

网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
void StackPop(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
if(!StackEmpty(ST))
ST->top–;
}
//获取栈顶元素
int StackTop(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
return ST->a[ST->top - 1];
}
//判断栈是否空
bool StackEmpty(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
return ST->top == 0 ? true : false;
}
//获取栈顶元素个数
int StackSize(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
return ST->top;
}
### 压栈
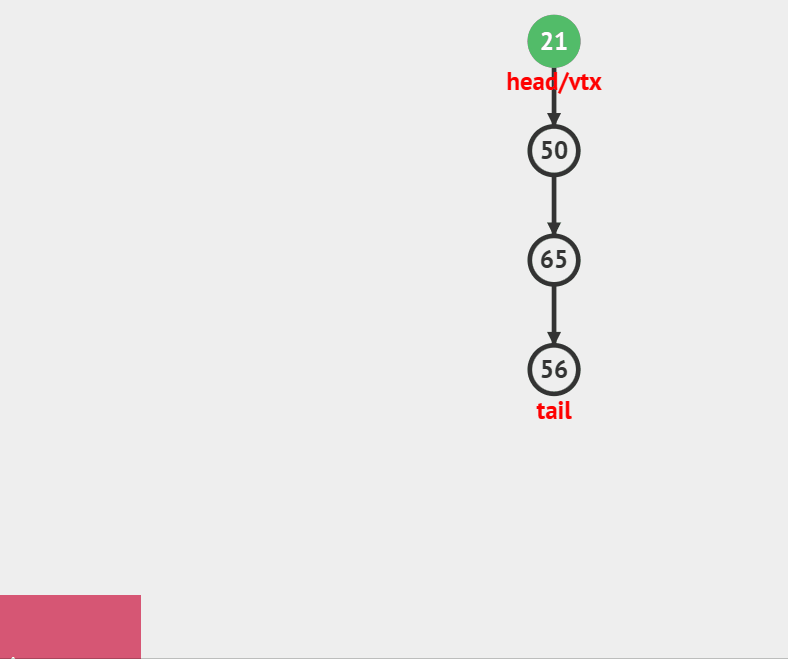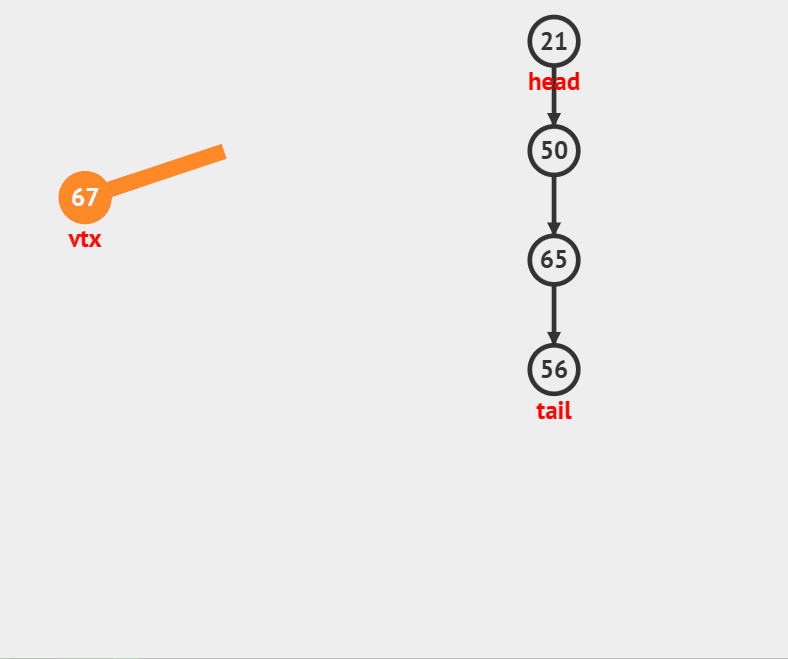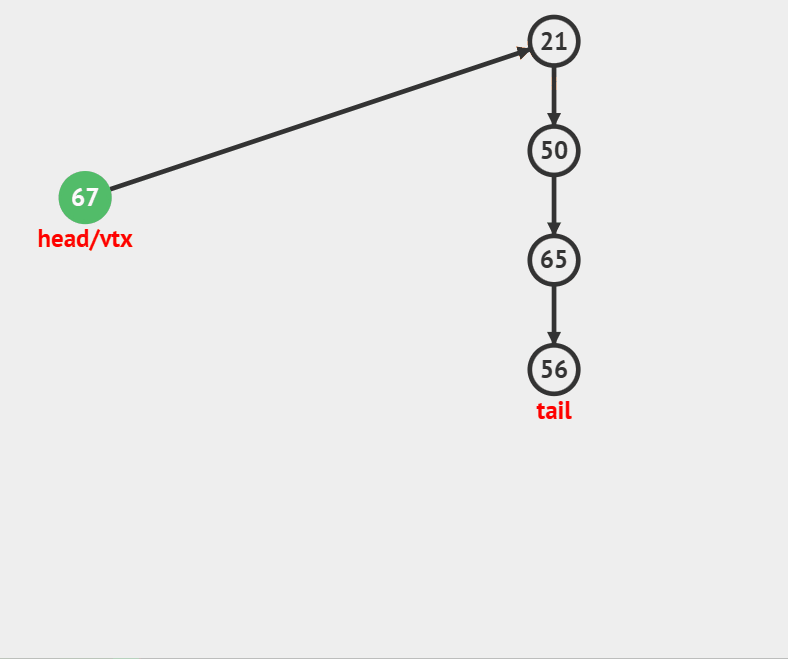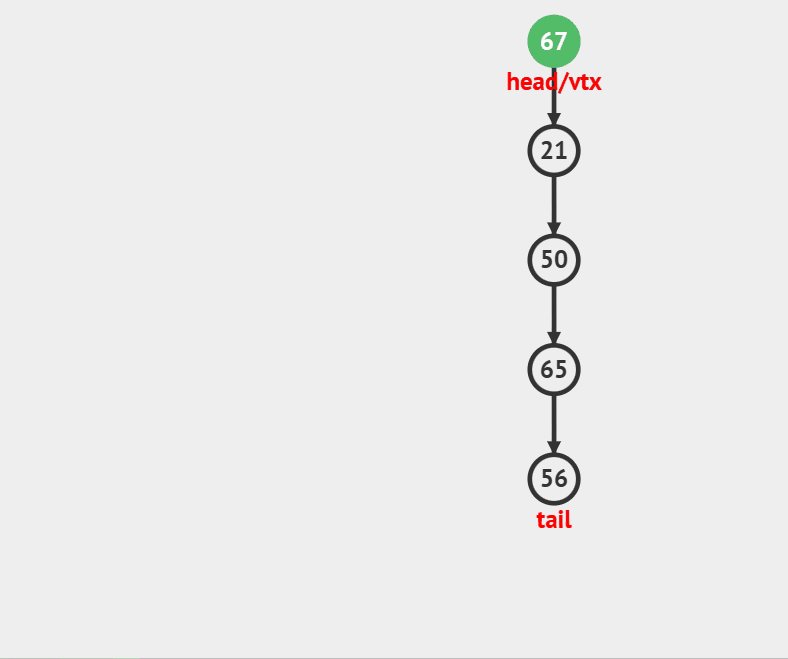
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack *ST, int x)
{
assert(ST);
if (ST->capacity == ST->top)
{
STData *tmp = realloc(ST->a,sizeof(STData) * ST->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror(“relloc:”);
exit(-1);
}
ST->a = tmp;
ST->capacity = ST->capacity * 2;
}
ST->a[ST->top++] = x;
}
### 出栈
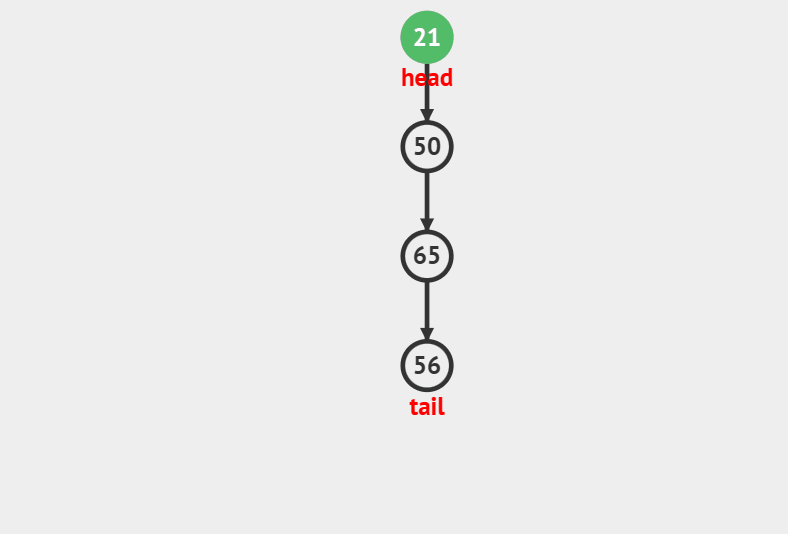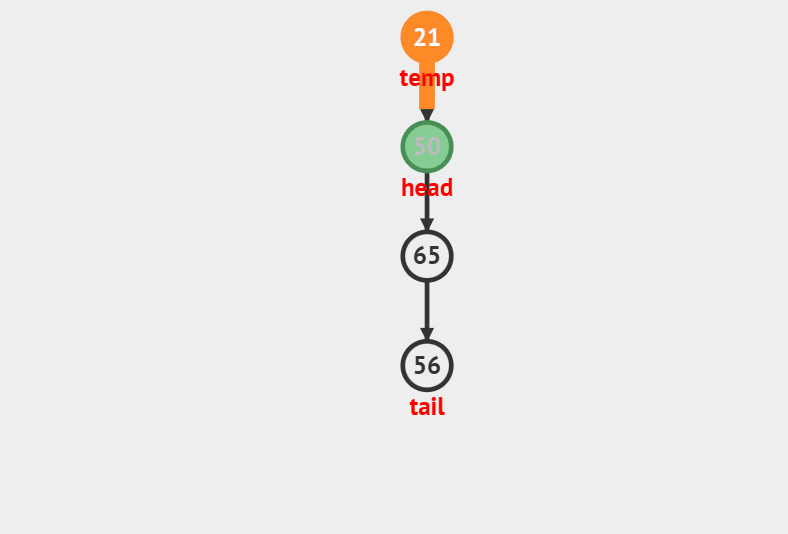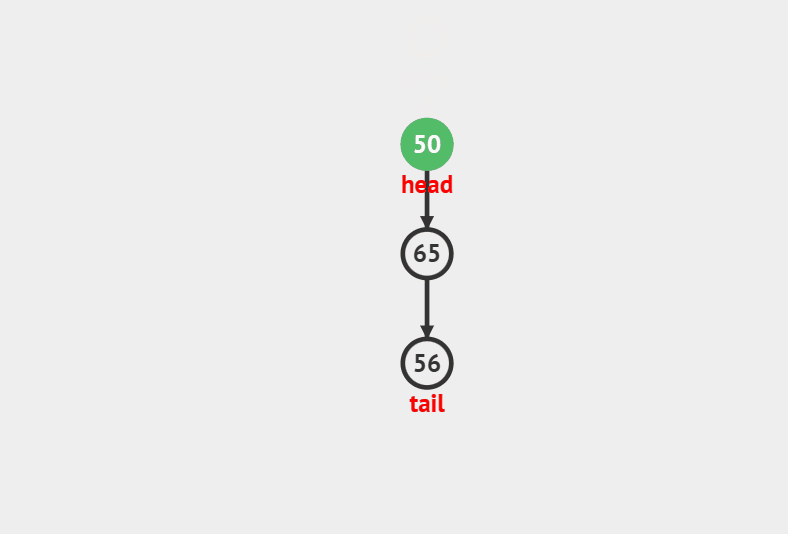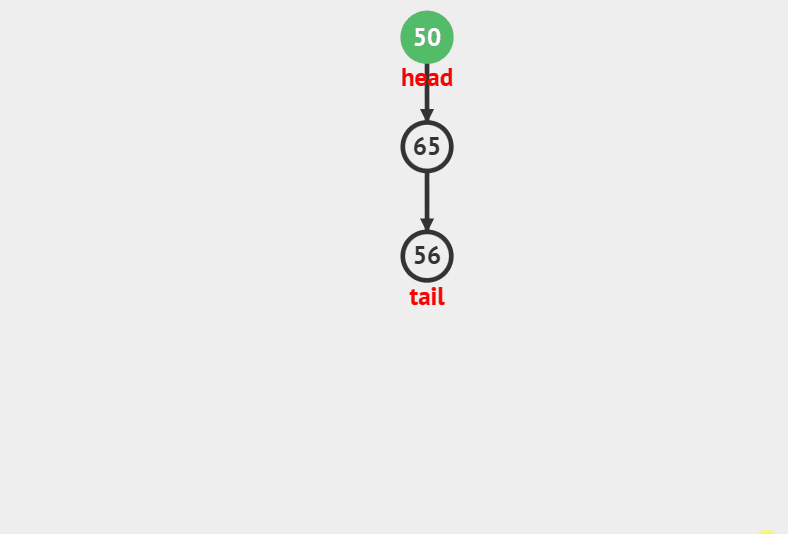
//弹栈
