Throwable类有两个子类,一个Error子类表示错误,一个Exception子类表示异常
异常又分为编译时期异常,运行时期异常
运行时期异常RunTimeException及其子类
编译时期异常除RunTimeException及其子类的所有异常
e.printStackTrace()打印详细的错误信息
创建异常对象
1.关键字 throw
异常处理方式 一 throws 无限上抛
throws缺点出现异常后一直上抛给jvm,按照jvm的方式解决异常,导致异常代码后的代码不被执行
关键字 throws
写在参数与代码体之间
public class DemoException01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{
String s ="1111.txt";
add(s);
}
//异常处理方式一 throws 向上抛
public static void add(String s) throws FileNotFoundException{
if(s.endsWith(".txt")){
//创建异常对象
throw new FileNotFoundException("未发现文件");
}
System.out.println("继续执行");
}
}throws多个异常
1.throws 异常一,异常二
public class DemoException02 {
//抛出多个异常
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
String s = null;
add(s);
}
//抛出多个异常
public static void add(String s) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
if(s==null){
//创建第一个异常
throw new IOException("IO异常");
}else if(s.endsWith(".txt")){
//创建第二个异常
throw new FileNotFoundException("未发现文件");
}
}
}2, throws 输出异常对象的父类也可以
public class DemoException02 {
//抛出多个异常
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = null;
add(s);
}
//抛出多个异常
public static void add(String s) throws IOException {
if(s==null){
//创建第一个异常
throw new IOException("IO异常");
}else if(s.endsWith(".txt")){
//创建第二个异常
throw new FileNotFoundException("未发现文件");
}
}
}
异常处理方式二 try...catch
catch单个异常
格式:
try{
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(要抓的异常类型){
解决办法
}
若try中代码异常并不是要catch的异常,按平常方式处理,影响下面代码的运行
catch多个异常
格式
try{
代码
}catch(异常一 对象名){
}catch(异常二 对象名){}.........
注意若多个异常中存在子父类关系,我们依然可以在catch中只写父类异常与其对finally
finally
- finally的内容必须被执行,不管是否触发异常,都必须被执行
- 都是配合try...catch...使用
- finally代码段优先被执行
public class DemoException03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = method();
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int method(){
try{
