📝 面试求职: 「面试试题小程序」 ,内容涵盖 测试基础、Linux操作系统、MySQL数据库、Web功能测试、接口测试、APPium移动端测试、Python知识、Selenium自动化测试相关、性能测试、性能测试、计算机网络知识、Jmeter、HR面试,命中率杠杠的。(大家刷起来…)
📝 职场经验干货:
前言:测试自动化的关键转型
在软件项目的快速迭代中,自动化测试已成为保障产品质量的核心手段。对于接口测试而言,HAR(HTTP Archive)文件作为记录真实用户交互的宝贵数据源,其转换价值常被严重低估。
本文将从实战角度深入解析如何将HAR文件转化为可执行的pytest测试用例,并探讨其中涉及的关键技术与最佳实践。
HAR文件深度解析
2.1 HAR文件结构解剖
HAR文件采用JSON格式存储,其核心结构包含:
{
"log": {
"version": "1.2",
"creator": {},
"entries": [
{
"request": {
"method": "GET",
"url": "https://api.example.com/v1/users",
"headers": [],
"queryString": [],
"postData": {}
},
"response": {
"status": 200,
"headers": [],
"content": {}
},
"timings": {}
}
]
}
}2.2 关键字段解读
-
request.url: 完整请求地址(含参数)
-
request.method: HTTP方法类型
-
request.headers: 认证头、内容类型等重要信息
-
request.postData.text: POST请求体内容
-
response.status: HTTP状态码
-
response.content.text: 响应正文
基础转换实战
3.1 环境搭建
安装必要依赖:
pip install pytest haralyzer requests3.2 HAR解析器实现
创建 har_parser.py:
from haralyzer import HarParser
classHARConverter:
def__init__(self, har_path):
with open(har_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.har_parser = HarParser(json.load(f))
defextract_requests(self):
return [
{
"method": entry['request']['method'],
"url": entry['request']['url'],
"headers": {h['name']: h['value'] for h in entry['request']['headers']},
"body": entry['request'].get('postData', {}).get('text')
}
for entry in self.har_parser.har_data['entries']
if entry['request']['url'].startswith('https://api.')
]3.3 测试用例生成
创建 test_api.py:
import pytest
import requests
from har_parser import HARConverter
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def api_requests():
converter = HARConverter("user_session.har")
return converter.extract_requests()
def test_user_flow(api_requests):
session = requests.Session()
for req in api_requests:
response = session.request(
method=req['method'],
url=req['url'],
headers=req['headers'],
data=req['body']
)
# 基础断言
assert response.status_code == 200
assert response.headers['Content-Type'] == 'application/json'
# 业务逻辑断言示例
if'users/me' in req['url']:
user_data = response.json()
assert user_data['email_verified'] is True动态数据处理策略
4.1 动态参数识别与替换
创建 dynamic_handler.py:
import re
from datetime import datetime
classDynamicParameterHandler:
TOKEN_PATTERN = r"Bearer\s+(\w{32})"
TIMESTAMP_PATTERN = r"\d{13}"
@classmethod
defreplace_tokens(cls, text):
return re.sub(cls.TOKEN_PATTERN, "Bearer ${TOKEN}", text)
@classmethod
