[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start
TimeoutSec=0
StandardOutput=tty
RemainAfterExit=yes
SysVStartPriority=99
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target

- 注:以上方法来自:linux就该这么学作者刘遄老师发的,实测可用,但他发的给与脚本权限文件有误,如下图:所以下面文章内容是修改过的,文章后面有做详细解释:


第二步、rc-local.service服务设置开机自启: :
systemctl enable rc-local.service
(注:如果不确定服务是否启动的:systemctl is-active rc-local.service ——状态是active即启动的,或者直接重启一下亦可:systemctl restart rc-local.service)

第三步、添加启动服务并赋予执行权限:
添加启动服务:vi /etc/rc.local
#!/bin/bash
THIS FILE IS ADDED FOR COMPATIBILITY PURPOSES
It is highly advisable to create own systemd services or udev rules
to run scripts during boot instead of using this file.
In contrast to previous versions due to parallel execution during boot
this script will NOT be run after all other services.
Please note that you must run ‘chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local’ to ensure
that this script will be executed during boot.
touch /var/lock/subsys/local
#下面这条是 要开机启动的命令
echo test >> /test
#可以写很多很多命令 也可以调用脚本
touch /test{1…5}
rm -f /test{2…5}
sh test.sh
#…
执行权限:chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local

有人可能遇到过:在Linux的启动脚本(/etc/rc.local)中添加一些命令,使之开机自动运行,可是添加过后怎么重启脚本中的命令都没有执行,百度后原因是/etc/rc.local没有执行权限,但查看权限也是都有的,所以就很懵逼:
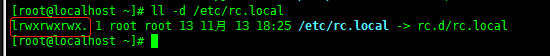
这里需要说明一下:/etc/rc.local 和 /etc/rd.d/rc.local 其实是一个文件:


刚入门的可能看不懂,其实/etc/rc.local是/etc/rc.d/rc.local的软连接,软连接的权限与文件本身实际是没有决定关系的:

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








