昨天训练时遇到一道树形dp的题目,今天来给大家分享一下。
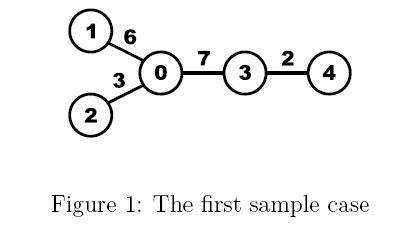
Given a tree, calculate the average distance between two vertices in the tree. For example, the average distance between two vertices in the following tree is (d01 + d02 + d03 + d04 + d12 +d13 +d14 +d23 +d24 +d34)/10 = (6+3+7+9+9+13+15+10+12+2)/10 = 8.6.
Input
On the first line an integer t (1 <= t <= 100): the number of test cases. Then for each test case:
One line with an integer n (2 <= n <= 10 000): the number of nodes in the tree. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
n - 1 lines, each with three integers a (0 <= a < n), b (0 <= b < n) and d (1 <= d <= 1 000). There is an edge between the nodes with numbers a and b of length d. The resulting graph will be a tree.
Output
For each testcase:
One line with the average distance between two vertices. This value should have either an absolute or a relative error of at most 10-6
Sample Input
1
5
0 1 6
0 2 3
0 3 7
3 4 2Sample Output
8.6简单说一下题意,就是给你一棵树,然后你需要计算出两个顶点之间的平均距离,平均距离就是任意两个顶点之间的距离和除以对应的通路数,看题目中的例子即可
在上个博客中我介绍了树的两种遍历更新方式,我们就先来用这种方法做一下,我们需要先记录一下以每个节点为根的子树中节点的个数,我们令dp[x][1]表示以x为根的子树中的所有点到x的距离和,我们令dp[x][2]表示图中所有点到x的距离和,如果对这两个数组的求法还不是很了解的话可以看我上次的博客(常见树形dp递归更新方法),下面直接给出代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=30003;
ll h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
ll dp[N][2];
ll cnt[N];
int n;
void add(int x,int y,int z)
{
e[idx]=y;
w[idx]=z;
ne[idx]=h[x];
h[x]=idx++;
}
void dfs1(int x,int father)
{
cnt[x]=1;
for(int i=h[x];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(j==father) continue;
dfs1(j,x);
cnt[x]+=cnt[j];//递归求出以x为根的子树中节点的个数
dp[x][1]+=dp[j][1]+cnt[j]*w[i];//求出以x为根的子树中的节点到x的距离和
}
}
void dfs2(int x,int father)
{
for(int i=h[x];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(j==father) continue;
dp[j][2]=dp[x][2]+(n-2*cnt[j])*w[i];//递归求出树中全部的点到j的距离和
dfs2(j,x);
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int u,v,l;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
idx=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&l);
add(u,v,l);add(v,u,l);
}
memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt);
memset(dp,0,sizeof dp);
dfs1(0,0);
dp[0][2]=dp[0][1];//以根节点为根的子树就是整棵树,如果忘记赋值就会出错
dfs2(0,0);
long long ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
ans+=dp[i][2];
printf("%.10lf\n",(double)ans/n/(n-1));
}
return 0;
}下面我再给出一种用边的贡献来解决本道题的思路

以题目中给的样例图为例,我们考虑0号点与3号点之间的边,我们计算任意两点之间的距离时,这条边一共被计算了多少次呢?换句话说两点之间的距离包含这条边时,这两个点具有什么关系呢?是不是这两个点分别在这条边的两端?也就是1,2,0三个点其中之一与3,4两个点其中之一的距离中才会包括这条边?所以我们只需要记录以每个点为根的子树中的节点个数即可,最后对(n-cnt[i])*cnt[i]*w取一个和即可,下面是代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=30000;
int h[N],e[N],w[N],ne[N],idx;
ll dp[N],cnt[N];
//dp[i]记录以i为根的子树中的边的边权贡献之和
int n;
void add(int x,int y,int z)
{
e[idx]=y;
w[idx]=z;
ne[idx]=h[x];
h[x]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int x,int father)
{
cnt[x]=1;
for(int i=h[x];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(j==father) continue;
dfs(j,x);
cnt[x]+=cnt[j];
dp[x]+=dp[j]+cnt[j]*(n-cnt[j])*w[i];
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
idx=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
int u,v,z;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&z);
add(u,v,z);add(v,u,z);
}
dfs(0,0);
printf("%.10lf\n",(double)dp[0]/n/(n-1)*2);
}
return 0;
}这道题目给了我一种计算满足某种和关系的全新方法,就是利用边的贡献来解决,由于这种方法我用的比较少,所以现在还没办法做出系统的总结,欢迎大佬补充!







 这篇博客分享了一种利用树形动态规划(DP)解决计算树中任意两点平均距离问题的方法。通过两种不同的递归更新策略,博主详细解释了如何计算每个节点的子树内以及全树中节点到该节点的平均距离,并提供了相应的C++代码实现。此外,还提出了利用边的贡献来简化问题,只计算以每个点为根的子树中的边权重贡献,进一步优化了解决方案。
这篇博客分享了一种利用树形动态规划(DP)解决计算树中任意两点平均距离问题的方法。通过两种不同的递归更新策略,博主详细解释了如何计算每个节点的子树内以及全树中节点到该节点的平均距离,并提供了相应的C++代码实现。此外,还提出了利用边的贡献来简化问题,只计算以每个点为根的子树中的边权重贡献,进一步优化了解决方案。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








