简介
AI虽能解决编程问题,但要真正用好AI编程(vibe coding),用户仍需专业知识。现阶段的AI常被过度营销,实际使用需配置详尽规则,这本身就是耗时工作。AI更适合帮助专业人士提升效率,而非替代学习。有效使用AI需设定角色、配置规则、分解任务,同时考虑成本控制。AI是让专业者更专业的工具,而非完全开箱即用的产品。
这是一个很有趣的问题,很多人觉得有了 AI 之后是不需要学习,因为 AI 可以帮助他解决大部分问题,但是如果你已经使用过一段时间 AI,或者说你正在使用 vibe coding ,那么你的实际体验会告诉你,你需要学习,甚至比之前了解更多。
❝
实际上有了 AI 之后,在某些方面我们确实不大需要去认真学习了,比如各种框架的 API ,因为 AI 总能找到合适的 API 来实现需求。
但是于此而言,作为使用者,我们需要去了解如何使用 AI ,甚至需要知道有什么技术框架,如何组织这种技术框架才能完成我们的需求。
相信大家应该都看过不少 AI 的营销广告,稍微输入几句话,就可以得到精美的页面,甚至完成一键部署,就像是曾经的精美页游广告,但是当自己进入游戏后才发现,为什么我的 AI 并没有想象中聪明?
首先第一点就是,现阶段的 AI 确实不够聪明,很多时候你看到的精美 AI 营销内容,不外乎两种情况:
- 可远观而不可亵玩的展示品,营销里的都会经过无数次尝试后给出的结果,而这个输出看似精美,但是实际根本不能用,那只是一个 Demo ,初见时美若天仙,但是如果你走近打开灯光,就会发现根本不能用:

- 专业的 vibe coding 大佬们通过各种详尽的规则,让 AI 的智商在当前项目得到了提升。
是的,用好 vibe coding 并不是一件简单的事情,在 vibe coding 领域,给一个项目写 rule 是一件非常耗时的过程,这也是为什么在今年 2025 的 stackoverflow 调查里, 为什么有 72% 的开发者对于完全使用 vibe code 不要放心:
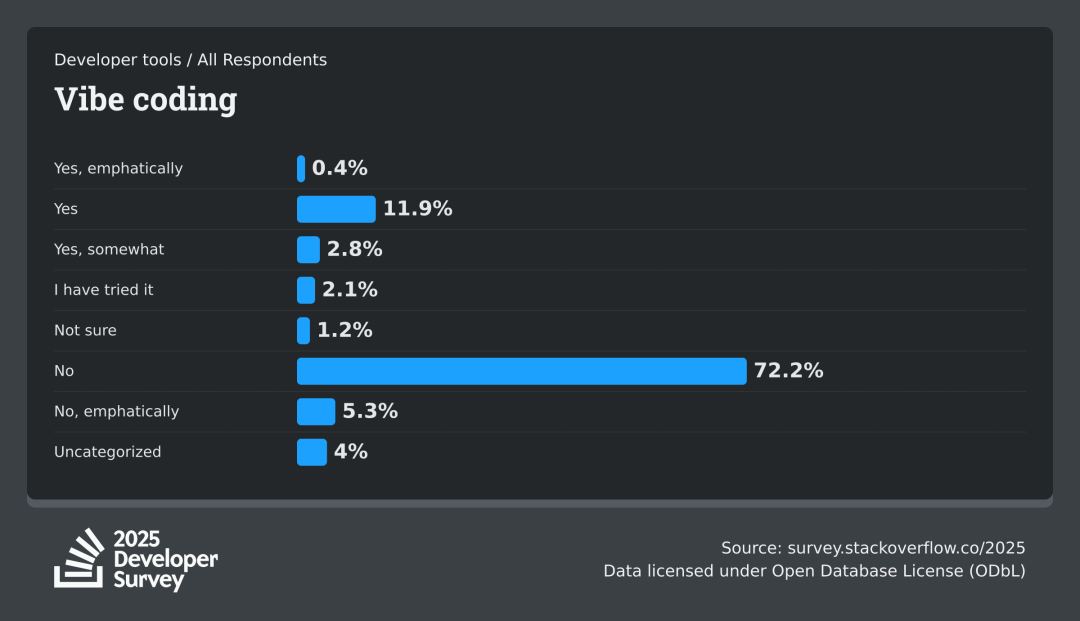
因为如果要用好 AI ,你就需要学会配置各种 rule ,但是配置 rule 的时间,大概率你已经把需求写完了,这样是目前 vibe coding 的现状。
❝
你觉得 AI 不好用,因为你没花费时间去调试规则和提示词,都是大家都是同个模型,为什么你用的和他的不一样,大多数原因就在于这里。
这么说可能不明显,在 AI 画图领域比代码更明显,因为画图是直接输出成果,不像代码这种中间过程,如果要你在 ChatGPT 画出这种图,你会用怎么做?
