===================================================================
EmployeeDao类:
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
@Autowired //按照类型注入
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//保存员工信息到数据库
public void save( Employee employee)
{
String sql=“insert employee values(?,?,?,?,?)”;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,employee.getId(),employee.getName(),employee.getDepartment(),
employee.getEamil(),employee.getGender());
}
//查询并返回对应员工信息
public Employee exist(Employee employee)
{
String sql=“select * from employee where name=? and id= ?”;
try{
Employee employee1 = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Employee.class), employee.getName(), employee.getId());
return employee1;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return null;
}
}
//删除某个员工的信息
public void delete(Employee employee)
{
String sql=“delete from employee where id=?”;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,employee.getId());
}
//返回所有员工的信息
public List getAllEmployees()
{
String sql=“select* from employee”;
List list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Employee.class));
return list;
}
}
==========================================================================
employee类:
@Component
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String department;
private String eamil;
private Integer gender;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(String department) {
this.department = department;
}
public String getEamil() {
return eamil;
}
public void setEamil(String eamil) {
this.eamil = eamil;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return “Employee{” +
“id=” + id +
“, name='” + name + ‘’’ +
“, department='” + department + ‘’’ +
“, eamil='” + eamil + ‘’’ +
“, gender=” + gender +
‘}’;
}
}
============================================================================
访问index.jsp---->直接发送/emps请求----->控制器查询所有员工-------->放在请求域中-------->转发到list页面进行展示
index.jsp:
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%–访问页面就直接展示员工列表页面–%>
<jsp:forward page=“/emps”></jsp:forward>
EmployeeController类:
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@RequestMapping(“/emps”)
public String getEmps(Model model)
{
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
for(Employee employee:all)
System.out.println(employee);
System.out.println(“当前方法调用一次”);
model.addAttribute(“employees”,all);
return “list”;
}
}
list.jsp:
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“c” uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” %>
<%–cellpadding标签属性:设定单元边沿与单元内容之间的间距–%>
<%–cellspacing 标签属性:设定单元格之间的间距–%>
<%–
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String department;
private String eamil;
private String gender;–%>
员工ID 员工姓名 员工部门 员工邮箱 员工性别 修改 删除<c:forEach items=“${employees}” var=“emp”>
<%-- 取出容器中的值–%>
${emp.id} ${emp.name} ${emp.department} ${emp.eamil} ${emp.gender==0?"女":"男"} 修改 删除</c:forEach>

===================================================================

EmployeeController类新增方法:
/从数据库中查询出所有部门信息/
@RequestMapping(“/toAddPage”)
public String toAddPage(Model model)
{
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
List departName = new LinkedList();
for(Employee employee:all)
{
departName.add(employee.getDepartment());
}
model.addAttribute(“departments”,departName);
return “addPage”;
}
addPage.jsp
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“c” uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” %>
添加员工
员工id:
姓名:
邮箱:
性别: 男
女
请选择员工所在部门:
<c:forEach items=“${departments}” var=“dept”>
${dept}</c:forEach>


