经典题目选讲(1)
题目一:The Skyline Problem
给定一个Ñ行3列的二维数组,每一行表示有一座大楼,一共有Ñ座大楼所有大楼的底部都坐落在X轴上,每一行的三个值(A,B, C)代表每座大楼的从(A,0)点开始,到(B,0)点结束,高度为C。输入的数据可以保证A<B,且A,B,C均为正数。大楼之间可以有重合。请输出整体的轮廓线。
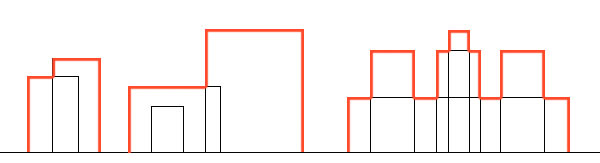
例如:给定一个二维数组[[1,3,3],[2,4,4],[5,6,1]
输出为轮廓线[[1,2,3],[2,4,4],[5,6,1]
思考:本题使用有序表结构,但关键在于设计处理流程。以[2,5,6]为例,将其变为(2,+6)和(5,-6)分别表示,在2的位置上,高度增加了6,在5的位置上,高度减了6.
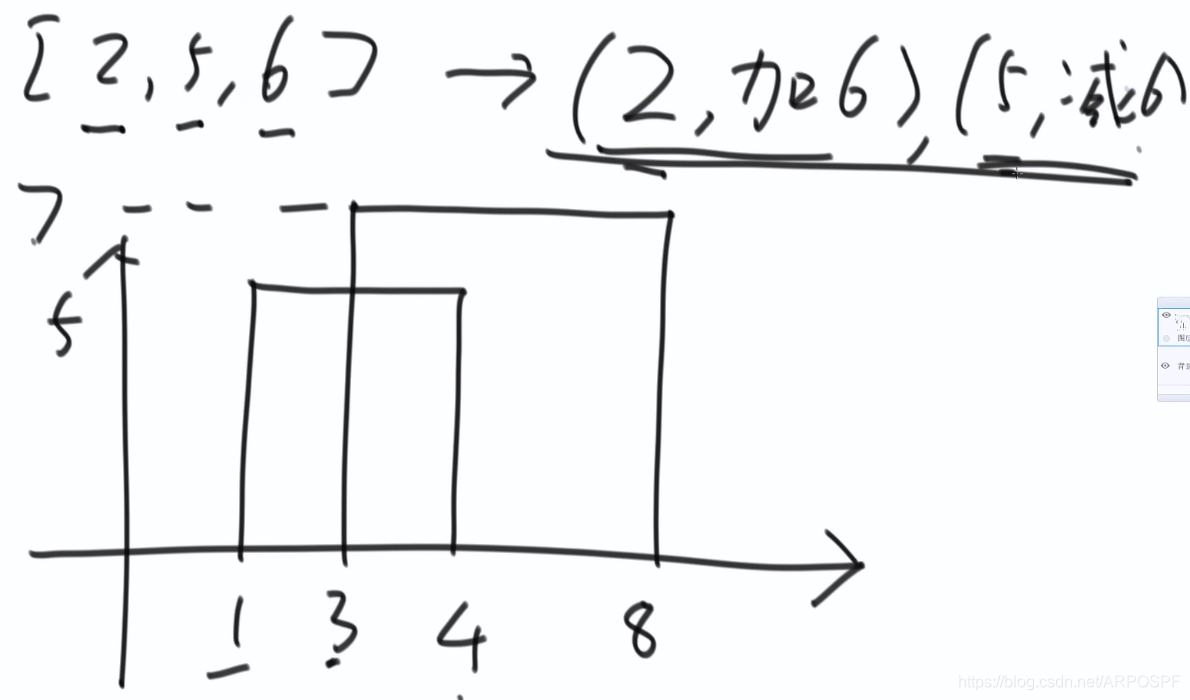
将这样的操作之后的数组排序:第一维(第一个数)从小到大,第一维相等的时候,第二维按照+的放在前面,-的放在后面,但是对于同样是+或-的两个值,谁放前面都可以。例如(6,-5),(6,-7),谁在前面都可以,但是(12,+4)必须放在(12,-5)之前。
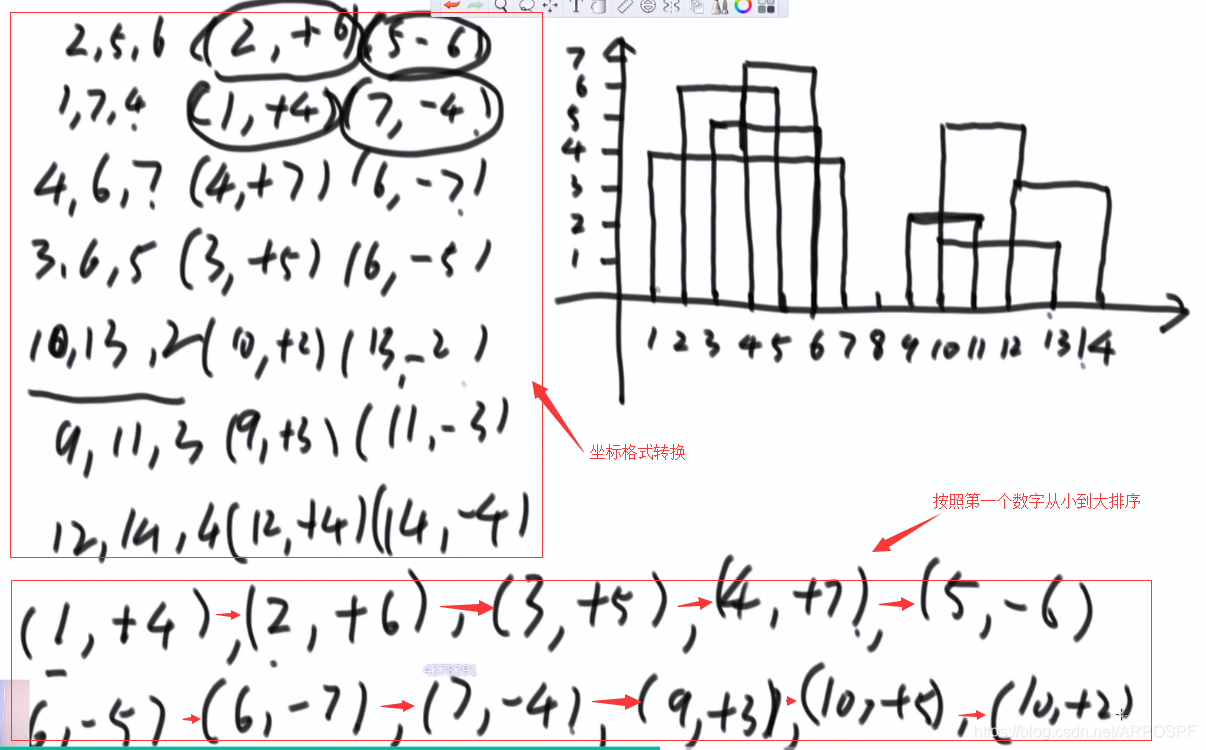
轮廓线的产生:最大高度发生了变化。定义有序表map,key是高度,value是次数。依次遍历数组,在此过程中根据最大高度的变化判定轮廓线的变化和高度。当次数减少到0的时候,删除该条记录。代码如下:
import java.util.*;
public class BuildingOutline {
/**
* 操作对象的类
*/
public static class Node {
public boolean isAdd; //true;false
public int x;
public int h;
public Node(boolean isAddHeight, int position, int height) {
isAdd = isAddHeight;
x = position;
h = height;
}
}
//比较器
public static class NodeComparator implements Comparator<Node> {
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
if (o1.x != o2.x) {
return o1.x - o2.x;
}
if (o1.isAdd != o2.isAdd) {
return o1.isAdd ? -1 : 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
/**
* @param buildings n行3列的矩阵
* @return
*/
public static List<List<Integer>> buildingOutline(int[][] buildings) {
Node[] nodes = new Node[buildings.length * 2];//操作数组
for (int i = 0; i < buildings.length; i++) {
nodes[i * 2] = new Node(true, buildings[i][0], buildings[i][2]);
nodes[i * 2 + 1] = new Node(false, buildings[i][1], buildings[i][2]);
}
Arrays.sort(nodes, new NodeComparator());
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> heightTimesMap = new TreeMap<>(); //某一个高度出现的次数
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> xMaxHeightMap = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++) {
if (nodes[i].isAdd) {//加高度的操作
if (!heightTimesMap.containsKey(nodes[i].h)) {//如果不含有此高度,则次数为1,否则次数加1
heightTimesMap.put(nodes[i].h, 1);
} else {
heightTimesMap.put(nodes[i].h, heightTimesMap.get(nodes[i].h) + 1);
}
} else {//减高度的操作
if (heightTimesMap.get(nodes[i].h) == 1) { //如果减完之后次数为0,则直接删除这条记录
heightTimesMap.remove(nodes[i].h);
} else {
heightTimesMap.put(nodes[i].h, heightTimesMap.get(nodes[i].h) - 1);
}
}
//跟踪记录最大高度的变化
if (heightTimesMap.isEmpty()) {
xMaxHeightMap.put(nodes[i].x, 0);
} else {
xMaxHeightMap.put(nodes[i].x, heightTimesMap.lastKey());
}
}
//生成最后的轮廓线
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int start = 0;
int height = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : xMaxHeightMap.entrySet()) {
int curPosition = entry.getKey();
int curMaxHeight = entry.getValue();
if (height != curMaxHeight) {
if (height != 0) {
List<Integer> newRecord = new ArrayList<>();
newRecord.add(start);
newRecord.add(curPosition);
newRecord.add(height);
res.add(newRecord);
}
start = curPosition;
height = curMaxHeight;
}
}
return res;
}
}
题目二:设计可以变更的缓存结构(LRU)
题目描述:设计一种缓存结构,该结构在构造时确定大小,假设大小为K,并由两个功能:
- 集(键,值):将记录(键,值)插入该结构