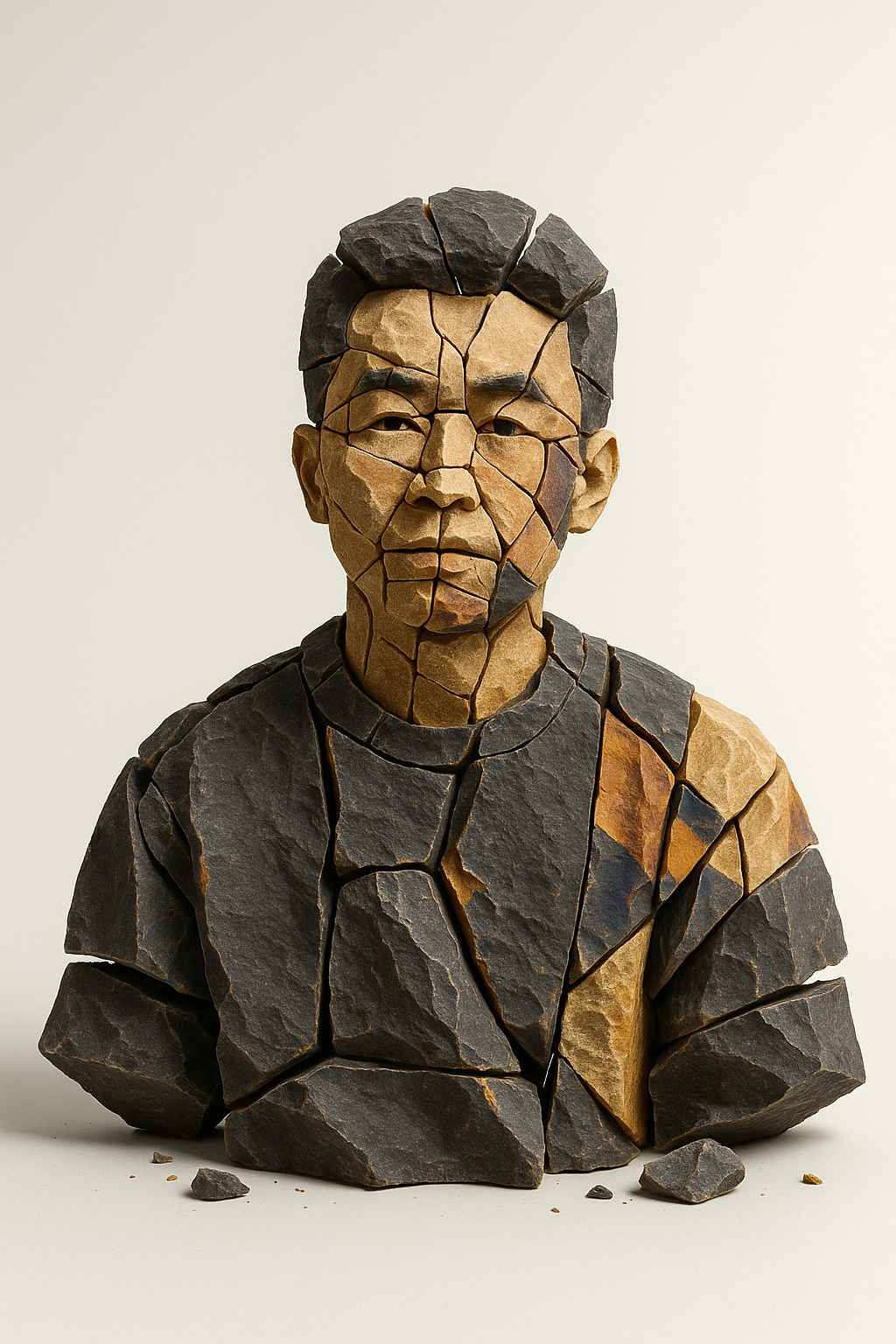

我们来看官方的提示词:
❝
创建一个超现实的3D构图,其中独立的岩石块组合成【主题】。风格:破碎板岩 + 砂岩碎片,每个部分明显分离,留有微小间隙;经过雕琢的边缘,可见的石纹。外观:极简的米白色背景,柔和的自左上方向下的工作室灯光,细腻的阴影,暗板岩中点缀着微暖的赭色色调。构图:居中,整洁,正面视角。添加几片微小碎片以增加深度。无文字,无额外道具。格式:【比例】。使各部分清晰分离且易于辨识。
可以看到,这里面都是细节,你需要告诉 AI :
- 风格:破碎板岩 + 砂岩碎片
- 每个部分明显分离,留有微小间隙
- 可见的石纹
- 灯光规则
- 各种色调
- 构图方式
- 地面细节
- ····
也许看起来是短短一段话,但是如果你没有专业知识打底,事实上你很难调试出这样一个图生图的效果,这其实在编程领域也是一样。
举一个另外很有趣的误区,那就是问模型它自己叫啥,然后发现好像和自己用的不一致,然后觉得自己被骗了,这其实也是幻觉所致,因为从训练的角度看,训练 Claude4 的时候,互联网语料还没有 Claude4 这个东西,不管是 Trae 还是 Cursor 都会出现这个问题,而官方之所以能正确,是在系统提示词方面增加了配置。
❝
当然,最重要的是 Claude 3.5、3.7、4.0 的 API 的价格是一样的,服务商也没必要特意去降模型。
当然这样暴露出另外一点,详尽提示词的重要性,因为你的提示词不够详细,就会增加幻觉的概率,而需要知道怎么丰富提示词,怎么指定规则,就需要你在这个领域有专业知识打底。
❝
所以目前来看,AI 更多是让你在专业领域更专业。
另外最重要的是什么?AI 是花钱的,它并不是可以肆意奴用的牛马,你肆意玩弄 AI 就等于侮辱自己的钱包,如果你预算充足那无所谓,但是如果你不想多花冤枉钱,那么对于如何使用 AI 还是需要了解和学习,毕竟 AI 真不是一个完全开箱即用的产品。
那么应该如何使用 AI ,这里简单介绍几个逻辑,首选就是设定角色:
❝
简单来说,比如你需要使用 Flutter 制作一个移动端 App ,那么在提示词开头可以描述:“你是一个 Flutter 专家,在 Andorid 和 iOS 领域很专业。。。。。。”
这种提示词其实很玄学,你加不加它不一定有用,但是不加有时候 AI 就会想 OOC (Out Of (one’s)Character),所以在 vibe coding 里这是必须加上的潜规则,你可以理解为这是一个类似工程动工前的开坛过程。
然后就是各种限定 Rule 的实现,这其实是 vibe coding 里最重要也是最繁琐的过程,我们使用 AI 的核心,就是给出尽可能详细和明确的需求和范围,目的就是减少幻觉。
为什么需要 Rules
- AI 有时会偏离技术栈,或使用不一致的技术导致失败,例如想用 SQL,但 AI 突然换成 JSON 文件存储,导致问题
- Rules 相当于 AI 的 “system prompt”,可清晰告诉 Agent 使用技术栈和编码偏好,确保一致性
如何配置 Rules
- 比如在 Cursor 的
project rules,会生成一个cursor文件夹,内部包含.mdc(或类似)规则文件 - 可同时加入用户级(通用)规则与项目级规则,推荐优先使用项目级设置,便于管理
常见规则类型和设置内容
| 必备规则 | 原因 |
|---|---|
| 技术栈限制 | 明确指定语言与工具,例如:使用 Flutter 3.29.3 版本 API,使用 Provider 6.1.2 作为状态管理框架,使用 dio 5.8.0+1 作为网络请求,使用 cherry_toast 1.12.0 作为提示框架·····这里的核心目的就是限定范围,越是限制越详细,幻觉就会越来越低,错误也就越来越少。 |
