- Tree
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-zigzag-path-in-a-binary-tree/
You are given the root of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
-
Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
-
If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
-
Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
-
Repeat the second and third steps until you can’t move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longest ZigZag path contained in that tree.
Example 1:
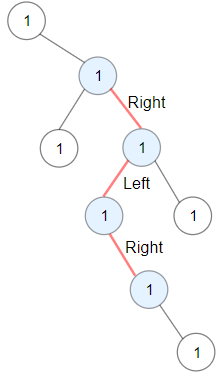
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1,null,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
Example 2:
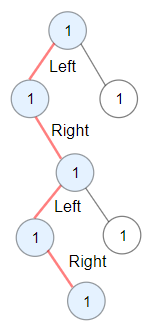
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [ 1 , 5 ∗ 1 0 4 ] [1, 5 * 10^4] [1,5∗104].
-
1 < = N o d e . v a l < = 100 1 <= Node.val <= 100 1<=Node.val<=100
方法一:自己写的。
方法二:别人写的1。
方法三:别人写的2。
方法四:别人写的3。
import com.lun.util.BinaryTree.TreeNode;
public class LongestZigZagPathInABinaryTree {
//方法一:我自己写的
public int longestZigZag(TreeNode root) {
int[] longest = {0};
longestZigZag(root, ‘n’, 0, longest);
return longest[0];
}
//Parameter ‘relationship’ means relationship between parent and current node.
//‘n’ means no parent, specially for root node.
//‘l’ means current node is parent’s left node.
//‘r’ means current node is parent’s right node.
private void longestZigZag(TreeNode node, char relationship, int count, int[] longest) {
if(node == null) return;
//when node is a leaf.
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
longest[0] = Math.max(longest[0], count);
return;
}
if(node.left != null) {
int temp = count;
if(relationship == ‘l’) {
longest[0] = Math.max(longest[0], count);
temp = 0;
}
longestZigZag(node.left, ‘l’, temp + 1, longest);
}
if(node.right != null) {
int temp = count;
if(relationship == ‘r’) {
longest[0] = Math.max(longest[0], count);
temp = 0;
}
longestZigZag(node.right, ‘r’, temp + 1, longest);
}
}
//方法二:别人写的1
public int longestZigZag2(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root)[2];
}
/**
-
Recursive return [left, right, result], where:
-
left is the maximum length in direction of root.left
-
right is the maximum length in direction of root.right
-
result is the maximum length in the whole sub tree.
-
@param root
-
@return
*/
private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return new int[]{-1, -1, -1};
int[] left = dfs(root.left), right = dfs(root.right);
int res = Math.max(Math.max(left[1], right[0]) + 1, Math.max(left[2], right[2]));
return new int[]{left[1] + 1, right[0] + 1, res};
}
//方法三:别人写的2
public int longestZigZag3(TreeNode root) {
int[] maxStep = {0};
dfs(root, true, 0, maxStep);
dfs(root, false, 0, maxStep);
return maxStep[0];
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, boolean isLeft, int step, int[] maxStep) {
if (root == null) return;
maxStep[0] = Math.max(maxStep[0], step); // update max step sofar
if (isLeft) {
dfs(root.left, false, step + 1, maxStep); // keep going from root to left
dfs(root.right, true, 1, maxStep); // restart going from root to right
} else {
dfs(root.right, true, step + 1, maxStep); // keep going from root to right
dfs(root.left, false, 1, maxStep); // restart going from root to left
}
}
//方法四:别人写的3
public int longestZigZag4(TreeNode root) {
int[] result = {0};
dfs(root, true, result);
return result[0];
}
public int dfs(TreeNode node, boolean isLeft, int[] result){
if(node == null){
return 0;
}
//try start here
int l = dfs(node.left, false, result);
int r = dfs(node.right, true, result);
result[0] = Math.max(result[0], l);
result[0] = Math.max(result[0], r);
//return sum for parent
return 1 + (isLeft ? l : r);
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








