
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
struct ListNode* cur = head;
//带哨兵位的头结点(简化尾插)
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
tail->next = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
struct ListNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
}
else
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = tail->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
//解决问题tail->next还是指向之前的结点
tail->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* del = head;
head = head->next;
free(del);//将哨兵位释放
return head;
}
## 2.逆置单链表
[力扣](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825)
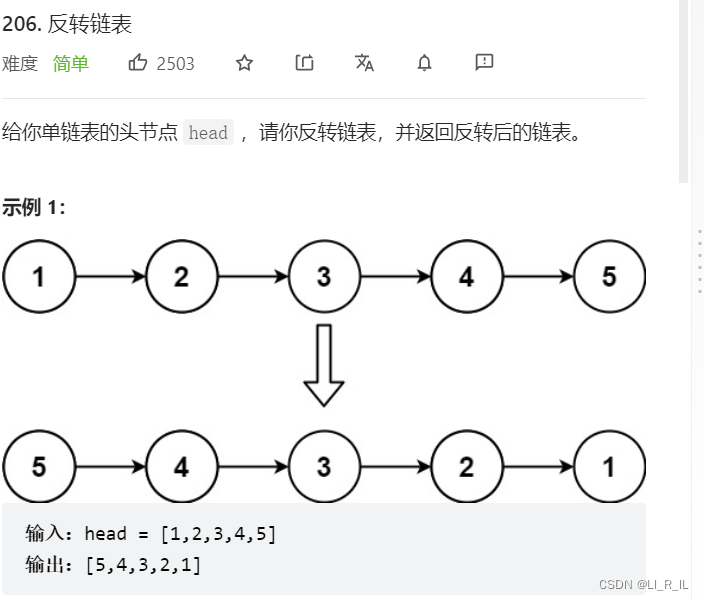
### 2.1头插思路:
/**
- Definition for singly-linked list.
- struct ListNode {
-
int val; -
struct ListNode *next; - };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//头插之前设置一个next,保留原链表剩余的结点
//头插
cur->next = newhead;//设置一个newhead指针指向NULL,然后将cur->next指向newhead
newhead = cur;//更新newhead,next赋值给cur
cur = next;//头插一次之后将下一个结点给cur
}
return newhead;
}
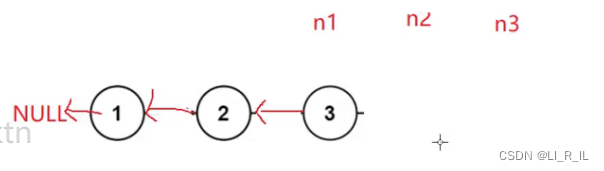
### 2.2指针方向颠倒:
定义n1,n2,n3
让n2的next指向n1
/**
- Definition for singly-linked list.
- struct ListNode {
-
int val; -
struct ListNode *next; - };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//空链表逆置还是空
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;//不加*就是定义结构体,加*是定义结构体指针
n1 = NULL;
n2 = head;
n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)//当n2走到NULL的时候结束
{
//倒指向
n2->next = n1;//原本n2->next指向的应该是n3,现在给它倒回去指向n1
//n1是NULL,相当于n2指向NULL
//迭代,迭代法也称辗转法,是一种不断用变量的旧值递推新值的过程
//往后走
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)//判断n3是否为空
n3 = n3->next;//n3如果不为null,就会一直往下走下去
//只需要设置逆置前面几个指针,后面的指针就会依次逆置下去
}
return n1;//n1变为新链表的头
}
## 3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
[力扣](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825)
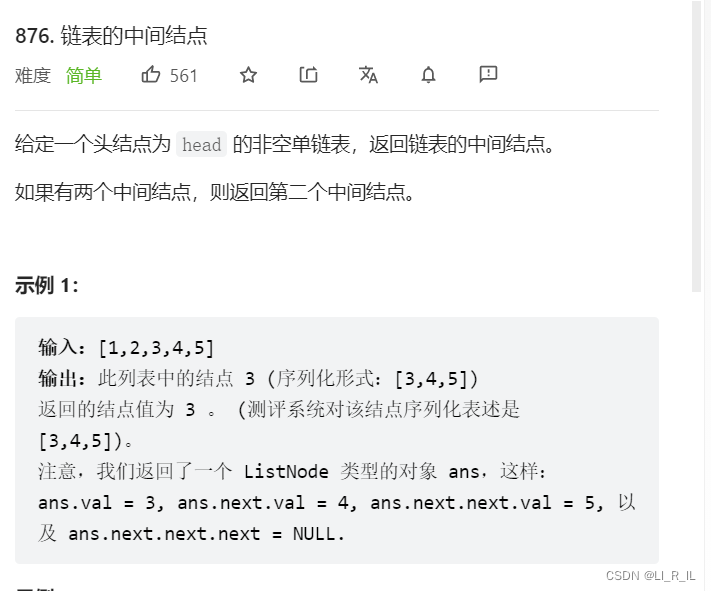
快慢指针
奇数:
slow一次一步
fast一次两步
fast走到最后一个结点,就找到中间结点
偶数(有两个中间结点要求返回第二个结点)
fast走到NULL
/**
- Definition for singly-linked list.