void StackPop(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
if(!StackEmpty(ST))
ST->top–;
}
## 队列
### 队列声明
typedef int QueDataTypef;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct Queue *next;
QueDataTypef data;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode *head;
QueueNode *tail;
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue *q);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue *q);
//队尾入队
void QueuePush(Queue *q, int x);
//队头出队
void QueuePop(Queue *q);
//判断空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *q);
//获取队头数据
QueDataTypef QueueFront(Queue *q);
//获取队尾数据
QueDataTypef QueueBack(Queue *q);
//求队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue *q);
### 队列实现
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue *q)
{
QueueNode* cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode \*next = (QueueNode \*)cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
//队尾入队
void QueuePush(Queue *q, int x)
{
assert(q);
QueueNode *newNode = (QueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
exit(-1);
perror(“QueuePush::malloc”);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (q->tail == NULL)
{
q->head = q->tail = newNode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = (Queue \*)newNode;
q->tail = newNode;
}
}
//队头出队
void QueuePop(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
if (q->head->next == NULL)
{
free(q->head);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QueueNode *next = (QueueNode *)q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
}
//判断空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL ? true : false;
}
//获取队头数据
QueDataTypef QueueFront(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
//获取队尾数据
QueDataTypef QueueBack(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
//求队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
int size = 0;
QueueNode *cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = (QueueNode *)cur->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
### 销毁
>
> 队列在销毁时,除了释放结点的内存,还要将头结点和尾结点置空
>
>
>
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue *q)
{
QueueNode* cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode \*next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
