-
100~199:指示信息,表示请求已接收,继续处理
-
200~299:请求成功,表示请求已被成功接收、理解
-
300~399:重定向,要完成请求必须进行更进一步的操作
-
400~499:客户端错误,请求有语法错误或请求无法实现
-
500~599:服务器端错误,服务器未能实现合法的请求
一、OKHttp请求流程
OKHttp内部的大致请求流程图如下所示:
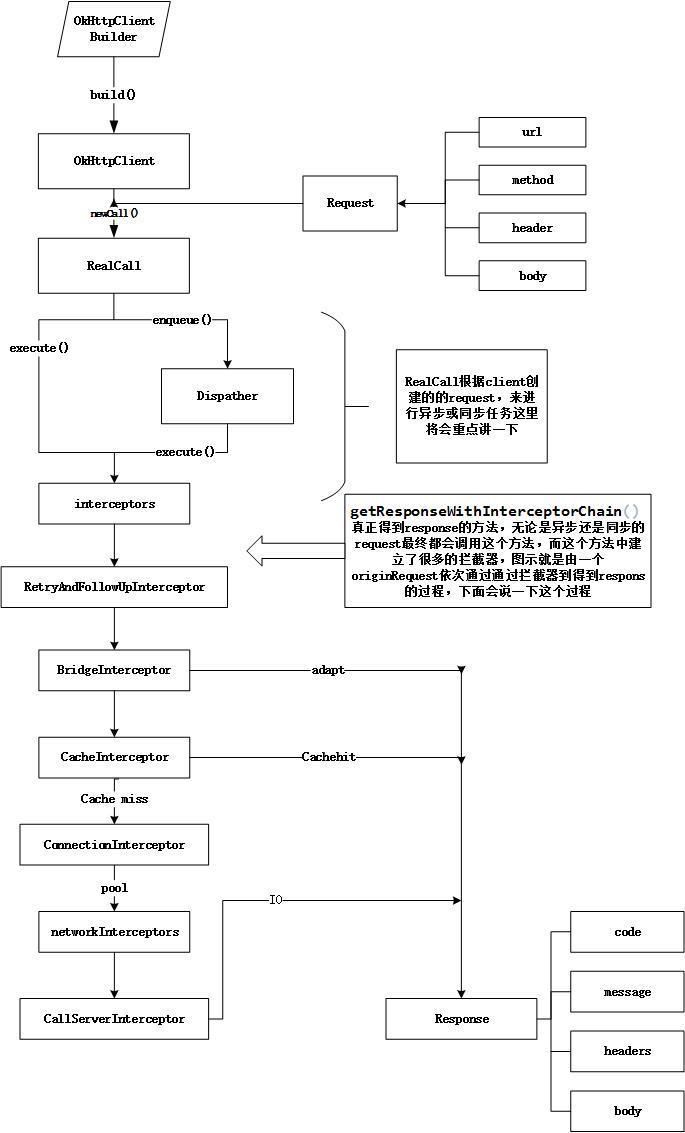
如下为使用OKHttp进行Get请求的步骤:
//1.新建OKHttpClient客户端
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
//新建一个Request对象
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.build();
//2.Response为OKHttp中的响应
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
复制代码
1.新建OKHttpClient客户端
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
public OkHttpClient() {
this(new Builder());
}
OkHttpClient(Builder builder) {
....
}
复制代码
可以看到,OkHttpClient使用了建造者模式,Builder里面的可配置参数如下:
public static final class Builder {
Dispatcher dispatcher;// 分发器
@Nullable Proxy proxy;
List<Protocol> protocols;
List<ConnectionSpec> connectionSpecs;// 传输层版本和连接协议
final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();// 拦截器
final List<Interceptor> networkInterceptors = new ArrayList<>();
EventListener.Factory eventListenerFactory;
ProxySelector proxySelector;
CookieJar cookieJar;
@Nullable Cache cache;
@Nullable InternalCache internalCache;// 内部缓存
SocketFactory socketFactory;
@Nullable SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory;// 安全套接层socket 工厂,用于HTTPS
@Nullable CertificateChainCleaner certificateChainCleaner;// 验证确认响应证书 适用 HTTPS 请求连接的主机名。
HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier;// 验证确认响应证书 适用 HTTPS 请求连接的主机名。
CertificatePinner certificatePinner;// 证书锁定,使用CertificatePinner来约束哪些认证机构被信任。
Authenticator proxyAuthenticator;// 代理身份验证
Authenticator authenticator;// 身份验证
ConnectionPool connectionPool;// 连接池
Dns dns;
boolean followSslRedirects; // 安全套接层重定向
boolean followRedirects;// 本地重定向
boolean retryOnConnectionFailure;// 重试连接失败
int callTimeout;
int connectTimeout;
int readTimeout;
int writeTimeout;
int pingInterval;
// 这里是默认配置的构建参数
public Builder() {
dispatcher = new Dispatcher();
protocols = DEFAULT_PROTOCOLS;
connectionSpecs = DEFAULT_CONNECTION_SPECS;
...