| 简洁优先 | 要求 AI 优先选择简单方案,避免代码重复,检查是否已有实现,不要盲目新建功能 |
| 环境区分 | 明确分隔 Dev、Test 和 Prod,确保修改只在 Dev 或 Test 环境执行,生产环境稳定 |
| 范围控制 | 只修改被明确请求的代码部分,不应产生副作用或引入新技术;如确需改动,务必先移除旧实现,避免重复逻辑,这在 AI 使用过程中是经常发生的,因为它时不时就会出现随机乱改的情况,所以类似要求必须有 |
| 避免脚本残留 | 不要在代码库中留下单次运行的脚本;执行完应删除,或者直接在代码中 inline 而非文件留存,这在 Agent 执行过程中经常存在,不管是 Github Copilot Agent 还是 Cursor |
| 文件大小限制 | 限制当个文件大小,比如文件超过 200–300 行需及早重构,防止庞大代码文件影响 AI 理解与测试,因为 AI 的上下文限制, AI 实际上是没办法完全理解一个超大型代码文件的,所以不生成超大型代码文件是基本要求 |
| API Key 安全 | 不允许 Agent 覆盖本地 .env 文件或 API 密钥配置,避免泄露或重置问题 |
| 测试覆盖 | 强制为所有重要功能编写测试,让每个功能都可以单独运行单元测试。 |
| 稳定性优先 | 稳定架构已有时,不允许 AI 引入大规模改结构除非明确指示;关注可能受影响模块 |
一直在更新,更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到优快云的官方了,有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】👇👇

其他建议
- 上下文管理:随着对话内容变多,AI 性能可能下降或者越觉增加,所以尽量在适当时候开启新 Chat,载入关键规则和代码片段,防止 context overflow 导致效率下降
- 请求粒度:保持任务微小、明确(例如“添加一个功能”),便于 AI 针对执行,不易引入错误
- 尽量不要使用 AI 直接对中大型项目进行重构,AI 最不擅长做的事是对中大型项目进行重构和迁移,因为如果你不给出详细的规则,实现步骤,审查逻辑和 fallback 规则,那么它就会充满自己的想法,迁移过程很难控制。
所以,不要给出像“帮我构建整个功能”这样冗长的提示 ,这样绝对会让 AI 会开始产生幻觉,然后胡乱造作,这样基本是在浪费 Token 去赌 AI 会不会有幻觉,AI 很难处理超长上下文的东西,所以才有 Agent 的场景,Agent 一般会帮你拆分需求,但是如果都让 Agent 去拆分,那么可能每次拆分的结果可能都不大一样,也就是幻觉的概率问题。
所以在使用 AI 过程中,你必须学会将任何想要添加的功能分解成几个阶段,尤其是在构建复杂功能时,与其一次性给出一个冗长的提示,不如根据你的用例将其分解成 3-5 个甚至更多的请求。
当然,更重要的是,你要用自己的专业的领域知识来约束和指向道路,这样 AI 才能走到对的放心,这也是为什么 vibe coding 的用户需要更多持续学习的原因。
❝
AI 是帮助专业的人变得更专业。
最后,一些框架也会提供它们的 AI 模板,例如 Flutter 就通过 https://docs.flutter.dev/ai/ai-rules 提供了对应的模板:
# AI rules for Flutter
You are an expert in Flutter and Dart development. Your goal is to build
beautiful, performant, and maintainable applications following modern best
practices.
## Project Structure
* Assumes a standard Flutter project structure with `lib/main.dart` as the