### 队尾入队
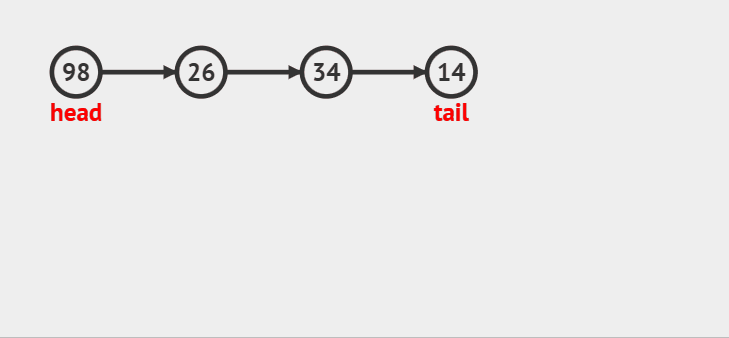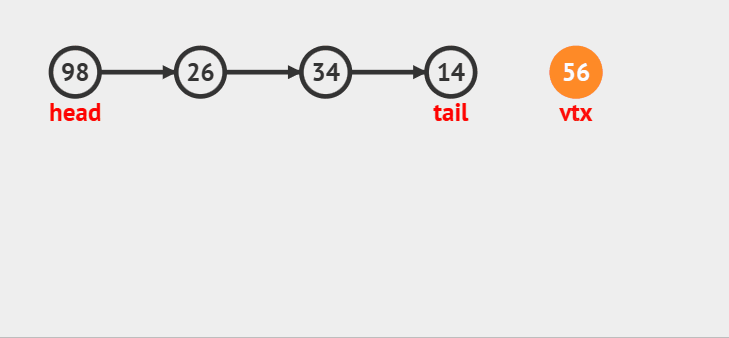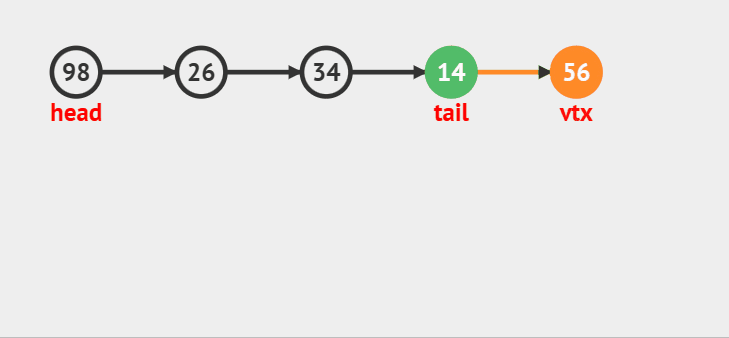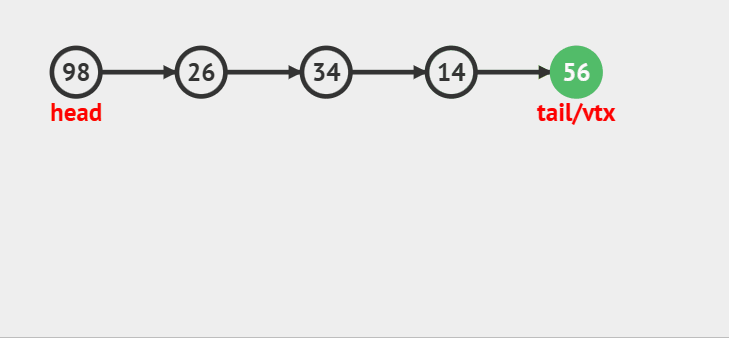
>
> 如果队头和队尾都是NULL的话,将新结点取下来做队头和队尾,如果队头不是空,就将新的结点尾插到tail的后面,让新结点做新的尾
>
>
>
//队尾入队
void QueuePush(Queue *q, int x)
{
assert(q);
QueueNode *newNode = (QueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
exit(-1);
perror(“QueuePush::malloc”);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
//队头队尾都是NULL
if (q->tail == NULL)
{
q->head = q->tail = newNode;
}
//取结点尾插入队,新结点成为新的尾
else
{
q->tail->next = newNode;
q->tail = newNode;
}
}
### 队头出队
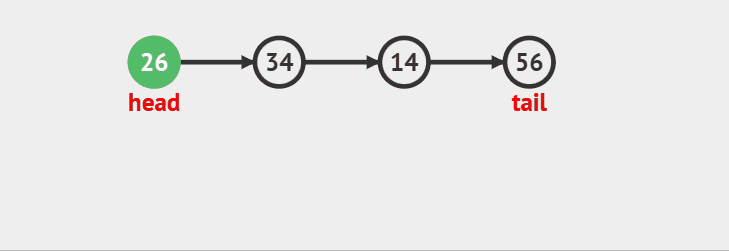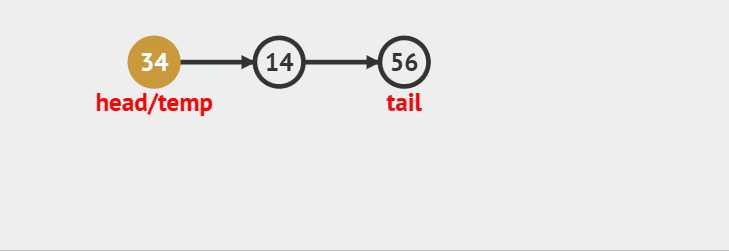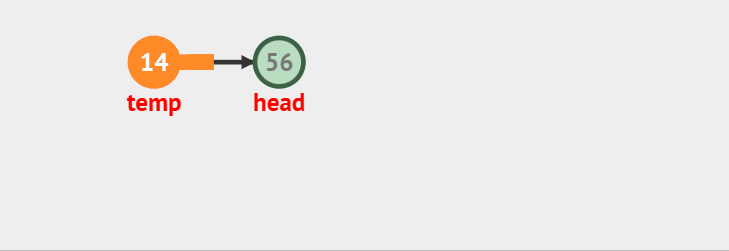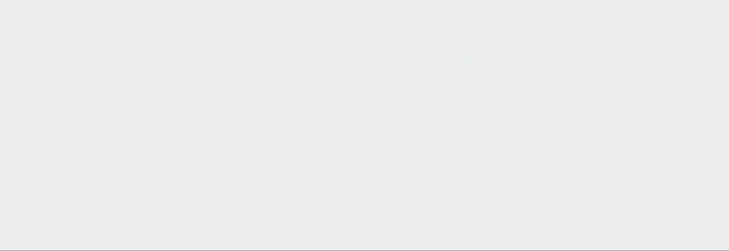
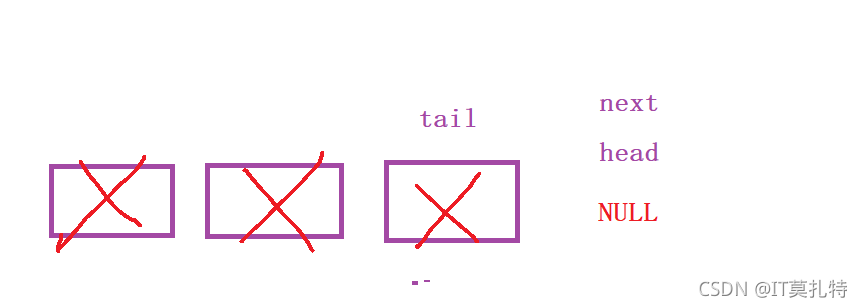
>
> 出队的时候考虑一种情况如果当只剩下一个结点了,不单独处理的话会让q->tail成为野指针
> 
>
>
>
//队头出数据
void QueuePop(Queue *q)
{
//出队只剩一个结点时,防止tail成为野指针
if (q->head->next == NULL)
{
free(q->head);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QueueNode *next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
}
### 判空
//判断空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL ? true : false;
}
### 获取队头数据
//获取队头数据
