Fox Ciel is playing a mobile puzzle game called "Two Dots". The basic levels are played on a board of size n × m cells, like this:
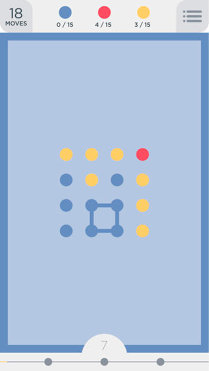
Each cell contains a dot that has some color. We will use different uppercase Latin characters to express different colors.
The key of this game is to find a cycle that contain dots of same color. Consider 4 blue dots on the picture forming a circle as an example. Formally, we call a sequence of dots d1, d2, ..., dk a cycle if and only if it meets the following condition:
- These k dots are different: if i ≠ j then di is different from dj.
- k is at least 4.
- All dots belong to the same color.
- For all 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: di and di + 1 are adjacent. Also, dk and d1 should also be adjacent. Cells x and y are called adjacent if they share an edge.
Determine if there exists a cycle on the field.
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50): the number of rows and columns of the board.
Then n lines follow, each line contains a string consisting of m characters, expressing colors of dots in each line. Each character is an uppercase Latin letter.
Output "Yes" if there exists a cycle, and "No" otherwise.
3 4 AAAA ABCA AAAA
Yes
3 4 AAAA ABCA AADA
No
4 4 YYYR BYBY BBBY BBBY
Yes
7 6 AAAAAB ABBBAB ABAAAB ABABBB ABAAAB ABBBAB AAAAAB
Yes
2 13 ABCDEFGHIJKLM NOPQRSTUVWXYZ
No
In first sample test all 'A' form a cycle.
In second sample there is no such cycle.
The third sample is displayed on the picture above ('Y' = Yellow, 'B' = Blue, 'R' = Red).
这道题很容易理解,就是判断是否存在相同颜色的小球构成环
大致思路就是用DFS,直到找到已经标记过的点,那么就找到一个环了
但是同时还要考虑到搜索深度的问题,因为当深度为2时,根据判断条件会误判为已经找到满足题意环
训练赛的时候一直想不好该怎么处理,快结束的时候就放弃欢脱地去吃饭了~(≧▽≦)/~
饭饱茶足回来,查了下别人的做法,真的很精练啊
改成了自己的代码交了上去
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50+5;
char G[maxn][maxn];
bool idx[maxn][maxn] = {false};
bool dfs(int i, int j, int t) {
if (idx[i][j] == true) return true;
idx[i][j] = true;
if (G[i][j] == G[i-1][j] && t!=2) if (dfs(i-1,j,1)) return true;
if (G[i][j] == G[i+1][j] && t!=1) if (dfs(i+1,j,2)) return true;
if (G[i][j] == G[i][j-1] && t!=4) if (dfs(i,j-1,3)) return true;
if (G[i][j] == G[i][j+1] && t!=3) if (dfs(i,j+1,4)) return true;
return false;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
memset(G, 0, sizeof(G));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> G[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (!idx[i][j])
if (dfs(i, j, 0)) {
cout << "Yes" << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}dfs函数还是很常见的写法,唯一值得一提的是增加了一个参量t用来记录搜索时的方向
这样就可以避免误判了,真是机智(^o^)/





 本文介绍了一种使用深度优先搜索(DFS)解决二维网格中寻找相同颜色点构成的环形路径的方法。通过方向标记避免了深度为2时的误判。
本文介绍了一种使用深度优先搜索(DFS)解决二维网格中寻找相同颜色点构成的环形路径的方法。通过方向标记避免了深度为2时的误判。
















 304
304

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