- 获得(键):返回键对应的值值
要求:
- 设置和获取方法的时间复杂度为O(1)。
- 某个键的设定或GET操作一旦发生,认为这个关键的记录成了最经常使用的。
- 当缓存的大小超过ķ时,移除最不经常使用的记录,即设置或获取最久远的。
举例:
假设缓存结构的实例是高速缓存,大小为3,并依次发生如下行为:
- cache.set( “A”,1)。最经常使用的记录为(“A”,1)。
- cache.set( “B”,2)。最经常使用的记录为(“B”,2),(“A”,1)变为最不经常的。
- cache.set( “C”,3)。最经常使用的记录为(“C”,2),(“A”,1)还是最不经常的。
- cache.get( “A”)。最经常使用的记录为(“A”,1),( “B”,2)变为最不经常的。
- cache.set( “d”,4)。大小超过了3,所以移除此时最不经常使用的记录(“B”,2),加入记录(“d”,4),并且为最经常使用的记录,然后(“C”,2)变为最不经常使用的记录。
思考:这种缓存结构可以由双端队列与哈希表相结合的方式实现。首先实现一个基本的双向链表节点的结构:
public class Node<V>{
public V value;
public Node<V> last;
public Node<V> next;
public Node(V value){
this.value=value;
}
}
根据双向链表节点结构Node,实现一种双向链表结构NodeDoubleLinkedList,在该结构中优先级最低的节点是head(头),优先级最高的节点是tail(尾)。这个结构有以下三种操作:
- 当加入一个节点时,将新加入的节点放在这个链表的尾部,并将这个节点设置为新的尾部,参见如下代码中的addNode方法。
- 对这个结构中的任意节点,都可以分离出来并放到整个链表的尾部,参见如下代码中的moveNodeToTail方法
- 移除head节点并返回这个节点,然后将head设置成老head节点的下一个,参见如下代码中的removeHead方法。
public class NodeDoubleLinkedList<V> {
private Node<V> head;
private Node<V> tail;
public NodeDoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
public void addNode(Node<V> newNode) {
if (newNode == null) {
return;
}
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.last = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
public void moveNodeToTail(Node<V> node) {
if (this.tail == node) {
return;
}
if (this.head == node) {
this.head = node.next;
this.head.last = null;
} else {
node.last.next = node.next;
node.next.last = node.last;
}
node.last = this.tail;
node.next = null;
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
public Node<V> removeHead() {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
Node<V> res = this.head;
if (this.head == this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head = res.next;
res.next = null;
this.head.last = null;
}
return res;
}
}
最后实现最终的缓存结构。如何把记录之间按照“访问经常度”来排序,就是上下文提到的NodeDoubleLinkedList结构。一旦接入新的记录,就把该记录加到NodeDoubleLinkedList的尾部(addNode)。一旦获得(get)或设置(set)一个记录的key,就将这个key对应的node在NodeDoubleLinkedList中调整到尾部(moveNodeToTail)。一旦cache满了,就删除“最不经常使用”的记录,也就是移除NodeDoubleLinkedList的当前头部(removeHead)。
为了能让每一个key都能找到在NodeDoubleLinkedList所对应的节点,同时让每一个node都能找到各自的key,我们还需要两个map分别记录key到node的映射,以及node到key的映射,就是如下MyCache结构中的keyNodeMap和nodeKeyMap。
public class MyCache<K, V> {
private HashMap<K, Node<V>> keyNodeMap;
private HashMap<Node<V>, K> nodeKeyMap;
private NodeDoubleLinkedList<V> nodeList;
private int capacity;
public MyCache(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Shoule be more than 0.");
}
this.keyNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
this.nodeKeyMap = new HashMap<>();
this.nodeList = new NodeDoubleLinkedList<>();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public V get(K key) {
if (this.keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
Node<V> res = this.keyNodeMap.get(key);
this.nodeList.moveNodeToTail(res);
return res.value;
}
return null;
}
public void set(K key, V value) {
if (this.keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
Node<V> node = this.keyNodeMap.get(key);
