protected boolean onTransact(int code, @NonNull Parcel data, @Nullable Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException {
switch (code){
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION:
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
case TRANSAVTION_getPerson:
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
List result = this.getPersonList();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeTypedList(result);
return true;
case TRANSAVTION_addPerson:
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
Person arg0 = null;
if (data.readInt() != 0) {
arg0 = Person.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
}
this.addPerson(arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
@Override
public IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
}
首先我们看asInterface方法,Binder驱动传来的IBinder对象,通过queryLocalInterface方法,查找本地Binder对象,如果返回的就是PersonManger,说明client和server处于同一个进程,直接返回,如果不是,返回给一个代理对象。
当然作为代理对象,也是需要实现服务接口
public class Proxy implements PersonManger {
private IBinder mIBinder;
public Proxy(IBinder mIBinder) {
this.mIBinder =mIBinder;
}
@Override
public void addPerson(Person mPerson) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel replay = Parcel.obtain();
try {
data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if (mPerson != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
mPerson.writeToParcel(data, 0);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
mIBinder.transact(BinderObj.TRANSAVTION_addPerson, data, replay, 0);
replay.readException();
} catch (RemoteException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
replay.recycle();
data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public List getPersonList() {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel replay = Parcel.obtain();
List result = null;
try {
data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mIBinder.transact(BinderObj.TRANSAVTION_getPerson, data, replay, 0);
replay.readException();
result = replay.createTypedArrayList(Person.CREATOR);
}catch (RemoteException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
replay.recycle();
data.recycle();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public IBinder asBinder() {
return null;
}
}
这里的代理对象实质就是client最终拿到的代理服务,通过这个就可以和Server进行通信了,首先通过Parcel将数据序列化,然后调用 remote.transact()将方法code,和data传输过去,对应的会回调在在Server中的onTransact()中
然后是我们的Server进程,onBind方法返回mStub对象,也就是Server中的Binder实体对象
public class ServerSevice extends Service {
private static final String TAG = “ServerSevice”;
private List mPeople = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void onCreate() {
mPeople.add(new Person());
super.onCreate();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mStub;
}
private BinderObj mStub = new BinderObj() {
@Override
public void addPerson(Person mPerson) {
if (mPerson==null){
mPerson = new Person();
Log.e(TAG,“null obj”);
}
mPeople.add(mPerson);
Log.e(TAG,mPeople.size()+“”);
}
@Override
public List getPersonList() {
return mPeople;
}
};
}
最终我们在客户端进程,bindService传入一个ServiceConnection对象,在与服务端建立连接时,通过我们定义好的BinderObj的asInterface方法返回一个代理对象,再调用方法进行交互
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private boolean isConnect = false;
private static final String TAG = “MainActivity”;
private PersonManger personManger;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
start();
findViewById(R.id.textView).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (personManger==null){
Log.e(TAG,“connect error”);
return;
}
personManger.addPerson(new Person());
Log.e(TAG,personManger.getPersonList().size()+“”);
}
});
}
private void start() {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ServerSevice.class);
bindService(intent,mServiceConnection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.e(TAG,“connect success”);
isConnect = true;
personManger = BinderObj.asInterface(service);
List personList = personManger.getPersonList();
Log.e(TAG,personList.size()+“”);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.e(TAG,“connect failed”);
isConnect = false;
}
};
}
这样的话,一次完成的进程间的交互就完成了~是不是感觉没有想象中那么难,最后建议大家在不借助 AIDL 的情况下手写实现 Client 和 Server 进程的通信,加深对 Binder 通信过程的理解。
本文在写作过程中参考了蛮多的文章和源码,感谢大佬们的无私奉献,溜了溜了~
参考文章
Android开发除了flutter还有什么是必须掌握的吗?
相信大多数从事Android开发的朋友们越来越发现,找工作越来越难了,面试的要求越来越高了
除了基础扎实的java知识,数据结构算法,设计模式还要求会底层源码,NDK技术,性能调优,还有会些小程序和跨平台,比如说flutter,以思维脑图的方式展示在下图;
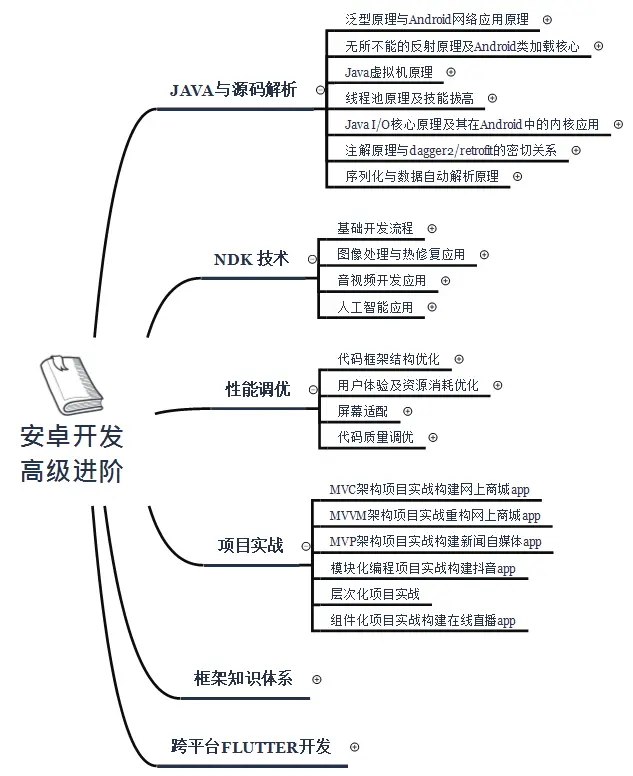
《Android学习笔记总结+移动架构视频+大厂面试真题+项目实战源码》,点击传送门,即可获取!
式还要求会底层源码,NDK技术,性能调优,还有会些小程序和跨平台,比如说flutter,以思维脑图的方式展示在下图;
[外链图片转存中…(img-1bsOIImK-1714373903389)]
《Android学习笔记总结+移动架构视频+大厂面试真题+项目实战源码》,点击传送门,即可获取!





 本文详细介绍了Android中的Binder机制,包括如何在不同进程中通过Proxy和Server实现实体对象的交互,以及onTransact方法的工作原理。作者鼓励读者亲手实践,以深化对Binder通信的理解。
本文详细介绍了Android中的Binder机制,包括如何在不同进程中通过Proxy和Server实现实体对象的交互,以及onTransact方法的工作原理。作者鼓励读者亲手实践,以深化对Binder通信的理解。
















 797
797

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