primary application entry point.
## Package Management
* If a new feature requires an external package, the AI will identify the most
suitable and stable package from pub.dev.
* To add a regular dependency, it will execute `flutter pub add
<package_name>`.
* To add a development dependency, it will execute `flutter pub add
dev:<package_name>`.
## Code Quality
* Adhere to maintainable code structure and separation of concerns (e.g., UI
logic separate from business logic).
* Adhere to meaningful and consistent naming conventions.
## Dart Best Practices
* Follow the official Effective Dart guidelines.
* Define related classes within the same library file. For large libraries,
export smaller, private libraries from a single top-level library.
* Group related libraries in the same folder.
* Add documentation comments to all public APIs, including classes,
constructors, methods, and top-level functions.
* Write clear comments for complex or non-obvious code. Avoid over-commenting.
* Don't add trailing comments.
* Ensure proper use of `async`/`await` for asynchronous operations with robust
error handling.
* Use pattern matching features where they simplify the code.
## Flutter Best Practices
* Widgets (especially `StatelessWidget`) are immutable; when the UI needs to
change, Flutter rebuilds the widget tree.
* Prefer composing smaller widgets over extending existing ones.
* Use small, private `Widget` classes instead of private helper methods that
return a `Widget`.
* Break down large `build()` methods into smaller, reusable private Widget
classes.
* Use `ListView.builder` to create lazy-loaded lists for performance.