}
// 这里传入自己配置的构建参数
Builder(OkHttpClient okHttpClient) {
this.dispatcher = okHttpClient.dispatcher;
this.proxy = okHttpClient.proxy;
this.protocols = okHttpClient.protocols;
this.connectionSpecs = okHttpClient.connectionSpecs;
this.interceptors.addAll(okHttpClient.interceptors);
this.networkInterceptors.addAll(okHttpClient.networkInterceptors);
...
}
复制代码
2.同步请求流程
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
/**
* Prepares the {@code request} to be executed at some point in the future.
*/
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false /* for web socket */);
}
// RealCall为真正的请求执行者
static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
// Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener.
RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
}
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
// 每个Call只能执行一次
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
timeout.enter();
eventListener.callStart(this);
try {
// 通知dispatcher已经进入执行状态
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
// 通过一系列的拦截器请求处理和响应处理得到最终的返回结果
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
e = timeoutExit(e);
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
} finally {
// 通知 dispatcher 自己已经执行完毕
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
// 在配置 OkHttpClient 时设置的 interceptors;
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
// 负责失败重试以及重定向
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
// 请求时,对必要的Header进行一些添加,接收响应时,移除必要的Header
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
// 负责读取缓存直接返回、更新缓存
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
// 负责和服务器建立连接
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
// 配置 OkHttpClient 时设置的 networkInterceptors
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
// 负责向服务器发送请求数据、从服务器读取响应数据
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
// 使用责任链模式开启链式调用
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
// StreamAllocation 对象,它相当于一个管理类,维护了服务器连接、并发流
// 和请求之间的关系,该类还会初始化一个 Socket 连接对象,获取输入/输出流对象。
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
...
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
// 实例化下一个拦截器对应的RealIterceptorChain对象
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec,
connection, index + 1, request, call, eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout);
// 得到当前的拦截器
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
// 调用当前拦截器的intercept()方法,并将下一个拦截器的RealIterceptorChain对象传递下去,最后得到响应
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
...
return response;
}
复制代码
3.异步请求的流程
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt")
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
...
}
void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
synchronized (this) {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
promoteAndExecute();
}
// 正在准备中的异步请求队列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 运行中的异步请求
private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 同步请求
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Promotes eligible calls from {@link #readyAsyncCalls} to {@link #runningAsyncCalls} and runs
// them on the executor service. Must not be called with synchronization because executing calls
// can call into user code.
private boolean promoteAndExecute() {
assert (!Thread.holdsLock(this));
List<AsyncCall> executableCalls = new ArrayList<>();
boolean isRunning;
synchronized (this) {
for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = i.next();
// 如果其中的runningAsynCalls不满,且call占用的host小于最大数量,则将call加入到runningAsyncCalls中执行,
// 同时利用线程池执行call;否者将call加入到readyAsyncCalls中。
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) break; // Max capacity.
if (runningCallsForHost(asyncCall) >= maxRequestsPerHost) continue; // Host max capacity.
i.remove();
executableCalls.add(asyncCall);
runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall);
}
isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0;
}
for (int i = 0, size = executableCalls.size(); i < size; i++) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = executableCalls.get(i);
asyncCall.executeOn(executorService());
}
return isRunning;
}
复制代码
最后,我们在看看AsynCall的代码。
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {
private final Callback responseCallback;
AsyncCall(Callback responseCallback) {
super("OkHttp %s", redactedUrl());
this.responseCallback = responseCallback;
}
String host() {
return originalRequest.url().host();
}
Request request() {
return originalRequest;
}
RealCall get() {
return RealCall.this;
}
/**
* Attempt to enqueue this async call on {@code executorService}. This will attempt to clean up
* if the executor has been shut down by reporting the call as failed.
*/
void executeOn(ExecutorService executorService) {
assert (!Thread.holdsLock(client.dispatcher()));
boolean success = false;
try {
executorService.execute(this);
success = true;
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
InterruptedIOException ioException = new InterruptedIOException("executor rejected");
ioException.initCause(e);
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, ioException);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, ioException);
} finally {
if (!success) {
client.dispatcher().finished(this); // This call is no longer running!