QueDataTypef QueueFront(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
### 获取队尾数据
//获取队尾数据
QueDataTypef QueueBack(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
### 求元素个数
//求队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
int size = 0;
QueueNode *cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = (QueueNode *)cur->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
## 力扣题
### 20. 有效的括号
链接: [link](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825).
>
> 原题描述:
> 给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
>
>
>
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
>
> 解题思路:
> 遍历字符串遇到左括号就入栈,遇到右括号就取出栈中的元素来匹配,如果匹配不上,就返回false,如果匹配上了,就将栈顶元素弹出,直到字符串遍历完了,最后判断栈是否为空
>
>
>
typedef char STData;
typedef struct Stack
{
STData *a;
int capacity;
int top;
}Stack;
//栈销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
free(ST->a);
ST->a = NULL;
ST->capacity = ST->top = 0;
}
//判断栈是否空
bool StackEmpty(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
return ST->top == 0 ? true : false;
}
//初始化
void StackInit(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
ST->a = (STData *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 4);
ST->capacity = 4;
ST->top = 0;
return;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack *ST, int x)
{
assert(ST);
if (ST->capacity == ST->top)
{
STData *tmp = realloc(ST->a,sizeof(STData) * ST->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror(“relloc:”);
exit(-1);
}
ST->a = tmp;
ST->capacity = ST->capacity * 2;
}
ST->a[ST->top++] = x;
}
//弹栈
void StackPop(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
if(!StackEmpty(ST))
ST->top–;
}
//获取栈顶元素
int StackTop(Stack *ST)
{
assert(ST);
return ST->a[ST->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char * s){
if(s == NULL)
return false;
Stack ST;
StackInit(&ST);
while(*s)
{
//左括号入栈
if(*s == ‘(’
|| *s == ‘{’
|| *s == ‘[’)
{
StackPush(&ST,*s);
}
else //右括号出栈
{
//防止越界,如果上来就是右括号
if(StackEmpty(&ST))
{
StackDestroy(&ST);
return false;
}
char ch = StackTop(&ST);
if(ch == ‘(’ && *s != ‘)’
|| ch == ‘{’ && *s != ‘}’
|| ch == ‘[’ && *s != ‘]’)
{
StackDestroy(&ST);
return false;
}
else
{
StackPop(&ST);
}
}
s++;
}
bool ret = StackEmpty(&ST);
StackDestroy(&ST);
return ret;
}
### 225. 用队列实现栈
链接: [link](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825).