node.value = value;
this.nodeList.moveNodeToTail(node);
} else {
Node<V> newNode = new Node<V>(value);
this.keyNodeMap.put(key, newNode);
this.nodeKeyMap.put(newNode, key);
this.nodeList.addNode(newNode);
if (this.keyNodeMap.size() == this.capacity + 1) {
this.removeMostUnusedCache();
}
}
}
private void removeMostUnusedCache() {
Node<V> removeNode = this.nodeList.removeHead();
K removeKey = this.nodeKeyMap.get(removeNode);
this.nodeKeyMap.remove(removeNode);
this.keyNodeMap.remove(removeKey);
}
}
完整代码如下:
package NowCoder2.Class04;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LRU {
public static class Node<K, V> { //双向链表结构
public K key;
public V value;
public Node<K, V> last;
public Node<K, V> next;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public static class NodeDoubleLinkedList<K, V> {
private Node<K, V> head;
private Node<K, V> tail;
public NodeDoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
public void addNode(Node<K, V> newNode) {
if (newNode == null) {
return;
}
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.last = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
//node已经在链表上
public void moveNodeToTail(Node<K, V> node) {
if (this.tail == node) {
return;
}
//node不是尾节点
if (this.head == node) {
this.head = node.next;
this.head.last = null;
} else {
node.last.next = node.next;
node.next.last = node.last;
}
node.last = this.tail;
node.next = null;
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
//头节点remove并且返回
public Node<K, V> removeHead() {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
Node<K, V> res = this.head;
if (this.head == this.tail) {//双向链表中只有一个节点的时候
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {//不止一个的时候
this.head = res.next;
res.next = null;
this.head.last = null;
}
return res;
}
}
public static class MyCache<K, V> {
private HashMap<K, Node<K, V>> keyNodeMap;
private NodeDoubleLinkedList<K, V> nodeList;
private int capacity; //缓存的容量,固定大小
public MyCache(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("should be more than 0");
}
this.keyNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
this.nodeList = new NodeDoubleLinkedList<>();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public V get(K key) {
if (this.keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
Node<K, V> res = this.keyNodeMap.get(key);
this.nodeList.moveNodeToTail(res);
return res.value;
}
return null;
}
public void set(K key, V value) {
if (this.keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
Node<K, V> node = this.keyNodeMap.get(key);
node.value = value;
this.nodeList.moveNodeToTail(node);
} else {//新建操作
Node<K, V> newNode = new Node<>(key, value);
this.keyNodeMap.put(key, newNode);
this.nodeList.addNode(newNode);
if (this.keyNodeMap.size() == this.capacity + 1) {
removeUnusedCache();
}
}
}
private void removeUnusedCache() {
this.keyNodeMap.remove(this.nodeList.removeHead().key);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache<String, Integer> testCache = new MyCache<>(3);
