尾声
面试成功其实都是必然发生的事情,因为在此之前我做足了充分的准备工作,不单单是纯粹的刷题,更多的还会去刷一些Android核心架构进阶知识点,比如:JVM、高并发、多线程、缓存、热修复设计、插件化框架解读、组件化框架设计、图片加载框架、网络、设计模式、设计思想与代码质量优化、程序性能优化、开发效率优化、设计模式、负载均衡、算法、数据结构、高级UI晋升、Framework内核解析、Android组件内核等。

不仅有学习文档,视频+笔记提高学习效率,还能稳固你的知识,形成良好的系统的知识体系。这里,笔者分享一份从架构哲学的层面来剖析的视频及资料分享给大家梳理了多年的架构经验,筹备近6个月最新录制的,相信这份视频能给你带来不一样的启发、收获。

Android进阶学习资料库
一共十个专题,包括了Android进阶所有学习资料,Android进阶视频,Flutter,java基础,kotlin,NDK模块,计算机网络,数据结构与算法,微信小程序,面试题解析,framework源码!

大厂面试真题
PS:之前因为秋招收集的二十套一二线互联网公司Android面试真题 (含BAT、小米、华为、美团、滴滴)和我自己整理Android复习笔记(包含Android基础知识点、Android扩展知识点、Android源码解析、设计模式汇总、Gradle知识点、常见算法题汇总。)

《2017-2021字节跳动Android面试历年真题解析》

网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
超过指定缓存的话,每次移除栈最大内存的缓存的对象
下面我们一起来看一下ImageLoader是怎样实现这些算法的
首先我们一起先来看一下类UML图
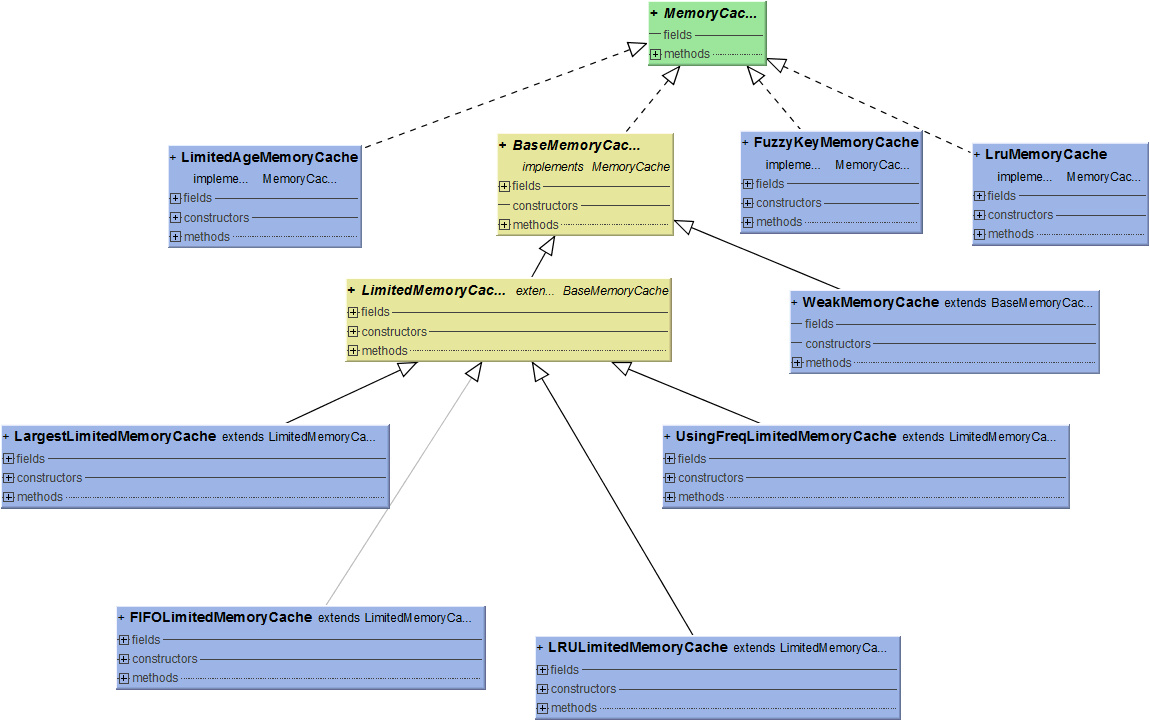
源码分析
- 1)首先我们先来看一下BaseMemoryCache做了什么?