}
}
}
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
timeout.enter();
try {
// 跟同步执行一样,最后都会调用到这里
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e = timeoutExit(e);
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
复制代码
从上面的源码可以知道,拦截链的处理OKHttp帮我们默认做了五步拦截处理,其中RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor、BridgeInterceptor、CallServerInterceptor内部的源码很简洁易懂,此处不再多说,下面将对OKHttp最为核心的两部分:缓存处理和连接处理(连接池)进行讲解。
二、网络请求缓存处理之CacheInterceptor
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
// 根据request得到cache中缓存的response
Response cacheCandidate = cache != null
? cache.get(chain.request())
: null;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
// request判断缓存的策略,是否要使用了网络,缓存或两者都使用
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
if (cache != null) {
cache.trackResponse(strategy);
}
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build();
}
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
// 调用下一个拦截器,决定从网络上来得到response
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
// 如果本地已经存在cacheResponse,那么让它和网络得到的networkResponse做比较,决定是否来更新缓存的cacheResponse
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Response response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
networkResponse.body().close();
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache.trackConditionalCacheHit();
cache.update(cacheResponse, response);
return response;
} else {
closeQuietly(cacheResponse.body());
}
}
Response response = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
if (cache != null) {
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
// 缓存未经缓存过的response
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method())) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response;
}
复制代码
缓存拦截器会根据请求的信息和缓存的响应的信息来判断是否存在缓存可用,如果有可以使用的缓存,那么就返回该缓存给用户,否则就继续使用责任链模式来从服务器中获取响应。当获取到响应的时候,又会把响应缓存到磁盘上面。
三、ConnectInterceptor之连接池
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
Request request = realChain.request();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
// We need the network to satisfy this request. Possibly for validating a conditional GET.
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !request.method().equals("GET");
// HttpCodec是对 HTTP 协议操作的抽象,有两个实现:Http1Codec和Http2Codec,顾名思义,它们分别对应 HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 版本的实现。在这个方法的内部实现连接池的复用处理
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
// Returns a connection to host a new stream. This // prefers the existing connection if it exists,
// then the pool, finally building a new connection.
// 调用 streamAllocation 的 newStream() 方法的时候,最终会经过一系列
// 的判断到达 StreamAllocation 中的 findConnection() 方法
private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException {
...
// Attempt to use an already-allocated connection. We need to be careful here because our
// already-allocated connection may have been restricted from creating new streams.
// 尝试使用已分配的连接,已经分配的连接可能已经被限制创建新的流
releasedConnection = this.connection;
// 释放当前连接的资源,如果该连接已经被限制创建新的流,就返回一个Socket以关闭连接
toClose = releaseIfNoNewStreams();
if (this.connection != null) {
// We had an already-allocated connection and it's good.
result = this.connection;
releasedConnection = null;
}
if (!reportedAcquired) {
// If the connection was never reported acquired, don't report it as released!
// 如果该连接从未被标记为获得,不要标记为发布状态,reportedAcquired 通过 acquire() 方法修改
releasedConnection = null;
}
if (result == null) {
// Attempt to get a connection from the pool.
// 尝试供连接池中获取一个连接
Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, null);
if (connection != null) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = connection;
} else {
selectedRoute = route;
}
}
}
// 关闭连接
closeQuietly(toClose);
if (releasedConnection != null) {
eventListener.connectionReleased(call, releasedConnection);
}
if (foundPooledConnection) {
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result);
}
if (result != null) {
// If we found an already-allocated or pooled connection, we're done.
// 如果已经从连接池中获取到了一个连接,就将其返回
return result;
}
// If we need a route selection, make one. This is a blocking operation.
boolean newRouteSelection = false;
if (selectedRoute == null && (routeSelection == null || !routeSelection.hasNext())) {
newRouteSelection = true;
routeSelection = routeSelector.next();
}
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (canceled) throw new IOException("Canceled");
if (newRouteSelection) {
// Now that we have a set of IP addresses, make another attempt at getting a connection from
// the pool. This could match due to connection coalescing.
// 根据一系列的 IP地址从连接池中获取一个链接
List<Route> routes = routeSelection.getAll();
for (int i = 0, size = routes.size(); i < size;i++) {
Route route = routes.get(i);
// 从连接池中获取一个连接
Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, route);
if (connection != null) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = connection;
this.route = route;
break;
}
}
}
if (!foundPooledConnection) {
if (selectedRoute == null) {
selectedRoute = routeSelection.next();
}
// Create a connection and assign it to this allocation immediately. This makes it possible
// for an asynchronous cancel() to interrupt the handshake we're about to do.
// 在连接池中如果没有该连接,则创建一个新的连接,并将其分配,这样我们就可以在握手之前进行终端
route = selectedRoute;
refusedStreamCount = 0;
result = new RealConnection(connectionPool, selectedRoute);
acquire(result, false);
}
}
// If we found a pooled connection on the 2nd time around, we're done.
if (foundPooledConnection) {
// 如果我们在第二次的时候发现了一个池连接,那么我们就将其返回
eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result);
return result;
}
// Do TCP + TLS handshakes. This is a blocking operation.
// 进行 TCP 和 TLS 握手
result.connect(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, pingIntervalMillis,
connectionRetryEnabled, call, eventListener);
routeDatabase().connected(result.route());
Socket socket = null;
synchronized (connectionPool) {
reportedAcquired = true;
// Pool the connection.
// 将该连接放进连接池中
Internal.instance.put(connectionPool, result);
// If another multiplexed connection to the same address was created concurrently, then























 757
757

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