testCache.set("A", 1);
testCache.set("B", 2);
testCache.set("C", 3);
System.out.println(testCache.get("B"));
System.out.println(testCache.get("A"));
testCache.set("D", 4);
System.out.println(testCache.get("D"));
System.out.println(testCache.get("C"));
}
}
题目三:实现LFU缓存结构
上一题实现了LRU缓存算法,LFU也是一个著名的缓存算法,自行了解之后实现LFU中的设置和GET。
要求:两个方法的时间复杂度都为O(1)。
LFU:在缓存中使用次数最小的被移除,如果次数都一样多,谁最早进缓存,删除谁。
思路:桶结构,桶表示次数,桶内部节点之间通过双向链表连接,桶与桶之间也通过双向链表连接。两张表和一个二维双向链表实现该数据结构。
代码:
package NowCoder2.Class04;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LFU {
public static class Node {
public Integer key;
public Integer value;
public Integer times;
public Node up;
public Node dowm;
public Node(int key, int value, int times) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.times = times;
}
}
public static class NodeBucket {
public Node head;
public Node tail;
public NodeBucket last;
public NodeBucket next;
public NodeBucket(Node node) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
public void addNodeFromHead(Node newHead) {
newHead.dowm = head;
head.up = newHead;
head = newHead;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//潜台词:node 已经确定在桶中
public void deleteNode(Node node) {
if (head == tail) {//只剩一个节点
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {//不止一个节点
if (node == head) {
head = node.dowm;
head.up = null;
} else if (node == tail) {
tail = node.up;
tail.dowm = null;
} else {
node.up.dowm = node.dowm;
node.dowm.up = node.up;
}
}
node.up = null;
node.dowm = null;
}
}
public static class LFUCache {
private int capacity;//总内存限制
private int size;//目前收了多少数据
private HashMap<Integer, Node> keyNodeMap;
private HashMap<Node, NodeBucket> nodeBucketMap;
private NodeBucket headBucket;
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
this.keyNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
this.nodeBucketMap = new HashMap<>();
headBucket = null;
}
public void set(int key, int value) {
if (keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {//更新
Node node = keyNodeMap.get(key);
node.value = value;
node.times++;
NodeBucket curNodeBucket = nodeBucketMap.get(node);
move(node, curNodeBucket);//node从老桶出,进次数+1的桶,有,直接进,无,新建
} else {//新建记录
if (size == capacity) {
Node deleteNode = headBucket.tail;
headBucket.deleteNode(deleteNode);
deleteBucketModifyHeadBucket(headBucket);
keyNodeMap.remove(deleteNode.key);
nodeBucketMap.remove(deleteNode);
size--;
}
//内存够用
Node node = new Node(key, value, 1);
if (headBucket == null) {
headBucket = new NodeBucket(node);
} else {
if (headBucket.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
headBucket.addNodeFromHead(node);
} else {//头桶词频不是1
NodeBucket newBucket = new NodeBucket(node);
newBucket.next = headBucket;
headBucket.last = newBucket;
headBucket = newBucket;
}
}
keyNodeMap.put(key, node);
nodeBucketMap.put(node, headBucket);
size++;
}
}
//已经确定node属于oldBucket
//但此时该node操作数量增加,所以需要从老的桶中,删掉
//加入到操作数量+1的新桶中
//如果操作数量+1的下一个桶已经存在,直接放
//否则,新建操作数量+1的下一个桶
//老桶可以会删除,删除的时候也可能存在换头桶的情况