需要在最上面导入Spring提供的标签库
<%@ taglib prefix=“form” uri=“http://www.springframework.org/tags/form” %>
好处
通过SpringMVC的表单标签可以实现将模型数据中的属性和HTML表单元素相绑定
以实现表单数据更便捷编辑和表单值的回显
spring标签库,替换上面的html写的form表单
form:form
<%–
path就是原来html----input标签里面的name项,即提交得到的key
path的作用:
1.当做原生的name项
2.自动回显隐含模型中某个对象对应的这个属性的值
–%>
员工id:<form:input path=“id”/>
姓名:<form:input path=“name”/>
邮箱:<form:input path=“eamil”/>
性别:
男:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“1”/>
女:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“0”/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<%–items:指定要遍历的集合,自动遍历
如果遍历出来的是一个自定义对象
itemLabel=“属性名”: 指定遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为optiob标签体的值—>在页面显示要选择的选项里面显示的内容
itemValue=“属性名”:指定刚才遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为要提交的value值–%>
<form:select path=“department” items=“${departments}”/>
<%–原生的html标签和spring标签混合使用–%>
</form:form>
注意:SpringMVC认为,表单数据中的每一项最终都是要回显的
path指定的是一个属性,这个属性是从隐含模型(请求域)中取出的某个对象中的属性
path指定的每一个属性,请求域中必须有一个对象,拥有这个属性
这个对象就是请求域中的command的值,没有就报错,错误如下:
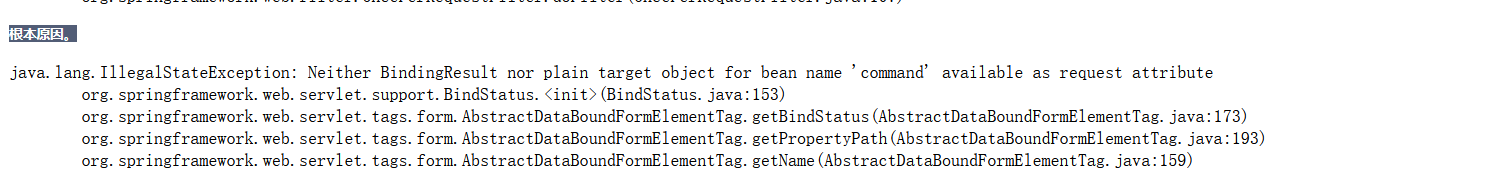
在隐含模型中放入command对象
EmployeeController类:
/从数据库中查询出所有部门信息/
@RequestMapping(“/toAddPage”)
public String toAddPage(Model model)
{
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
List departName = new LinkedList();
for(Employee employee:all)
{
departName.add(employee.getDepartment());
}
model.addAttribute(“departments”,departName);
/在隐含模型中放入一个command对象/
model.addAttribute(“command”,new Employee());
return “addPage”;
}
addPages.jsp:
form:form
<%–
path就是原来html----input标签里面的name项,即提交得到的key
path的作用:
1.当做原生的name项
2.自动回显隐含模型中某个对象对应的这个属性的值
–%>
员工id:<form:input path=“id”/>
姓名:<form:input path=“name”/>
邮箱:<form:input path=“eamil”/>
性别:
男:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“1”/>
女:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“0”/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<%–items:指定要遍历的集合,自动遍历
如果遍历出来的是一个自定义对象
itemLabel=“属性名”: 指定遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为optiob标签体的值—>在页面显示要选择的选项里面显示的内容
itemValue=“属性名”:指定刚才遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为要提交的value值–%>
<form:select path=“department” items=“${departments}”/>
<%–原生的html标签和spring标签混合使用–%>
</form:form>

以前我们表单标签会从请求域中获取一个command对象,把这个对象中每一个属性对应的显示在页面上
可以告诉SpringMVC不要去取command的值了,我放了一个modelAttribute指定的值,取对象用的key就使用我modelAttribute指定的
演示:
EmployeeController类:
/从数据库中查询出所有部门信息/
@RequestMapping(“/toAddPage”)
public String toAddPage(Model model)
{
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
List departName = new LinkedList();
for(Employee employee:all)
{
departName.add(employee.getDepartment());
}
model.addAttribute(“departments”,departName);
/在隐含模型中放入一个employee对象/
model.addAttribute(“employee”,new Employee(null,“超级大忽悠”,“空军部”,“@307667”,1));
return “addPage”;
}
addPage.jsp
<form:form modelAttribute=“employee”>
<%–
path就是原来html----input标签里面的name项,即提交得到的key
path的作用:
1.当做原生的name项
2.自动回显隐含模型中某个对象对应的这个属性的值
–%>
员工id:<form:input path=“id”/>
姓名:<form:input path=“name”/>
邮箱:<form:input path=“eamil”/>
性别:
男:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“1”/>
女:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“0”/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<%–items:指定要遍历的集合,自动遍历
如果遍历出来的是一个自定义对象
itemLabel=“属性名”: 指定遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为optiob标签体的值—>在页面显示要选择的选项里面显示的内容
itemValue=“属性名”:指定刚才遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为要提交的value值–%>
<form:select path=“department” items=“${departments}”/>
<%–原生的html标签和spring标签混合使用–%>
</form:form>

