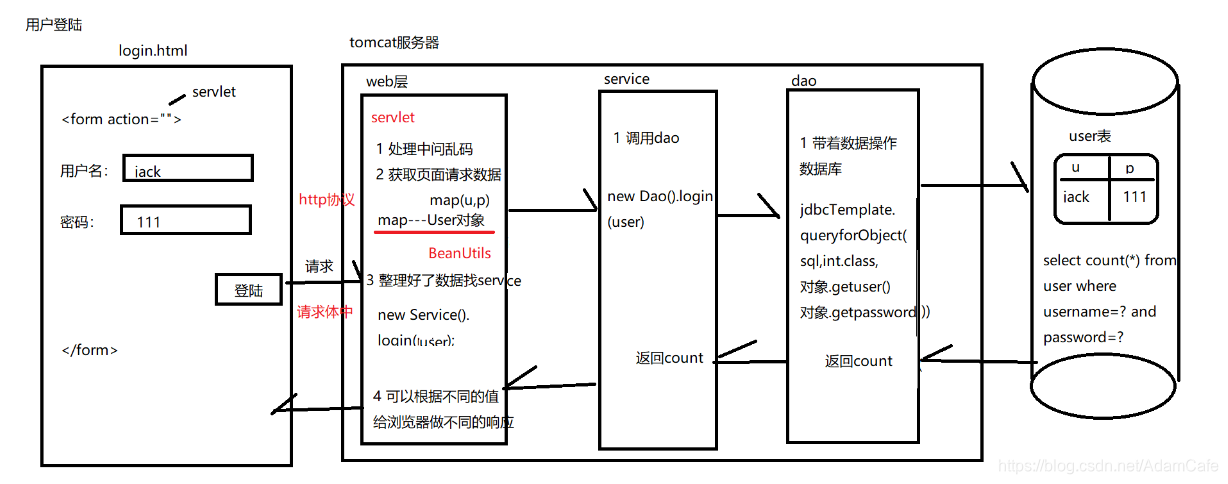
1.用户登录端 html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录案例</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>用户登录</h2>
<form action="/day_02/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
2.tomcat服务器 web层
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
// 1 处理中文乱码
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//2 接受页面表单数据
Map<String, String[]> map = request.getParameterMap();
// map---user的属性--->工具类(BeanUtils)
// 1 导包 (2个) 2 调用api:BeanUtils.populate(对象,map);
User user = new User();
BeanUtils.populate(user,map);
// 3 调用service
LoginService loginService = new LoginService();
int count = loginService.login(user);
// 4 根据结果给浏览器做响应
if(count>0){
response.getWriter().print("恭喜你,登录成功~");
}else{
response.getWriter().print("用户名或密码错误~");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}
}
web.xml内配置如下:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>cn.itcast.web.LoginServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/login</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
3.tomcat服务器 service层
public class LoginService {
// 登录业务
public int login(User user) {
LoginDao loginDao = new LoginDao();
int count = loginDao.login(user);
return count;
}
}
4.tomcat服务器 dao层
public class LoginDao {
//登录的查询语句
public int login(User user) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
String sql="select count(*) from user where username=? and password=?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, int.class, user.getUsername(), user.getPassword());
return count;
}
}
5.jdbc的工具类
// jdbc的工具类
public class JDBCUtils {
private static DataSource dataSource=null;
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream is = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
properties.load(is);
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接池
public static DataSource getDataSource() {
// 获取连接池
return dataSource;
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
// 从连接池中获取连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
return connection; // 来源于连接池
}
// 释放资源
public static void closeZY(ResultSet rs, Statement statement, Connection connection){
// 关闭resultSet
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 关闭statement
try {
if(statement!=null){
statement.close();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 关闭connection
try {
if(connection!=null){
connection.close();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
6.user对象
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}





 本文深入解析HTTP协议的工作原理,包括GET与POST请求的区别、请求行、请求头及请求体的详细说明。同时,介绍了Servlet如何利用request对象处理客户端请求,包括数据获取与转发机制。
本文深入解析HTTP协议的工作原理,包括GET与POST请求的区别、请求行、请求头及请求体的详细说明。同时,介绍了Servlet如何利用request对象处理客户端请求,包括数据获取与转发机制。
















 1251
1251

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