public abstract class BaseMemoryCache implements MemoryCache {
/** Stores not strong references to objects */
private final Map<String, Reference> softMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, Reference>());
@Override
public Bitmap get(String key) {
Bitmap result = null;
Reference reference = softMap.get(key);
if (reference != null) {
result = reference.get();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
softMap.put(key, createReference(value));
return true;
}
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
Reference bmpRef = softMap.remove(key);
return bmpRef == null ? null : bmpRef.get();
}
@Override
public Collection keys() {
synchronized (softMap) {
return new HashSet(softMap.keySet());
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
softMap.clear();
}
/** Creates {@linkplain Reference not strong} reference of value */
protected abstract Reference createReference(Bitmap value);
}
其实就是保存着一份弱引用而已,而它的父类Memory只是定义了几个接口方法,统一标准而已
- 2)接着我们来看LimitedMemoryCache做了什么?
public abstract class LimitedMemoryCache extends BaseMemoryCache {
private static final int MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB = 16;
private static final int MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE = MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB * 1024 * 1024;
private final int sizeLimit;
private final AtomicInteger cacheSize;
/**
-
Contains strong references to stored objects. Each next object is added last. If hard cache size will exceed
-
limit then first object is deleted (but it continue exist at {@link #softMap} and can be collected by GC at any
-
time)
*/
private final List hardCache = Collections.synchronizedList(
new LinkedList());
/** @param sizeLimit Maximum size for cache (in bytes) */
public LimitedMemoryCache(int sizeLimit) {
this.sizeLimit = sizeLimit;
cacheSize = new AtomicInteger();
if (sizeLimit > MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE) {
L.w(“You set too large memory cache size (more than %1$d Mb)”,
MAX_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE_IN_MB);
}
}
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
boolean putSuccessfully = false;
// Try to add value to hard cache
int valueSize = getSize(value);
int sizeLimit = getSizeLimit();
int curCacheSize = cacheSize.get();
if (valueSize < sizeLimit) {
while (curCacheSize + valueSize > sizeLimit) {
Bitmap removedValue = removeNext();
if (hardCache.remove(removedValue)) {
curCacheSize = cacheSize.addAndGet(-getSize(removedValue));
}
}
hardCache.add(value);
cacheSize.addAndGet(valueSize);
putSuccessfully = true;
}
// Add value to soft cache
super.put(key, value);
return putSuccessfully;
}
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
if (value != null) {
if (hardCache.remove(value)) {
cacheSize.addAndGet(-getSize(value));
}
}
return super.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
hardCache.clear();
cacheSize.set(0);
super.clear();
}
protected int getSizeLimit() {
return sizeLimit;
}
protected abstract int getSize(Bitmap value);
protected abstract Bitmap removeNext();
}
LimitedMemoryCache所做的工作可以分为以下几步
- 1) 保存着一份强引用
private final List hardCache = Collections.synchronizedList(
new LinkedList());
-
- 其实在我们调用put方法的时候,即我们把bitmap存进内存的时候,他会判断是否超出我们的最大值,超出我们的最大值就会调用removeNext();来获得我们将要移除的bitmap对象,最终再调用hardCache.remove(removedValue)去移除它。
-
- 注意到removeNext()方法是抽象方法,交给子类自己去实现自己的算法逻辑。
注意事项
结合BaseMemoryCache和LimitedMemoryCache,我们可以知道LimitedMemoryCache的子类,至少可以访问两份Bitmap 的缓存,一份是BaseMemoryCache所拥有的softMap ,是弱引用;一份是LimitedMemoryCachehar所拥有的hardCache 集合
//父类BaseMemoryCache的成员变量,并且每次在操作的时候都会把bitmap的弱引用存进去
private final Map<String, Reference> softMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(
new HashMap<String, Reference>());
//LimitedMemoryCache的成员变量,缓存的bitmap是强引用
private final List hardCache = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList());
有人可能会有疑问了这些成员变量不是私有的吗?为什么说LimitedMemoryCache的子类,至少可以访问两份引用,这点我们可以从他们的put方法和get方法中知道,只需要调用super.put()即可把我们的bitmap缓存存到父类,调用super.get()即可从父类中 访问我们保存的Bitmap对象 。
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
boolean putSuccessfully = false;
// Try to add value to hard cache
int valueSize = getSize(value);
int sizeLimit = getSizeLimit();
int curCacheSize = cacheSize.get();
if (valueSize < sizeLimit) {
while (curCacheSize + valueSize > sizeLimit) {
Bitmap removedValue = removeNext();
if (hardCache.remove(removedValue)) {
curCacheSize = cacheSize.addAndGet(-getSize(removedValue));
}
}
hardCache.add(value);
cacheSize.addAndGet(valueSize);
putSuccessfully = true;
}
// Add value to soft cache
super.put(key, value);
return putSuccessfully;
}
同理LimitedMemoryCache的子类put也会调用LimitedMemoryCache的put方法,代码见下面分析。
同时从上面的分析当中我们可以知道主要关心put和removeNext()这两个方法就可以了,put()方法其实就是把bitmap对象存进我们的queue队列中
下面我们在看一下UsingFreqLimitedMemoryCache是怎样实现的?