以后jsp页面什么form表单的action提交路径,a标签的herf属性都写绝对路径,因此需要先获取项目根路径
//将当前项目的根路径存储再pageContext域中
<%pageContext.setAttribute(“ctp”,request.getContextPath());%>
<form:form modelAttribute=“employee” action=“${ctp}/emp” method=“post”>
处理表单提交请求的方法
//只接收Post请求
@RequestMapping(value = “/emp”,method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addEmp(Employee employee)//这里会自动赋值
{
System.out.println(“要添加的员工信息:”+employee);
employeeDao.save(employee);
//返回列表页面,直接重定向到查询所有员工的请求
return “redirect:/emps”;
}



===================================================================
注意:被@ModelAttribute注解的方法会在所有的controller方法执行之前执行,即每一个controller方法执行之前,都会执行该方法
被@ModelAttribute注解的方法和目标controller方法用的都是一套的resolve方法,因此目标方法里面能写什么,获取什么,注解方法里面也能写和获取对应的内容

在EmployeeDao类中新增一个按照id查找对应员工的方法:
//按照员工的id查找对应的员工
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id)
{
String sql=“select * from employee where id= ?”;
try{
Employee employee1 = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Employee.class),id);
return employee1;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return null;
}
}
EmployeeController类:按照id查询对应的员工
@RequestMapping(“/emp/{id}”)
public String getEmp(@PathVariable(“id”)Integer id,Model model)
{
//1.按照对应id去数据库中查出对应的员工信息
Employee emp = employeeDao.getEmpById(id);
//2.放在隐含模型中
model.addAttribute(“EditEmp”,emp);
//3.全部的部门信息放到隐含模型中,是为了可以在下拉框中修改部门信息
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
List departName = new LinkedList();
for(Employee employee:all)
{
departName.add(employee.getDepartment());
}
model.addAttribute(“departments”,departName);
return “edit”;
}
UpdateEmp方法:修改员工的方法,只有put请求才会接收
modelAttributes方法:取出数据库中的对应对象,在该对象的基础上进行修改,而不是新建一个对象
/*虽然上面也有/emp/{id}的请求路径方式,但是没有限制请求方式,而下面我们限制了请求方式
优先精确匹配*/
/修改员工的方法,只有put请求才会接收/
@RequestMapping(value = “/emp/{id}”,method = RequestMethod.PUT)
//在从数据库取出来的对象数据的基础上进行修改
public String UpdateEmp(@ModelAttribute(“employee”) Employee employee)
{
System.out.println(“要修改的员工:”+employee);
//调用数据库中修改对象数据的方法,员工的id是不变的
employeeDao.UpdateEmp(employee);
return “redirect:/emps”;
}
@ModelAttribute
/从请求参数中拿到id/
public void modelAttributes(@RequestParam(value = “id”,required = false)Integer id,Model model)
{
if(id!=null)
{
Employee emp = employeeDao.getEmpById(id);
model.addAttribute(“employee”,emp);
}
System.out.println(“提前运行的方法调用了”);
}
edit.jsp
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“form” uri=“http://www.springframework.org/tags/form” %>
员工信息修改
<% pageContext.setAttribute(“ctp”,request.getContextPath());%>
<%–modelAttribute:这个表单的所有内容显示绑定的是请求域中EditEmp的值–%>
<form:form action=“ c t p / e m p / {ctp}/emp/ ctp/emp/{EditEmp.id}”
modelAttribute=“EditEmp”
method=“post”>
<%–put---->对应Rest风格的更新请求,这里hiiden是为了不在页面上显示处理,隐藏数据–%>
<%–员工id不能修改,可以采用隐藏数据的模式,但是不安全–%>
姓名:<form:input path=“name”/>
邮箱:<form:input path=“eamil”/>
性别:
男:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“1”/>
女:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“0”/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<form:select path=“department” items=“${departments}”/>
</form:form>




这里逻辑有一个小bug,部门的种类应该单独创建一个类,而不是按照扫描当前数据库所有员工获取所有的部门种类,这里懒的改了
=====================================================================
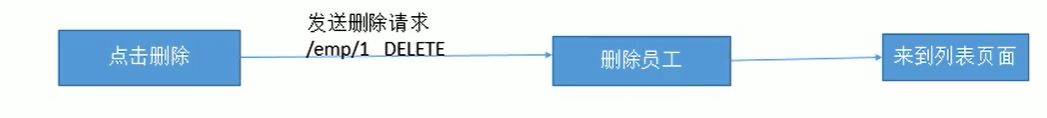
list.jsp:
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“c” uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute(“ctp”,request.getContextPath());%>
<%–cellpadding标签属性:设定单元边沿与单元内容之间的间距–%>
<%–cellspacing 标签属性:设定单元格之间的间距–%>
<c:forEach items=“${employees}” var=“emp”>
<%-- 取出容器中的值–%>
${emp.id} ${emp.name} ${emp.department} ${emp.eamil} ${emp.gender==0?"女":"男"} 修改</c:forEach>
deleteEmp方法:负责删除员工
//删除方法
@RequestMapping(value = “/emp/{id}”,method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteEmp(@PathVariable(“id”) Integer id)
{
employeeDao.delete(id);
return “redirect:/emps”;
}

