消费生产者模式
package ThreadWork.MyThread.lianxi;
class Producer extends Thread{
ComUser c;
public void setC(ComUser c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
while (true){
System.out.println("生产者 "+ ++Demo5.i);
if (Demo5.i==10){
synchronized (c){ c.notify();}
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
class ComUser extends Thread{
Producer p;
public void setP(Producer p) {
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("消费者"+ --Demo5.i);
try {
sleep(400);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (Demo5.i==0){
synchronized (p){ p.notify();}
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class Demo5 {
static int i=10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Producer p=new Producer();
ComUser c=new ComUser();
p.setC(c);
c.setP(p);
c.start();
p.start();
}
}
删除线格式
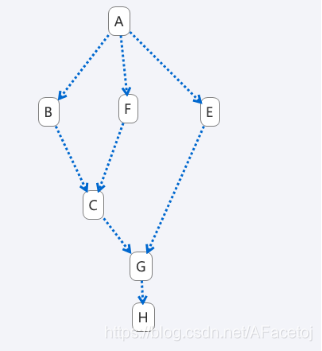
建立并启动线程,要求线程执行完成上图的执行顺序。
package ThreadWork.MyThread.WorkMain;
class A1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (this){
notifyAll();
}
}
}
class B extends Thread{
A1 a;
C c;
public B(A1 a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void setC(C c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (a){
try {
a.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
System.out.println("B");
synchronized (c){c.notify();}
}
}
class C extends Thread{
G g;
public void setG(G g) {
this.g = g;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("C");
synchronized (g){g.notify();}
}
}
class E extends Thread{
A1 a;
G g;
public void setG(G g) {
this.g = g;
}
public E(A1 a) {
this.a = a;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (a){
try {
a.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
System.out.println("E");
synchronized (g){g.notify();}
}
}
class F extends Thread{
A1 a;
C c;
public F(A1 a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void setC(C c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (a){
try {
a.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
System.out.println("F");
synchronized (c){c.notify();}
}
}
class G extends Thread{
H h;
public G(H h) {
this.h = h;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("G");
synchronized (h){h.notify();}
}
}
class H extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("H");
}
}
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A1 a=new A1();
B b=new B(a);
F f=new F(a);
E e=new E(a);
C c=new C();
H h=new H();
G g=new G(h);
c.setG(g);
b.setC(c);
f.setC(c);
e.setG(g);
a.start();
b.start();
f.start();
e.start();
c.start();
g.start();
h.start();
}
}
另外的实现方式(利用死循环)
package ThreadWork.MyThread.Work;
//import Fanshe.Work.R;
//import Fanshe.Work.R;
class H implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
System.out.println("你好");
}
}
class G implements Runnable{
H h;
public G(H h) {
this.h = h;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
synchronized (h){
System.out.println("h 被唤醒");
h.notify();
}
}
}
class E implements Runnable{
G g;
public E(G g) {
this.g = g;
}
static boolean flagE=false;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
flagE=true;
// System.out.println("flagCnew"+C.flagC);
while (true){
if (C.flagC){
synchronized (g){System.out.println("g 被唤醒");g.notify();}
break;
}
}
}
}
class C implements Runnable{
static boolean flagC=false;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
flagC=true;
// System.out.println("flagC"+flagC);
}
}
class B implements Runnable{
C c;
public B(C c) {
this.c = c;
}
static boolean flagB=false;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
flagB=true;
// System.out.println("flagF"+F.flagF);
while (true){
if (F.flagF){
synchronized (c){
System.out.println("c 被唤醒");
c.notify();
}
break;
}
}
// System.out.println("B");
}
}
class F implements Runnable{
static boolean flagF=false;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
flagF=true;
// System.out.println(flagF);
}
}
class A implements Runnable{
B b;
F f;
E e;
public A(B b, F f, E e) {
this.b = b;
this.f = f;
this.e = e;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (b){System.out.println("b 被唤醒");b.notify(); }
synchronized (f){System.out.println("f 被唤醒");f.notify();}
synchronized (e){System.out.println("e 被唤醒");e.notify();}
}
}
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
H h=new H();
G g=new G(h);
C c=new C();
E e=new E(g);
B b=new B(c);
F f=new F();
A a=new A(b,f,e);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(h);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(g);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(c);
Thread thread4 = new Thread(e);
Thread thread5 = new Thread(b);
Thread thread6 = new Thread(f);
Thread thread7 = new Thread(a);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
thread5.start();
thread6.start();
thread7.start();
}
}





















 2024
2024

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