//并且保持桶之间,依然是双向链表连接
private void move(Node node, NodeBucket oldBucket) {
oldBucket.deleteNode(node);
//node要放入新桶中,对于新桶来说,前一个是谁
NodeBucket preBucket = deleteBucketModifyHeadBucket(oldBucket) ? oldBucket.last :oldBucket;
NodeBucket nextBucket = oldBucket.next;
//新桶目前还没有建立出来
if (nextBucket == null) {//node之前就是最大词频,需要更大词频的桶
NodeBucket newBucket = new NodeBucket(node);
if (preBucket != null) {
preBucket.next = nextBucket;
}
newBucket.last = preBucket;
if (headBucket == null) {//第一个桶刚刚被建立的情况
headBucket = newBucket;
}
nodeBucketMap.put(node, newBucket);
} else {//node原来的桶,存在下一个桶
if (nextBucket.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
nextBucket.addNodeFromHead(node);
nodeBucketMap.put(node, nextBucket);
} else {//老桶下一个桶的词频,比node词频++之后大
NodeBucket newBucket = new NodeBucket(node);
if (preBucket != null) {
preBucket.next = nextBucket;
}
newBucket.last = preBucket;
newBucket.next = nextBucket;
newBucket.last = newBucket;
if (headBucket == nextBucket) {
headBucket = newBucket;
}
nodeBucketMap.put(node, newBucket);
}
}
}
//如果当前的桶是空的,删掉他
//如果删掉的桶又是头桶的话,换头桶
//如果真的删了,返回true
//如果不需要删,返回false
private boolean deleteBucketModifyHeadBucket(NodeBucket bucket) {
if (bucket.isEmpty()) {
if (headBucket == bucket) {
headBucket = bucket.next;
if (headBucket != null) {
headBucket.last = null;
}
} else {
bucket.last.next = bucket.next;
if (bucket.next != null) {
bucket.next.last = bucket.last;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node node = keyNodeMap.get(key);
node.times++;
NodeBucket curNodeList = nodeBucketMap.get(node);
move(node, curNodeList);
return node.value;
}
}
}
题目四:找到二叉树中的最大搜索二叉子树
题目描述:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,已知其中所有节点的值都不一样,找到含有节点最多的搜索二叉子树,并返回这棵子树的头节点。
要求:如果节点数为N,要求时间复杂度为O(N),额外空间复杂度为O(h),h为二叉树的高度。
思路:
以节点node为头的树中,最大的搜索二叉子树只可能来自以下两种情况:
第一种:如果来自node左子树上的最大搜索二叉子树是以node.left为头的;来自node右子树上的最大搜索二叉子树是以node.right为头的;node左子树上的最大搜索二叉子树的最大值小于node.value;node右子树上的最大搜索二叉子树的最小值大于node.value,那么以节点node为头的整课树都是搜索二叉树。
第二种:如果不满足第一种情况,说明以节点node为头的数整体不能连成搜索二叉树,这种情况下,以node为头的树上的最大搜索二叉子树是来自node的左子树上的最大搜索二叉子树和来自node的右子树上的最大搜索二叉子树之间,节点数较多的那个。
通过以上的分析,求解的具体过程如下:
- 整体过程是二叉树的后序遍历
- 遍历到当前节点记为cur时,先遍历cur的左子树收集4个信息,分别是左子树上的最大搜索二叉子树的头节点(lBST)、节点数(lSize)、最小值(lMin)和最大值(lMax)。在遍历cur的右子树收集4个信息,分别是右子树上最大搜索二叉子树的头节点(rBST)、节点数(rSize)、最小值(rMin)和最大值(rMax)。
- 根据步骤2所收集的信息,判断是否满足第一种情况,如果满足第一种情况,就返回cur节点,如果满足第二种情况,就返回lBST和rBST中较大的一个。
- 可以使用全局变量的方式实现步骤2中收集节点数、最小值和最大值的问题。
代码:
package NowCoder2.Class04;
public class BiggestSubBST {
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public Node biggestSubBST(Node head) {
int[] record = new int[3];
return posOrder(head, record);
}
private Node posOrder(Node head, int[] record) {
if (head == null) {
record[0] = 0;
record[1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
record[2] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return null;
}
int value = head.value;
Node left = head.left;
Node right = head.right;
Node lBST = posOrder(left, record);
int lSize = record[0];
int lMin = record[1];
