所以比较合适的方式是通过添加一个异步线程池异步刷新数据,在 Guava Cache 中实现方案是重写 CacheLoader 的 reload 方法。
private static final LoadingCache<String, String> ASYNC_CACHE = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.build(
CacheLoader.asyncReloading(new CacheLoader<String, String>() {
@Override
public String load(String key) {
return key;
}
@Override
public ListenableFuture reload(String key, String oldValue) throws Exception {
return super.reload(key, oldValue);
}
}, new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>()))
);
LocalCache 源码分析
先整体看下 Cache 的类结构,下面的这些子类表示了不同的创建方式本质还都是 LocalCache
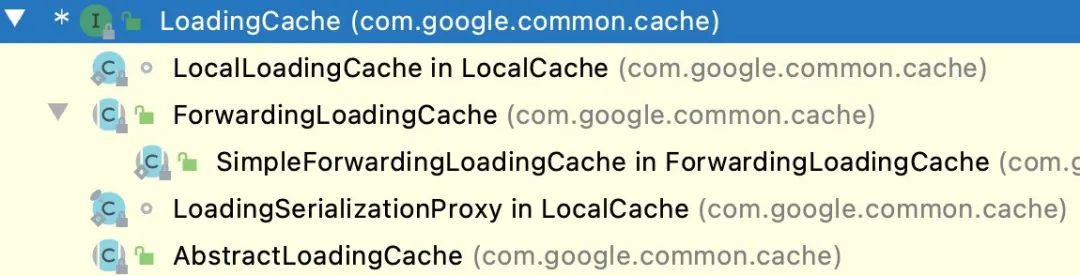
【Cache 类图】
核心代码都在 LocalCache 这个文件中,并且通过这个继承关系可以看出 Guava Cache 的本质就是 ConcurrentMap。

【LocalCache 继承与实现】
在看源码之前先理一下流程,先理清思路。如果想直接看源码理解流程可以先跳过这张图 ~
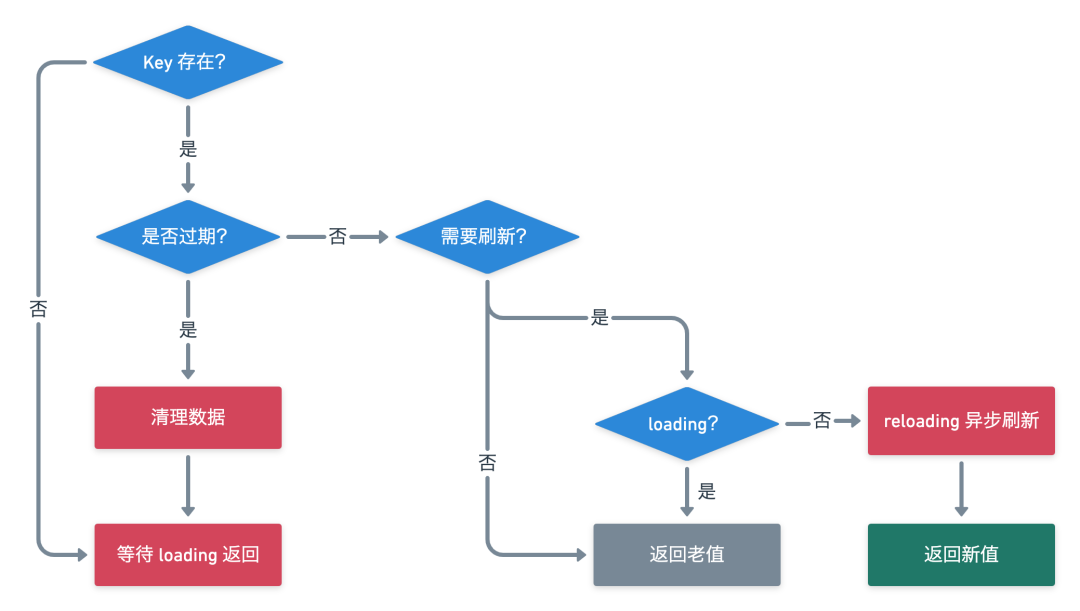
【 get 缓存数据流程图】
这里核心理一下 Get 的流程,put 阶段比较简单就不做分析了。
▐ LocalCache#get
V get(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
int hash = hash(checkNotNull(key));
// 根据 hash 获取对应的 segment 然后从 segment 获取具体值
return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash, loader);
}
▐ Segment#get
V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(key);
checkNotNull(loader);
try {
// count 表示在这个 segment 中存活的项目个数
if (count != 0) {
// 获取 segment 中的元素 (ReferenceEntry) 包含正在 load 的数据
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getEntry(key, hash);
if (e != null) {
long now = map.ticker.read();
// 获取缓存值,如果是 load,invalid,expired 返回 null,同时检查是否过期了,过期移除并返回 null
V value = getLiveValue(e, now);
if (value != null) {
// 记录访问时间
recordRead(e, now);
// 记录缓存命中一次
statsCounter.recordHits(1);
// 刷新缓存并返回缓存值 ,后面展开
return scheduleRefresh(e, key, hash, value, now, loader);
}
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
// 如果在 loading 等着 ,后面展开
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueRefere








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 5647
5647

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








