题目描述
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle
示例:
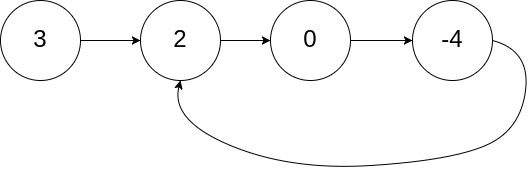
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
题解
下面搬运部分官方算法说明与分析
方法一:哈希表
思路
我们可以通过检查一个结点此前是否被访问过来判断链表是否为环形链表。常用的方法是使用哈希表。
算法
我们遍历所有结点并在哈希表中存储每个结点的引用(或内存地址)。如果当前结点为空结点 null(即已检测到链表尾部的下一个结点),那么我们已经遍历完整个链表,并且该链表不是环形链表。如果当前结点的引用已经存在于哈希表中,那么返回 true(即该链表为环形链表)。
代码
# 哈希表法
def hasCycle(self, head):
set0 = set()
while True:
if head not in set0:
set0.add(head)
if head is None:
return False
else:
head = head.next
else:
return True
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),对于含有 n 个元素的链表,我们访问每个元素最多一次。添加一个结点到哈希表中只需要花费 O(1) 的时间。
空间复杂度:O(n),空间取决于添加到哈希表中的元素数目,最多可以添加 n 个元素。
方法二:双指针
思路
想象一下,两名运动员以不同的速度在环形赛道上跑步会发生什么?
算法
通过使用具有 不同速度 的快、慢两个指针遍历链表,空间复杂度可以被降低至 O(1)O(1)。慢指针每次移动一步,而快指针每次移动两步。
如果列表中不存在环,最终快指针将会最先到达尾部,此时我们可以返回 false。
现在考虑一个环形链表,把慢指针和快指针想象成两个在环形赛道上跑步的运动员(分别称之为慢跑者与快跑者)。而快跑者最终一定会追上慢跑者。这是为什么呢?考虑下面这种情况(记作情况 A)- 假如快跑者只落后慢跑者一步,在下一次迭代中,它们就会分别跑了一步或两步并相遇。
其他情况又会怎样呢?例如,我们没有考虑快跑者在慢跑者之后两步或三步的情况。但其实不难想到,因为在下一次或者下下次迭代后,又会变成上面提到的情况 A。
代码
# 快慢指针法
def hasCycle(self, head):
if head == None: return False
slow = head
fast = head
while fast.next is not None and fast.next.next is not None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast: return True
return False
复杂的分析
时间复杂度 O(n).
空间复杂度 O(1).
完整代码
'''
leetcode 141.环形链表
'''
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head): # 不是空间复杂度为常量的哈希表算法
set0 = set()
while True:
if head not in set0:
set0.add(head)
if head is None:
return False
else:
head = head.next
else:
return True
def hasCycle2(self, head): # 双指针算法
if head == None: return False
slow = head
fast = head
while fast.next is not None and fast.next.next is not None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast: return True
return False
def creatListNode(head, pos):
'''
description:
创建环形链表, head给出链表数值, pos指出链表尾巴链接到的位置
parameter:
head: type list
pos: type int
return:
type: ListNode
'''
if head == []: return None
temp0 = ListNode(head[0])
out_head = temp0
link = None
for i in head[1:]:
if pos == 0: link = temp0
pos -= 1
temp1 = ListNode(i)
temp0.next = temp1
temp0 = temp1
temp0.next = link
return out_head
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 5, 3, 0]
pos = 1
h = creatListNode(head, pos)
solv = Solution()
print(solv.hasCycle2(h))
参考链接
[1] 官方题解 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/solution/huan-xing-lian-biao-by-leetcode/





 本文介绍两种检测链表中是否存在环的有效方法:哈希表法和双指针法。哈希表法通过记录已访问节点判断环的存在,而双指针法则利用快慢指针在环形链表中必然相遇的特性进行检测。
本文介绍两种检测链表中是否存在环的有效方法:哈希表法和双指针法。哈希表法通过记录已访问节点判断环的存在,而双指针法则利用快慢指针在环形链表中必然相遇的特性进行检测。
















 1360
1360

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








