Log.d(TAG, "arrayMapSample: key = " + set.getKey() + ";value = " + set.getValue());
}
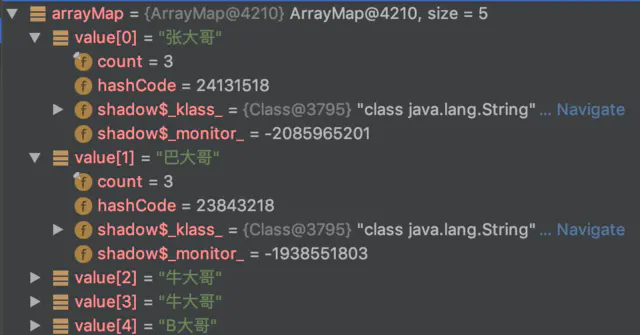
代码中,实际插入了 6 个 Key-Value,然而输出只有 5 个,其中 Key 为 “abcd” 的重复了而发生了覆盖。另外,还有一点注意的是 null 为 key 是允许插入的。以下是其输出的结果。
arrayMapSample: key = null;value = 张大哥 arrayMapSample: key = aabb;value = 巴大哥 arrayMapSample: key = aacc;value = 牛大哥 arrayMapSample: key = aadd;value = 牛大哥 arrayMapSample: key = abcd;value = B大哥
通过 Android Studio 的 Debug 功能,也可以简单观察一下其在内存中的存储。
2.源码分析
先来简单看一下 ArrayMap 的类图结构。
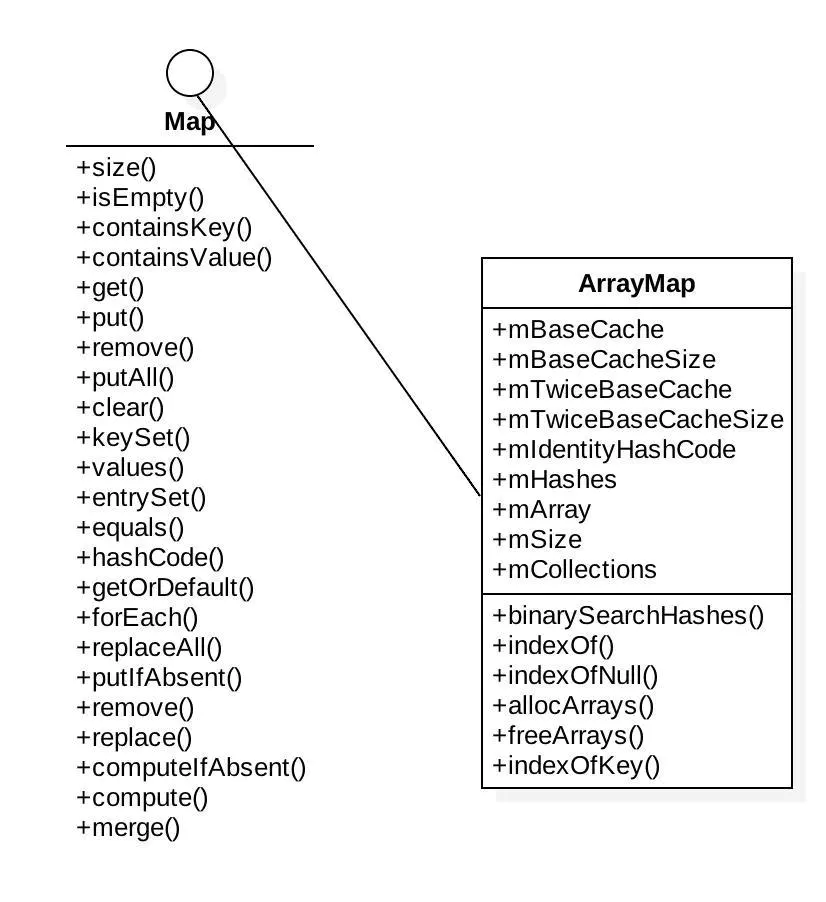
与 HashMap 不同的是,它是直接实现自接口 map。同样,存储 key-value 的方式也不同。ArrayMap 是通过数组直接存储了所有的 key-value。其中,mHashes 在 index 处存储了 key 的 hash code,而 mArray 则在 hash code 的 index<<1 处存储 key,在 index<<1 + 1 处存储 value。简单点说就是偶数处存储 key,相邻奇数处存储 value。
- ArrayMap 的初始化
/**
-
Create a new empty ArrayMap. The default capacity of an array map is 0, and
-
will grow once items are added to it.
*/
public ArrayMap() {
this(0, false);
}
/**
- Create a new ArrayMap with a given initial capacity.
*/
public ArrayMap(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
/** {@hide} */
public ArrayMap(int capacity, boolean identityHashCode) {
mIdentityHashCode = identityHashCode;
// If this is immutable, use the sentinal EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS
// instance instead of the usual EmptyArray.INT. The reference
// is checked later to see if the array is allowed to grow.
if (capacity < 0) {
mHashes = EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else if (capacity == 0) {
mHashes = EmptyArray.INT;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
allocArrays(capacity);
}
mSize = 0;
}
ArrayMap 的构造方法有 3 个重载的版本都列在上面了,一般我们都用默认的构造








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