int lMax = record[2];
Node rBST = posOrder(right, record);
int rSize = record[0];
int rMin = record[1];
int rMax = record[2];
record[1] = Math.min(lMin, value);
record[2] = Math.max(rMax, value);
if (left == lBST && right == rBST && lMax < value && value < rMin) {
record[0] = lSize + rSize + 1;
return head;
}
record[0] = Math.max(lSize, rSize);
return lSize > rSize ? lBST : rBST;
}
}
题目五:给定一棵二叉树的头节点的头,请返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小
题目描述:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,已知所有节点的值都不一样,返回其中最大的且符合搜索二叉树条件的最大拓扑结构的大小。
思考:
方法一:二叉树的节点数为N,时间复杂度为O(N^2)的方法。
首先来看这样一个问题,以节点head为头的树中,在拓扑结构中也必须以head为头的情况下,怎么找到符合搜索二叉树条件的最大结构?这个问题有一种比较容易理解的解法,先考察head的孩子节点,根据孩子节点的值从head开始按照二叉搜索的方式移动,如果最后能移动到同一个孩子节点上,说明这个孩子节点可以作为这个拓扑的一部分,并继续考查这个孩子节点的孩子节点,一直延伸下去。
也就是说,我们根据一个节点的值,根据这个值的大小,共head开始,每次向左或向右移动,如果最后能移动到原来的节点上,说明该节点可以作为以head为头的拓扑的一部分。
解决了以节点head为头的树中,在拓扑结构也必须以head为头的情况下,怎么找到符合搜索二叉树条件的最大结构?接下来只需要遍历所有的二叉树节点,并在以每个节点为头的子树中都求一遍其中的最大拓扑结构,其中最大的那个就是我们想找的结构,它的大小就是返回值。
方法二:二叉树的节点数为N、时间复杂度最好为O(N)、最差为O(NlogN)的方法。
首先介绍一个非常重要的概念——拓扑贡献记录。每个节点的旁边都有被括号括起来的两个值,把它称为节点对当前头节点的拓扑贡献记录。第一个值代表节点的左子树可以为当前头节点的拓扑贡献几个节点,第二个值代表节点的右子树可以为当前头节点的拓扑贡献几个节点。整个方法二的核心就是如果分别得到了head左右两个孩子为头的拓扑贡献记录,可以快速得到以head为头的拓扑贡献记录。
当我们得到以head为头的拓扑贡献记录后,相当于求出了以head为头的最大拓扑的大小。方法二正是不断地用这种方法,从小树的记录整合成大树的记录,从而求出整棵树中符合搜索二叉树条件的最大拓扑的大小。所以整个过程大体说来是利用二叉树的后序遍历,对每个节点来说,先生成其左孩子的记录,然后是右孩子的记录,接着把两组记录修改成以这个节点为头的拓扑贡献记录,并找出所有节点的最大拓扑大小中最大的那个。
方法一和方法二的代码如下:
package NowCoder2.Class04;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class BSTTopoSize {
// ****** 方法一 ******
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public int bstTopoSize1(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
int max = maxTopo(head, head);
max = Math.max(bstTopoSize1(head.left), max);
max = Math.max(bstTopoSize1(head.right), max);
return max;
}
public int maxTopo(Node h, Node n) {
if (h != null && n != null && isBSTNode(h, n, n.value)) {
return maxTopo(h, n.left) + maxTopo(h, n.right) + 1;
}
return 0;
}
public boolean isBSTNode(Node h, Node n, int value) {
if (h == null) {
return false;
}
if (h == n) {
return true;
}
return isBSTNode(h.value > value ? h.left : h.right, n, value);
}
// ****** 方法一结束 *******
// ****** 方法二 ********
public class Record {
public int l;
public int r;
public Record(int left, int right) {
this.l = left;
this.r = right;
}
}
public int bstTopoSize2(Node head) {
Map<Node, Record> map = new HashMap<>();
return posOrder(head, map);
}
public int posOrder(Node h, Map<Node, Record> map) {
if (h == null) {
return 0;
}
int ls = posOrder(h.left, map);
int rs = posOrder(h.right, map);
modifyMap(h.left, h.value, map, true);
modifyMap(h.right, h.value, map, false);
Record lr = map.get(h.left);
Record rr = map.get(h.right);
int lbst = lr == null ? 0 : lr.l + lr.r + 1;
int rbst = rr == null ? 0 : rr.l + rr.r + 1;
map.put(h, new Record(lbst, rbst));
return Math.max(lbst + rbst + 1, Math.max(ls, rs));
}
public int modifyMap(Node n, int v, Map<Node, Record> m, boolean s) {