defhandle_timestamps(cls, text):
return re.sub(cls.TIMESTAMP_PATTERN, "${TIMESTAMP}", text)
@classmethod
defprocess_request(cls, request):
request['url'] = cls.handle_timestamps(request['url'])
if request['body']:
request['body'] = cls.replace_tokens(
cls.handle_timestamps(request['body'])
)
return request4.2 参数化测试用例改造
@pytest.mark.parametrize("request_data", api_requests)
deftest_parametrized_requests(request_data):
processed = DynamicParameterHandler.process_request(request_data)
# 使用环境变量替换动态值
headers = {
**processed['headers'],
"Authorization": os.getenv("API_TOKEN")
}
response = requests.request(
method=processed['method'],
url=processed['url'].replace("${TIMESTAMP}", str(int(time.time()*1000))),
headers=headers,
data=processed['body']
)
validate_response_schema(response)高级转换技巧
5.1 请求依赖管理
实现请求链处理:
defbuild_dependency_graph(requests):
graph = {}
for idx, req in enumerate(requests):
if idx == 0:
graph[idx] = []
continue
# 检测响应中的后续请求参数
prev_res = requests[idx-1]['response']['content']['text']
if'session_id'in prev_res:
graph[idx] = [idx-1]
else:
graph[idx] = []
return graph5.2 智能断言引擎
创建响应验证器:
from jsonschema import validate
SCHEMA_REGISTRY = {
"/users": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"data": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"id": {"type": "number"},
"name": {"type": "string"}
}
}
}
}
}
defvalidate_response_schema(response):
path = urlparse(response.url).path
if path in SCHEMA_REGISTRY:
validate(
instance=response.json(),
schema=SCHEMA_REGISTRY[path]
)持续集成集成方案
6.1 Jenkins Pipeline配置
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
API_TOKEN = credentials('api-token')
}
stages {
stage('ConvertHAR') {
steps {
sh 'python har_converter.py session.har'
}
}
stage('RunTests') {
steps {
sh 'pytest tests/ --junitxml=report.xml'
}
}
stage('Report'){
steps {
junit 'report.xml'
emailext body: '${JELLY_SCRIPT,template="html"}',
subject: 'API Test Results',
to: 'team@example.com'
}
}
}
}性能优化策略
7.1 并行执行配置
# pytest.ini
[pytest]
addopts = -n auto7.2 请求缓存实现
import diskcache
cache = diskcache.Cache('tmp/request_cache')
@pytest.fixture
def cached_session():
session = requests.Session()
session = CacheControl(session, cache=cache)
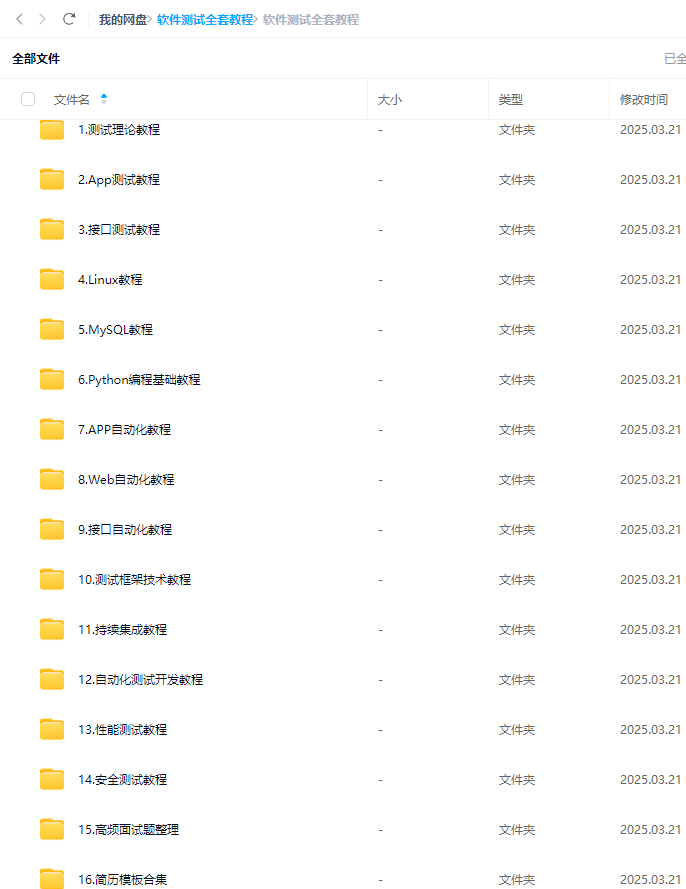
returnsession最后: 下方这份完整的软件测试视频教程已经整理上传完成,需要的朋友们可以自行领取【保证100%免费】
























 892
892

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