=======================================================================

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version=“2.4”
xmlns=“http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee”
xmlns:xsi=“http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”
xsi:schemaLocation=“http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd”>
DispatcherServlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:SpringMVC.xml
1
DispatcherServlet
/
CharacterEncodingFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter
encoding
UTF-8
forceEncoding
true
CharacterEncodingFilter
/*
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
/*
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%–访问页面就直接展示员工列表页面–%>
<jsp:forward page=“/emps”></jsp:forward>
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“c” uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“form” uri=“http://www.springframework.org/tags/form” %>
<%pageContext.setAttribute(“ctp”,request.getContextPath());%>
<form:form modelAttribute=“employee” action=“${ctp}/emp” method=“post”>
<%–
path就是原来html----input标签里面的name项,即提交得到的key
path的作用:
1.当做原生的name项
2.自动回显隐含模型中某个对象对应的这个属性的值
–%>
员工id:<form:input path=“id”/>
姓名:<form:input path=“name”/>
邮箱:<form:input path=“eamil”/>
性别:
男:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“1”/>
女:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“0”/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<%–items:指定要遍历的集合,自动遍历
如果遍历出来的是一个自定义对象
itemLabel=“属性名”: 指定遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为optiob标签体的值—>在页面显示要选择的选项里面显示的内容
itemValue=“属性名”:指定刚才遍历出来的这个对象的哪个属性是作为要提交的value值–%>
<form:select path=“department” items=“${departments}”/>
</form:form>
<%–原生的html标签和spring标签混合使用–%>
<%–
添加员工
员工id:
姓名:
邮箱:
性别: 男
女
请选择员工所在部门:
<c:forEach items=“${departments}” var=“dept”>
${dept}</c:forEach>
--%><%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“form” uri=“http://www.springframework.org/tags/form” %>
员工信息修改
<% pageContext.setAttribute(“ctp”,request.getContextPath());%>
<%–modelAttribute:这个表单的所有内容显示绑定的是请求域中EditEmp的值–%>
<form:form action=“ c t p / e m p / {ctp}/emp/ ctp/emp/{EditEmp.id}”
modelAttribute=“EditEmp”
method=“post”>
<%–put---->对应Rest风格的更新请求,这里hiiden是为了不在页面上显示处理,隐藏数据–%>
<%–员工id不能修改,可以采用隐藏数据的模式,但是不安全–%>
姓名:<form:input path=“name”/>
邮箱:<form:input path=“eamil”/>
性别:
男:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“1”/>
女:<form:radiobutton path=“gender” value=“0”/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<form:select path=“department” items=“${departments}”/>
</form:form>
<%@ page contentType=“text/html;charset=UTF-8” language=“java” %>
<%@ taglib prefix=“c” uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute(“ctp”,request.getContextPath());%>
<%–cellpadding标签属性:设定单元边沿与单元内容之间的间距–%>
<%–cellspacing 标签属性:设定单元格之间的间距–%>
<c:forEach items=“${employees}” var=“emp”>
<%-- 取出容器中的值–%>
${emp.id} ${emp.name} ${emp.department} ${emp.eamil} ${emp.gender==0?"女":"男"} 修改</c:forEach>
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tx
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=xxxxx
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans”
xmlns:context=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
xmlns:mvc=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc”
xmlns:xsi=“http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<context:component-scan base-package=“com”/>
<context:property-placeholder location=“classpath:jdbc.properties”/>
package com.Controller;
import com.Dao.EmployeeDao;
import com.POJO.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeDao employeeDao;
/从数据库中查询出所有员工信息/
@RequestMapping(“/emps”)
public String getEmps(Model model)
{
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
model.addAttribute(“employees”,all);
System.out.println(“得到所有的员工”);
return “list”;
}
/从数据库中查询出所有部门信息/
@RequestMapping(“/toAddPage”)
public String toAddPage(Model model)
{
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
List departName = new LinkedList();
for(Employee employee:all)
{
departName.add(employee.getDepartment());
}
model.addAttribute(“departments”,departName);