if (n == null || (!m.containsKey(n))) {
return 0;
}
Record r = m.get(n);
if ((s & n.value > v) || ((!s) && n.value < v)) {
m.remove(n);
return r.l + r.r + 1;
} else {
int minus = modifyMap(s ? n.right : n.left, v, m, s);
if (s) {
r.r = r.r - minus;
} else {
r.l = r.l - minus;
}
m.put(n, r);
return minus;
}
}
// ****** 方法二结束 *******
}
题目六:未排序数组中累加和为给定值的最长子数组系列问题
题目描述:给定一个无序数组arr,其中元素可正、可负、可0,给定一个整数k,求arr所有的子数组中累加和等于k的最长子数组的长度
示例:arr = {7,3,2,1,1,7,7,7} num = 7
其中有很多的子数组累加和等于7,但是最长的子数组是{3,2,1,1},所以返回其长度4。
补充题目1:给定一个无序数组arr,其中元素可正、可负、可0。求arr所有的子数组中正数与负数个数相等的最长子数组长度。
补充题目2:给定一个无序数组arr,其中元素只是1或0。求arr所有的子数组中0和1个数相等的最长子数组长度。
解法:
先定义s的概念,s(i)代表子数组arr[0...i]所有元素的累加和。那么子数组arr[j...i](0<=j<=i<arr.length)的累加和为s(i)-s(j-1),因为根据定义,s(i)= arr[0...i]的累加和=arr[0....j-1]的累加和+arr[j...i]的累加和,又有arr[0...j-1]的累加和为s(j-1)。所以arr[j...i]的累加和为s(i)-s(j-1),这个结论是求解本题的核心。
原问题的解法只遍历一次arr,具体过程为:
- 设置变量sum=0,表示从0位置开始一直加到i位置所有元素的和。设置变量len=0,表示累加和为k的最长子数组长度。设置哈希表map,其中key表示从arr最左边开始累加的过程中出现过的sum值,对应的value值则表示sum值最早出现的位置。
- 从左到右开始遍历,遍历的当前元素为arr[i]。
- 令sum=sum+arr[i],即之前所有元素的累加和为s(i),在map中查看是否存在sum-k。
- 如果sum-k存在,从map中取出sum-k对应的value值,记为j,j代表从左到右不断累加的过程中第一次加出sum-k这个累加和的位置。根据之前得出的结论,arr[j+1...i]的累加和为s(i)-s(j),此时s(i)=sum,又有s(j)=sum-k,所以arr[j+1...i]的累加和为k。同时因为map中只记录每一个累加和最早出现的位置,所以此时的arr[j+1...i]是在必须以arr[i]结尾的所有子数组中,最长的累加和为k的子数组,如果该子数组的长度大于len,就更新len。
- 如果sum-k不存在,说明必须以arr[i]结尾的情况下没有累加和为k的子数组。
- 检查当前的sum(即s(i))是否在map中。如果不存在,说明此时的sum值是第一次出现的,就把记录(sum,i)加入到map中。如果sum存在,说明之前已经出现过sum,map只记录一个累加和最早出现的位置,所以此时什么记录也不加。
- 令sum=sum+arr[i],即之前所有元素的累加和为s(i),在map中查看是否存在sum-k。
- 继续遍历下一个元素,直到所有的元素遍历完。
还有一个问题需要处理:根据arr[j+1...i]的累加和为s(i)-s(j),所以,如果从0位置开始累加,会导致j+1>=1。也就是说,所有从0位置开始的子数组都没有考虑过。所以,应该从-1位置开始累加,也就是在遍历之前先把(0,-1)这个记录放进map,这个记录的意义是如果任何一个数也不加时,累加和为0,这样,从0位置开始的子数组就被我们考虑到了。
明白了原问题的解法,补充问题就可迎刃而解了。第一个补充问题,先把数组arr中的正数全部1,负数全部变成-1,0不变,然后求累加和为0的最长子数组长度即可。第二个补充问题,先把数组arr中的0全部变成-1,1不变,然后求累加和为0的最长子数组长度即可。
原问题的代码如下:
package NowCoder2.Class04;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* 求未排序数组中累加和为给定值的最长子数组系列问题
*/
public class LongestSumSubArrayLength {
public static int maxLength(int[] arr, int k) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, -1);//重要
int len = 0;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
if (map.containsKey(sum - k)) {
len = Math.max(i - map.get(sum - k), len);
}
if (!map.containsKey(sum)) {
map.put(sum, i);
}
}
return len;
}
/**
* 随机生成数组
*
* @param size
* @return
*/
public static int[] generateArray(int size) {
int[] result = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i != size; i++) {
result[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 11) - 5;
}
return result;
}
/**
* 打印数组元素
*
* @param arr
*/
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i != arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = generateArray(20);
printArray(arr);
System.out.println(maxLength(arr, 10));
}
}
题目七:定义数组的异或和的概念:
数组中所有的数异或起来,得到的结果叫做数组的异或和,比如数组{3,2,1}的异或和是3 ^ 2 ^ 1 = 0
给定一个数组arr,你可以任意把arr分成很多不相容的子数组,你的目的是:分出来的子数组中,异或和为0的子数组最多。
请返回:分出来的子数组中,异或和为0的子数组最多是多少?