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.length());
}catch (Exception e){
return 1;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally内容必须被执行");
//return 3;
}
return 0;
}
}运行结果为
finally内容必须被执行
1
先执行finally的sout,在执行catch的return1;
public class DemoException03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = method();
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int method(){
try{
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.length());
}catch (Exception e){
return 1;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally内容必须被执行");
return 3;
}
}
}运行结果为
finally内容必须被执行
3
证明finally被优先执行
finally使用场景
关闭资源,创建的对象如果没有用了就会被GC回收,释放内存,但是某些对象并不能被GC回收,Connection,IO,Socket等,这些内容我们用在finally代码段中手动回收
继承体系中抛异常
- 父类抛异常,子类重写可抛可不抛
- 父类不抛,子类重写也不抛
try_catch与throws使用时机
如果处理后仍像是后续代码正常运行,用try_catch
如果方法之间是递进关系,我们可以先throws,后再最表层try_catch统一进行异常处理
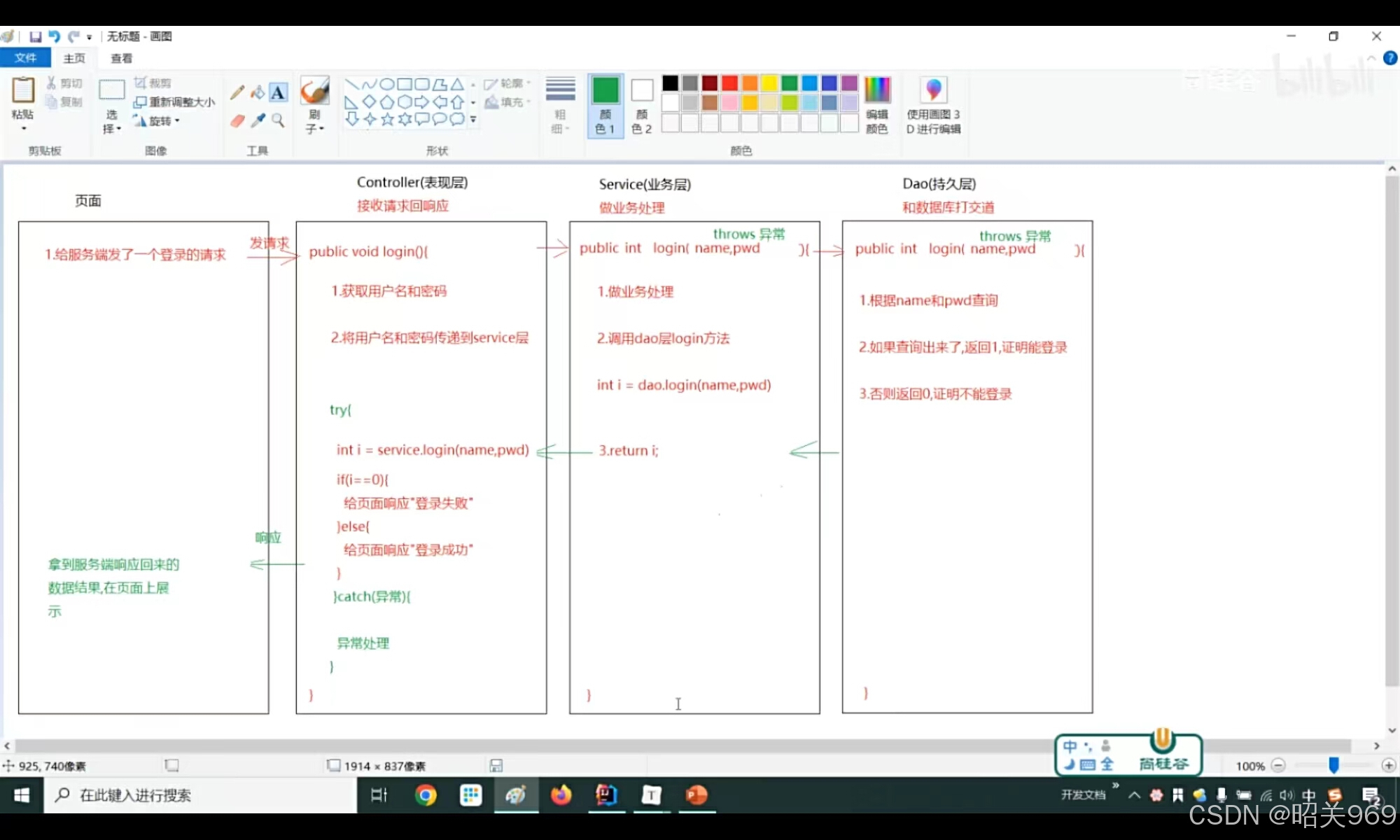
编译时期异常必须进行处理,无法运行
运行时期异常一般不处理,一般就是代码出问题,直接修改
自定义异常
创建异常类,继承Exception类或RunTimeException类表明为异常
public class DemoException04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws LoginUserException{
//设置已存在的登录名
String userName = "root";
//输入用户名
System.out.println("请输入登录名");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.next();
//判断用户是否存在
if(name.equals(userName)){
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}else{
//创建自定义异常对象,在自定义异常类中创建有参构造获取输入的异常信息
throw new LoginUserException("登陆失败了");
}
}
}创建自定义异常,创建有参构造获取输入的异常信息
public class LoginUserException extends Exception{
//创建有参构造,获取错误信息
public LoginUserException() {
}
public LoginUserException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}打印异常信息的三种方法
- e.toString() 输出异常类型及设置的异常信息
- e.getMessage()输出设置异常信息
- e.printStackTrace()输出最详细,包括异常类型,设置的异常信息,异常出现的行数等























 3064
3064

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