* Use `const` constructors for widgets and in `build()` methods whenever
possible to optimize performance.
* Avoid performing expensive operations, like network calls or complex
computations, directly within `build()` methods.
## Application Architecture
* Aim for separation of concerns similar to MVC/MVVM, with defined Model,
View, and ViewModel/Controller roles.
### State Management
* Default to Flutter's built-in state management solutions. Do not use a
third-party package unless explicitly requested.
* Use `Streams` and `StreamBuilder` for handling a sequence of asynchronous
events.
* Use `Futures` and `FutureBuilder` for handling a single asynchronous
operation that will complete in the future.
* Use `ValueNotifier` with `ValueListenableBuilder` for simple, local state
that involves a single value.
```dart
// Define a ValueNotifier to hold the state.
final ValueNotifier<int> _counter = ValueNotifier<int>(0);
// Use ValueListenableBuilder to listen and rebuild.
ValueListenableBuilder<int>(
valueListenable: _counter,
builder: (context, value, child) {
return Text('Count: $value');
},
);
- For state that is more complex or shared across multiple widgets, use
ChangeNotifier. - Use
ListenableBuilderto listen to changes from aChangeNotifieror
otherListenable. - When a more robust solution is needed, structure the app using the
Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern. - Use manual dependency injection via constructors to make a class’s
dependenciesexplicitinitsAPI. - Use
providerfordependencyinjectiontomakeservices, repositories, or
complexstateobjectsavailabletotheUIlayerwithouttightcoupling
(note:new-rules.mdgenerallydefaultsagainstthird-partypackagesfor
statemanagementunlessexplicitlyrequested).
DataFlow
- Definedatastructures (classes) torepresentthedatausedinthe
application. - Abstractdatasources (e.g., APIcalls, databaseoperations) using
Repositories/Servicestopromotetestability.
Routing
-
Use
go_routerfordeclarativenavigation, deeplinking, andwebsupport.// 1. Addthedependency // flutterpubaddgo_router // 2. Configuretherouter
finalGoRouter_router = GoRouter(
routes: [
GoRoute(
path: ‘/’,
builder: (context, state) => constHomeScreen(),
routes: [
GoRoute(
path: ‘details/:id’, // Routewithapathparameter
builder: (context, state) {
finalString id = state.pathParameters[‘id’]!;
return DetailScreen(id: id);
},
),
],
),
],
);
// 3. Use it in your MaterialApp
MaterialApp.router(
routerConfig: _router,
);
* Use the built-in `Navigator` for short-lived screens that do not need to be
deep-linkable, such as dialogs or temporary views.
```dart
// Push a new screen onto the stack
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => const DetailsScreen()),
);
// Pop the current screen to go back
Navigator.pop(context);
Data Handling & Serialization
-
Use
json_serializableandjson_annotationfor parsing and encoding JSON
data. -
When encoding data, use
fieldRename: FieldRename.snaketo convert Dart’s
camelCase fields to snake_case JSON keys.// In your model file import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart'; part 'user.g.dart'; (fieldRename: FieldRename.snake) class User { final String firstName; final String lastName; User({required this.firstName, required this.lastName}); factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json); Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this); }
Logging
-
Use the
logfunction fromdart:developerfor structured logging that
integrates with Dart DevTools.import 'dart:developer' as developer; // For simple messages developer.log('User logged in successfully.'); // For structured error logging try { // ... code that might fail } catch (e, s) { developer.log( 'Failed to fetch data', name: 'myapp.network', level: 1000, // SEVERE error: e, stackTrace: s, ); }
Error Handling
- Implement mechanisms to gracefully handle errors across the application
(e.g., using try-catch blocks, Either types for functional error handling,
or global error handlers).
Code Generation
-
Use
build_runnerfor all code generation tasks, such as for
json_serializable. -
After modifying files that require code generation, run the build command:
dart run build_runner build --delete-conflicting-outputs
Testing
- Use
package:testfor unit tests. - Use
package:flutter_testfor widget tests. - Use
package:integration_testfor integration tests. - Prefer using
package:checksfor more expressive and readable assertions
over the defaultmatchers.