解答:
本题属于动态规划问题。
代码:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Most_EOR {
public static int mostEOR(int[] arr) {
//dp[i]->arr[0~i]这个范围上,最多划分出几个异或和为0的子数组
int[] dp = new int[arr.length];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, -1);//一个数都没有的时候,异或和为0
int eor_all = arr[0];//0~i 前缀异或和
dp[0] = arr[0] == 0 ? 1 : 0; //0~0 答案显而易见
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
eor_all ^= arr[i];
if (map.containsKey(eor_all)) {
//map.get(eor_all) 就是最后一个有效部分的,前一个位置j
int k = map.get(eor_all); //k+1 ->j ,k最后一个有效部分的前一个位置
dp[i] = k == -1 ? 1 : dp[k] + 1;
}
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i]);
map.put(eor_all, i);
}
return dp[arr.length - 1];
}
}
题目八:给定一个字符串str,str表示一个公式,公式里可能有整数,加减乘除符号和左右括号,返回公式的计算结果。
例如:
STR = “48 *((70-65)-43)+ 8 * 1” 时,返回-1816。
STR =“3 + 1 * 4”,返回7.str = “3+(1 * 4)”,返回7
说明:
- 可以认为给定的字符串一定是正确的公式,即不需要对STR做公式有效性检查。
- 如果是负数,就需要用括号括起来,比如“4 *( - 3)”。但如果负数作为公式的开头或括号部分的开头,则可以没有括号,比如“-3 * 4”和“( - 3 * 4)”都是合法的。
- 不用考虑计算过程中会发生溢出的情况。
思路:本体可以使用递归的方法,具体过程如下:
从左到右遍历str,如果遇到左括号就进入递归,相当于将括号里的内容当成一个新的公式,等括号里的内容计算完成后将结果返回,此时再接着继续遍历str,直到str遍历完或者遇到右括号,这样就相当于str中不再包含左右括号。递归过程需要返回两个结果,一个是当前子公式计算的结果,一个是当前遍历到的str的位置。这样上级递归函数就可以根据这两个数据继续向后遍历。计算公式的结果时,先将乘法和除法计算完,最后再统一计算计算加法和减法。
既然在递归过程中遇到‘(’就交给下一层的递归过程处理,自己只用接收‘(’和‘)’之间的公式字符子串的结果,所以对所有的递归过程来说,可以看作计算的公式都是不含有'('和')'字符的。所以只要想清楚如何计算一个不含有'('和')'的公式字符串,整个实现就完成了。
代码如下:
package NowCoder2.Class04;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 公式字符串求值
*/
public class ExpressionCompute {
//公式字符串求值
public static int getValue(String exp) {
return value(exp.toCharArray(), 0)[0];
}
private static int[] value(char[] chars, int i) {
Deque<String> deq = new LinkedList<String>();
int pre = 0;
int[] bra = null;
while (i < chars.length && chars[i] != ')') {
if (chars[i] >= '0' && chars[i] <= '9') {
pre = pre * 10 + chars[i++] - '0';
} else if (chars[i] != '(') {
addNum(deq, pre);
deq.addLast(String.valueOf(chars[i++]));
pre = 0;
} else {
bra = value(chars, i + 1);
pre = bra[0];
i = bra[1] + 1;
}
}
addNum(deq, pre);
return new int[]{getNum(deq), i};
}
//计算乘法除法
private static void addNum(Deque<String> deq, int num) {
if (!deq.isEmpty()) {
int cur = 0;
String top = deq.pollLast();
if (top.equals("+") || top.equals("-")) {
deq.addLast(top);
} else {
cur = Integer.valueOf(deq.pollLast());
num = top.equals("*") ? (cur * num) : (cur / num);
}
}
deq.addLast(String.valueOf(num));
}
//计算加法减法
private static int getNum(Deque<String> deq) {
int res = 0;
boolean add = true;
String cur = null;
int num = 0;
while (!deq.isEmpty()) {
cur = deq.pollFirst();
if (cur.equals("+")) {
add = true;
} else if (cur.equals("-")) {
add = false;
} else {
num = Integer.valueOf(cur);
res += add ? num : (-num);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String exp = "48*((70-65)-43)+8*1";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "4*(6+78)+53-9/2+45*8";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "10-5*3";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "-3*4";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "3+1*4";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
}
}





 本文精选了八个经典算法题目,涵盖二叉树、缓存结构、数组处理和公式计算等领域,详细解析了每道题目的核心思路与代码实现,旨在帮助读者深入理解算法设计与优化。
本文精选了八个经典算法题目,涵盖二叉树、缓存结构、数组处理和公式计算等领域,详细解析了每道题目的核心思路与代码实现,旨在帮助读者深入理解算法设计与优化。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