- struct ListNode {
-
int val; -
struct ListNode *next; - };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow = fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
## 4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
[链表中倒数第k个结点\_牛客题霸\_牛客网](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825)
快慢指针:
1.fast先走k步 fast走到NULL
2.fast先走k-1步 fast走到尾
fast先走,然后与slow同时走,两个指针之间就会有k(k-1)步距离
k--就是走k步
--k就是k-1次
k大于链表的长度会出现段错误
fast还没有走出k步,链表没有k步长
代码中有两个while循环时是先走完一个循环,再往下走第二个循环
比如以下代码中,先走让fast走k步的循环,再走fast为NULL时结束的循环
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
struct ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow = fast = pListHead;//从头指针开始,默认不带哨兵位
//先走k步
while(k--)
{
//处理fast还没有走出k步,链表没有k步长的情况
if(fast == NULL)
return NULL;
fast = fast->next;
}
//当fast走到NULL的时候就找到倒数第k个结点
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
//返回倒数第k个结点
return slow;
}
};
## 5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。
新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有结点组成的
[力扣](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618668825)
**链表经典题:逆置+合并**
归并:
将两个有序的链表归并成一个大的链表,归并之后依旧有序
分别用两个指针指向两个链表的第一个结点,从头比较,取小的尾插到新链表
结束:其中有一个走完
>
> 三种情况:
>
>
> 1. list1为NULL返回list2
> 2. list2为NULL返回list1
> 3. list1和list2都不为NULL
>
>
>
### 5.1不带哨兵位的写法:
/**
-
Definition for singly-linked list.
-
struct ListNode {
-
int val; -
ListNode *next; -
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} -
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} -
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} -
};
/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;struct ListNode* head,*tail; head = tail = NULL; while(list1 && list2) { //当list1小于list2的时候就把list1尾插 //相等的情况下就无所谓的,谁先尾插都行 if(list1->val < list2->val) { //第一次尾插 if(tail == NULL) { head = tail = list1;//小的先尾插进去 } //tail不等于NULL的时候 else { tail->next = list1; tail = tail->next; } list1 = list1->next; } //list2比list1小 >= else { if(tail == NULL) { head = tail = list2; } else { tail->next = list2; tail = tail->next; } list2 = list2->next; } } //当其中一个为NULL时就结束了 if(list1) tail->next = list1; if(list2) tail->next = list2; //不用更新tail,因为返回的是head return head;}
};
### 5.2带哨兵位的写法:
/**
-
Definition for singly-linked list.
-
struct ListNode {
-
int val; -
ListNode *next; -
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} -
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} -
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} -
};
/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {struct ListNode* head,*tail; head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));


网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
{
struct ListNode* head,*tail;
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
[外链图片转存中…(img-x6J7JdBX-1715711817489)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-z2YrlKZl-1715711817490)]
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