Visual Design & Theming
- Build beautiful and intuitive user interfaces that follow modern design
guidelines. - Ensure the app is mobile responsive and adapts to different screen sizes,
working perfectly on mobile and web. - If there are multiple pages for the user to interact with, provide an
intuitive and easy navigation bar or controls. - Stress and emphasize font sizes to ease understanding, e.g., hero text,
section headlines, list headlines, keywords in paragraphs. - Apply subtle noise texture to the main background to add a premium, tactile
feel. - Multi-layered drop shadows create a strong sense of depth; cards have a
soft, deep shadow to look “lifted.” - Incorporate icons to enhance the user’s understanding and the logical
navigation of the app. - Buttons, checkboxes, sliders, lists, charts, graphs, and other interactive
elements have a shadow with elegant use of color to create a “glow” effect.
Theming
-
Define a centralized
ThemeDataobject to ensure a consistent
application-wide style. -
Use Material 3 by setting
useMaterial3: truein yourThemeData. -
Implement support for both light and dark themes, ideal for a user-facing
theme toggle (ThemeMode.light,ThemeMode.dark,ThemeMode.system). -
Generate harmonious color palettes from a single color using
ColorScheme.fromSeed.final ThemeData lightTheme = ThemeData( useMaterial3: true, colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed( seedColor: Colors.deepPurple, brightness: Brightness.light, ), // ... other theme properties ); -
Include a wide range of color concentrations and hues in the palette to
create a vibrant and energetic look and feel. -
Use specific theme properties (e.g.,
appBarTheme,elevatedButtonTheme)
to customize the appearance of individual Material components. -
For custom fonts, use the
google_fontspackage. Define aTextThemeto
apply fonts consistently.// 1. Add the dependency // flutter pub add google_fonts // 2. Define a TextTheme with a custom font final TextTheme appTextTheme = TextTheme( displayLarge: GoogleFonts.oswald(fontSize: 57, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold), titleLarge: GoogleFonts.roboto(fontSize: 22, fontWeight: FontWeight.w500), bodyMedium: GoogleFonts.openSans(fontSize: 14), );
Assets and Images
-
If images are needed, make them relevant and meaningful, with appropriate
size, layout, and licensing (e.g., freely available). Provide placeholder
images if real ones are not available. -
Declare all asset paths in your
pubspec.yamlfile.flutter: uses-material-design: true assets: - assets/images/ -
Use
Image.assetto display local images from your asset bundle.Image.asset('assets/images/placeholder.png') -
Displays an icon from an
ImageProvider, useful for custom icons not in
Iconsclass. -
Use
Image.networkto display images from a URL, and always include
loadingBuilderanderrorBuilderfor a better user experience.Image.network( 'https://picsum.photos/200/300', loadingBuilder: (context, child, progress) {
if (progress == null) return child;
returnconst Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
},
errorBuilder: (context, error, stackTrace) {
returnconst Icon(Icons.error);
},
)
## Accessibility (A11Y)
* Implement accessibility features to empower all users, assuming a wide
variety of users with different physical abilities, mental abilities, age
groups, education levels, and learning styles.
xt, child, progress) {
if (progress == null) return child;
returnconst Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
},
errorBuilder: (context, error, stackTrace) {
returnconst Icon(Icons.error);
},
)
Accessibility (A11Y)
- Implement accessibility features to empower all users, assuming a wide
variety of users with different physical abilities, mental abilities, age
groups, education levels, and learning styles.
如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
一直在更新,更多的大模型学习和面试资料已经上传带到优快云的官方了,有需要的朋友可以扫描下方二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】👇👇

01.大模型风口已至:月薪30K+的AI岗正在批量诞生

2025年大模型应用呈现爆发式增长,根据工信部最新数据:
国内大模型相关岗位缺口达47万
初级工程师平均薪资28K(数据来源:BOSS直聘报告)
70%企业存在"能用模型不会调优"的痛点
真实案例:某二本机械专业学员,通过4个月系统学习,成功拿到某AI医疗公司大模型优化岗offer,薪资直接翻3倍!
02.大模型 AI 学习和面试资料
1️⃣ 提示词工程:把ChatGPT从玩具变成生产工具
2️⃣ RAG系统:让大模型精准输出行业知识
3️⃣ 智能体开发:用AutoGPT打造24小时数字员工
📦熬了三个大夜整理的《AI进化工具包》送你:
✔️ 大厂内部LLM落地手册(含58个真实案例)
✔️ 提示词设计模板库(覆盖12大应用场景)
✔️ 私藏学习路径图(0基础到项目实战仅需90天)






第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- …
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- …
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- …
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- …
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