public class UsingFreqLimitedMemoryCache extends LimitedMemoryCache {
/**
-
Contains strong references to stored objects (keys) and last object usage date (in milliseconds). If hard cache
-
size will exceed limit then object with the least frequently usage is deleted (but it continue exist at
-
{@link #softMap} and can be collected by GC at any time)
*/
private final Map<Bitmap, Integer> usingCounts = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Bitmap, Integer>());
public UsingFreqLimitedMemoryCache(int sizeLimit) {
super(sizeLimit);
}
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
if (super.put(key, value)) {
usingCounts.put(value, 0);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Bitmap get(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
// Increment usage count for value if value is contained in hardCahe
if (value != null) {
Integer usageCount = usingCounts.get(value);
if (usageCount != null) {
usingCounts.put(value, usageCount + 1);
}
}
return value;
}
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
if (value != null) {
usingCounts.remove(value);
}
return super.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
usingCounts.clear();
super.clear();
}
@Override
protected int getSize(Bitmap value) {
return value.getRowBytes() * value.getHeight();
}
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Integer minUsageCount = null;
Bitmap leastUsedValue = null;
Set<Entry<Bitmap, Integer>> entries = usingCounts.entrySet();
synchronized (usingCounts) {
for (Entry<Bitmap, Integer> entry : entries) {
if (leastUsedValue == null) {
leastUsedValue = entry.getKey();
minUsageCount = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer lastValueUsage = entry.getValue();
if (lastValueUsage < minUsageCount) {
minUsageCount = lastValueUsage;
leastUsedValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
usingCounts.remove(leastUsedValue);
return leastUsedValue;
}
@Override
protected Reference createReference(Bitmap value) {
return new WeakReference(value);
}
}
思路解析
- 当我们调用put方法,把bitmap存进内存的时候,他会判断是否超出我们的最大值,超出我们的最大值就会调用removeNext();来获得我们将要移除的bitmap对象,最终再调用hardCache.remove(removedValue)去移除它。
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
boolean putSuccessfully = false;
// Try to add value to hard cache
int valueSize = getSize(value);
int sizeLimit = getSizeLimit();
int curCacheSize = cacheSize.get();
if (valueSize < sizeLimit) {
while (curCacheSize + valueSize > sizeLimit) {
Bitmap removedValue = removeNext();
if (hardCache.remove(removedValue)) {
curCacheSize = cacheSize.addAndGet(-getSize(removedValue));
}
}
hardCache.add(value);
cacheSize.addAndGet(valueSize);
putSuccessfully = true;
}
// Add value to soft cache
super.put(key, value);
return putSuccessfully;
}
···
- 下面我们来看一下removeNext()是怎样获得将要移除的bitmap对象的?
private final Map<Bitmap, Integer> usingCounts = Collections.
synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Bitmap, Integer>());
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Integer minUsageCount = null;
Bitmap leastUsedValue = null;
Set<Entry<Bitmap, Integer>> entries = usingCounts.entrySet();
synchronized (usingCounts) {
for (Entry<Bitmap, Integer> entry : entries) {
if (leastUsedValue == null) {
leastUsedValue = entry.getKey();
minUsageCount = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer lastValueUsage = entry.getValue();
if (lastValueUsage < minUsageCount) {
minUsageCount = lastValueUsage;
leastUsedValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
usingCounts.remove(leastUsedValue);
return leastUsedValue;
}
其实就是将usingCounts中出现次数最少的节点移除掉。
那它实在什么时候计算bitmap的使用次数的呢?相信大多数人会想到,既然是使用频率,那肯定是在取图片的过程中计算的,没错,下面让我们一起来看一下是怎样实现的?