原题描述:
>
> 请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
>
>
>
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
>
> 实现思路:
> 用两个队列互相倒入数据,入数据,往不为空的那个队列入,保持另一个队列为空,出数据,不为空的队列前size-1个倒出队列存放到另一个空队列中,队列元素的交换,再输出队尾的数据,这样就实现了后进先出的原则
> 
>
>
>
typedef int QueDataTypef;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct Queue *next;
QueDataTypef data;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode *head;
QueueNode *tail;
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue *q);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue *q);
//队尾入队
void QueuePush(Queue *q, int x);
//队头出队
void QueuePop(Queue *q);
//判断空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *q);
//获取队头数据
QueDataTypef QueueFront(Queue *q);
//获取队尾数据
QueDataTypef QueueBack(Queue *q);
//求队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue *q);
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue *q)
{
QueueNode* cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode \*next = (QueueNode \*)cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
//队尾入队
void QueuePush(Queue *q, int x)
{
assert(q);
QueueNode *newNode = (QueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
exit(-1);
perror(“QueuePush::malloc”);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (q->tail == NULL)
{
q->head = q->tail = newNode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = (Queue \*)newNode;
q->tail = newNode;
}
}
//队头出队
void QueuePop(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
if (q->head->next == NULL)
{
free(q->head);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QueueNode *next = (QueueNode *)q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
}
//判断空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL ? true : false;
}
//获取队头数据
QueDataTypef QueueFront(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
//获取队尾数据
QueDataTypef QueueBack(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
//求队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue *q)
{
assert(q);
int size = 0;
QueueNode *cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = (QueueNode *)cur->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj = (MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
//往不为空的队列里面倒数据,保证一个队列是空的
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
//非空队列往空队列里面倒数据,只剩一个数据的时候就将他释放并返回
Queue *pnoEmpty = &obj->q1;
Queue *pEmpty = &obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(pnoEmpty))
{
pEmpty = &obj->q1;
pnoEmpty = &obj->q2;
}
while(QueueSize(pnoEmpty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(pEmpty,QueueFront(pnoEmpty));
QueuePop(pnoEmpty);
}
int ret = QueueBack(pnoEmpty);
QueuePop(pnoEmpty);
return ret;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
//队列的尾部元素,等于栈顶的元素,取非空队列的尾部元素
int ret = 0;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
ret = QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
ret = QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
return ret;
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
//两个队列都不为空栈就不为空
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
//两个队列都释放,最后释放obj
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
### 232. 用栈实现队列
链接: [link](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825).
>
> 题目描述
**既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上C C++开发知识点,真正体系化!**
**由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新**
**[如果你需要这些资料,可以戳这里获取](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825)**
obj->q1))
{
ret = QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
ret = QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
return ret;
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack\* obj) {
//两个队列都不为空栈就不为空
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack\* obj) {
//两个队列都释放,最后释放obj
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
232. 用栈实现队列
链接: link.
题目描述
[外链图片转存中…(img-p2UiOEYT-1715707840661)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-aMPwxOB5-1715707840661)]
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上C C++开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








