1.项目启动,servlet容器(Tomcat)回去读取web.xml文件,加载<context-param>和<listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-config.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
2.接着,容器会创建servletContext上下文,(该项目中全局共享)
3.加载<context-param>的指定配置到IOC容器(WebApplicationContext,由ContextLoaderListener创建的)中,WebApplicationContext以键值对的形式保存到servletContext中
(容器初始化web.xml中其他的servlet,并将WebApplicationContext设置为这些servlet的父容器)
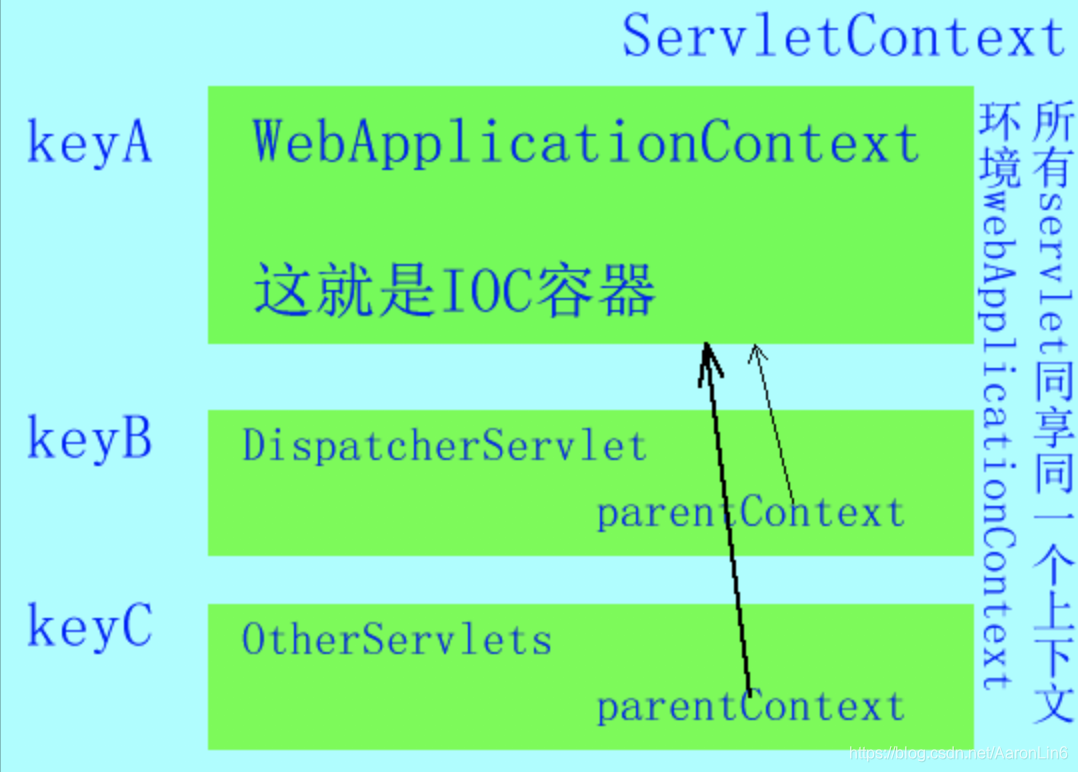
因此对于作用域上,DespatcherServlet中可以引用到webApplicationContext中到内容;反过来调用不行;Spring在加载webApplication的getBeans()时,如果在自己的context中找不到对应的Bean,则会到父级到Context中找。
二.Spring配置细节:
spring配置时:<context:exclude-filter>的使用原因,为什么在applicationContext.xml中排除controller,而在spring-mvc.xml中incloud这个controller
既然知道了spring的启动流程,那么web容器初始化webApplicationContext时作为公共的上下文环境,只需要将service、dao等的配置信息在这里加载,而servlet自己的上下文环境信息不需要加载(每个servlet自己独有的信息加载在自己到context中就行)。故,在applicationContext.xml中将@Controller注释的组件排除在外,而在dispatcherServlet加载的配置文件中将@Controller注释的组件加载进来,方便dispatcherServlet进行控制和查找。故,配置如下:
applicationContext.mxl中:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.linkage.edumanage">
<context:exclude-filter expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" type="annotation" />
</context:component-scan>
spring-mvc.xml中:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.brolanda.cloud" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" type="annotation" />
</context:component-scan>
 Spring MVC启动流程与配置详解
Spring MVC启动流程与配置详解




 本文详细解析了Spring MVC的启动过程,包括Tomcat读取web.xml文件、加载context-param和listener,创建servletContext上下文,以及如何通过ContextLoaderListener加载Spring配置。同时,阐述了在applicationContext.xml中排除Controller的原因,以及在spring-mvc.xml中包含Controller的必要性。
本文详细解析了Spring MVC的启动过程,包括Tomcat读取web.xml文件、加载context-param和listener,创建servletContext上下文,以及如何通过ContextLoaderListener加载Spring配置。同时,阐述了在applicationContext.xml中排除Controller的原因,以及在spring-mvc.xml中包含Controller的必要性。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