@Override
public Bitmap get(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
// Increment usage count for value if value is contained in hardCahe
if (value != null) {
Integer usageCount = usingCounts.get(value);
if (usageCount != null) {
usingCounts.put(value, usageCount + 1);
}
}
return value;
}
其实也很简单,判断是否存在缓存value,存在的话,使用次数加一
好的,到此UsingFreqLimitedMemoryCache的源码分析位置
public class FIFOLimitedMemoryCache extends LimitedMemoryCache {
private final List queue = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList());
public FIFOLimitedMemoryCache(int sizeLimit) {
super(sizeLimit);
}
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
if (super.put(key, value)) {
queue.add(value);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
if (value != null) {
queue.remove(value);
}
return super.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
queue.clear();
super.clear();
}
@Override
protected int getSize(Bitmap value) {
return value.getRowBytes() * value.getHeight();
}
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
return queue.remove(0);
}
@Override
protected Reference createReference(Bitmap value) {
return new WeakReference(value);
}
}
-
1)从上面的分析当中我们可以知道主要关心put和removeNext()这两个方法就可以了,put()方法其实就是把bitmap对象存进我们的queue队列中
-
2)remove方法其实就是一出队列的第一个bitmap对象,将先进先出,符合我们的FIFO原则
@Override
public Bitmap get(String key) {
Bitmap result = null;
Reference reference = softMap.get(key);
if (reference != null) {
result = reference.get();
}
return result;
}
public class LargestLimitedMemoryCache extends LimitedMemoryCache {
/**
-
Contains strong references to stored objects (keys) and sizes of the objects. If hard cache
-
size will exceed limit then object with the largest size is deleted (but it continue exist at
-
{@link #softMap} and can be collected by GC at any time)
*/
private final Map<Bitmap, Integer> valueSizes = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Bitmap, Integer>());
public LargestLimitedMemoryCache(int sizeLimit) {
super(sizeLimit);
}
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
if (super.put(key, value)) {
valueSizes.put(value, getSize(value));
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Bitmap remove(String key) {
Bitmap value = super.get(key);
if (value != null) {
valueSizes.remove(value);
}
return super.remove(key);
}
//这里我们省略若干个方法,有兴趣的话讲源码去,下面有提供源码下载地址
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Integer maxSize = null;
Bitmap largestValue = null;
Set<Entry<Bitmap, Integer>> entries = valueSizes.entrySet();
synchronized (valueSizes) {
for (Entry<Bitmap, Integer> entry : entries) {
if (largestValue == null) {
largestValue = entry.getKey();
maxSize = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer size = entry.getValue();
if (size > maxSize) {
maxSize = size;
largestValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
valueSizes.remove(largestValue);
return largestValue;
}
}
同样我们只关心put方法和removeNext()方法
@Override
public boolean put(String key, Bitmap value) {
if (super.put(key, value)) {
valueSizes.put(value, getSize(value));
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
protected Bitmap removeNext() {
Integer maxSize = null;
Bitmap largestValue = null;
Set<Entry<Bitmap, Integer>> entries = valueSizes.entrySet();
synchronized (valueSizes) {
for (Entry<Bitmap, Integer> entry : entries) {
if (largestValue == null) {
largestValue = entry.getKey();
maxSize = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer size = entry.getValue();
if (size > maxSize) {
maxSize = size;
largestValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
valueSizes.remove(largestValue);
return largestValue;
}
-
1)其实就是put方法的时候( valueSizes.put(value, getSize(value));),我们将bitmap做为key,大小作为value,存进valueSizesM集合
-
2)在超过最大缓存数量的时候,遍历移除掉valueSizes中最大的bitmap。
下面我们来看一下LruMemoryCache是怎样实现的
源码我们就不贴出来了
主要逻辑在put方法中
最后
以前一直是自己在网上东平西凑的找,找到的东西也是零零散散,很多时候都是看着看着就没了,时间浪费了,问题却还没得到解决,很让人抓狂。
后面我就自己整理了一套资料,还别说,真香!
资料有条理,有系统,还很全面,我不方便直接放出来,大家可以先看看有没有用得到的地方吧。




网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
null) {
largestValue = entry.getKey();
maxSize = entry.getValue();
} else {
Integer size = entry.getValue();
if (size > maxSize) {
maxSize = size;
largestValue = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
}
valueSizes.remove(largestValue);
return largestValue;
}
-
1)其实就是put方法的时候( valueSizes.put(value, getSize(value));),我们将bitmap做为key,大小作为value,存进valueSizesM集合
-
2)在超过最大缓存数量的时候,遍历移除掉valueSizes中最大的bitmap。
下面我们来看一下LruMemoryCache是怎样实现的
源码我们就不贴出来了
主要逻辑在put方法中
最后
以前一直是自己在网上东平西凑的找,找到的东西也是零零散散,很多时候都是看着看着就没了,时间浪费了,问题却还没得到解决,很让人抓狂。
后面我就自己整理了一套资料,还别说,真香!
资料有条理,有系统,还很全面,我不方便直接放出来,大家可以先看看有没有用得到的地方吧。
[外链图片转存中…(img-98B1rUnZ-1715825884324)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-oLNZrHfT-1715825884324)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-WctG54BX-1715825884325)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-qJ5RWNkP-1715825884325)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-PYr7eXgo-1715825884325)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-7OQ9AJAM-1715825884326)]
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