/在隐含模型中放入一个employee对象/
model.addAttribute(“employee”,new Employee(null,“超级大忽悠”,“空军部”,“@307667”,1));
return “addPage”;
}
//只接收Post请求
@RequestMapping(value = “/emp”,method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addEmp(Employee employee)//这里会自动赋值
{
System.out.println(“要添加的员工信息:”+employee);
employeeDao.save(employee);
//返回列表页面,直接重定向到查询所有员工的请求
return “redirect:/emps”;
}
@RequestMapping(“/emp/{id}”)
public String getEmp(@PathVariable(“id”)Integer id,Model model)
{
//1.按照对应id去数据库中查出对应的员工信息
Employee emp = employeeDao.getEmpById(id);
//2.放在隐含模型中
model.addAttribute(“EditEmp”,emp);
//3.全部的部门信息放到隐含模型中
List all = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
List departName = new LinkedList();
for(Employee employee:all)
{
departName.add(employee.getDepartment());
}
model.addAttribute(“departments”,departName);
return “edit”;
}
/*虽然上面也有/emp/{id}的请求路径方式,但是没有限制请求方式,而下面我们限制了请求方式
优先精确匹配*/
/修改员工的方法,只有put请求才会接收/
@RequestMapping(value = “/emp/{id}”,method = RequestMethod.PUT)
//在从数据库取出来的对象数据的基础上进行修改
public String UpdateEmp(@ModelAttribute(“employee”) Employee employee)
{
System.out.println(“要修改的员工:”+employee);
//调用数据库中修改对象数据的方法,员工的id是不变的
employeeDao.UpdateEmp(employee);
return “redirect:/emps”;
}
@ModelAttribute
/从请求参数中拿到id/
public void modelAttributes(@RequestParam(value = “id”,required = false)Integer id,Model model)
{
if(id!=null)
{
Employee emp = employeeDao.getEmpById(id);
model.addAttribute(“employee”,emp);
}
System.out.println(“提前运行的方法调用了”);
}
//删除方法
@RequestMapping(value = “/emp/{id}”,method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteEmp(@PathVariable(“id”) Integer id)
{
employeeDao.delete(id);
return “redirect:/emps”;
}
}
package com.Dao;
import com.POJO.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
@Autowired //按照类型注入
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//保存员工信息到数据库
public void save( Employee employee)
{
String sql=“insert employee values(?,?,?,?,?)”;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,employee.getId(),employee.getName(),employee.getDepartment(),
employee.getEamil(),employee.getGender());
}
//查询并返回对应员工信息
public Employee exist(Employee employee)
{
String sql=“select * from employee where name=? and id= ?”;
try{
Employee employee1 = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Employee.class), employee.getName(), employee.getId());
return employee1;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return null;
}
}
//删除某个员工的信息
public void delete(Integer id)
{
String sql=“delete from employee where id=?”;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
}
//返回所有员工的信息
public List getAllEmployees()
{
String sql=“select* from employee”;
List list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Employee.class));
return list;
}
//按照员工的id查找对应的员工
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id)
{
String sql=“select * from employee where id= ?”;
try{
Employee employee1 = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Employee.class),id);
return employee1;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return null;
}
}
//修改员工的信息
public void UpdateEmp(Employee employee)
{
//对员工进行进行修改
String sql=“update employee set name=? ,department=? ,eamil=? ,gender=? where id=?”;
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,employee.getName(),employee.getDepartment(),employee.getEamil(),employee.getGender()
,employee.getId());
}
}
package com.POJO;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String department;
private String eamil;
private Integer gender;
public Employee(Integer id, String name, String department, String eamil, Integer gender) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.department = department;
this.eamil = eamil;
this.gender = gender;
}
public Employee() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(String department) {
this.department = department;
}
public String getEamil() {
return eamil;
}
public void setEamil(String eamil) {
this.eamil = eamil;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}























 4923
4923

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








