喵,12.21写的题目让我来补下错题,当时期末周好忙。
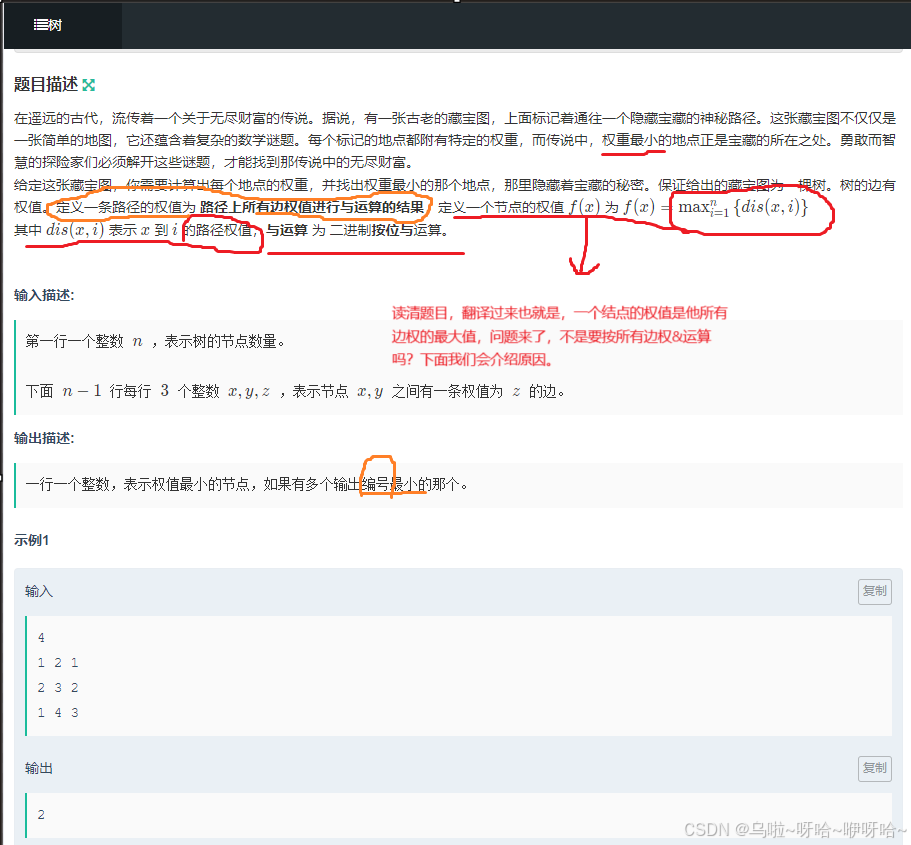
A.树
答案代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
ll n;cin>>n;
vector<vector<pair<ll,ll>> >mp(n+1);
for(ll i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
ll x,y,z;cin>>x>>y>>z;
mp[x].push_back({y,z});
mp[y].push_back({x,z});
}
vector<ll> res(n+1,0);
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
ll x=i;
for(ll j=0;j<mp[x].size();j++){
res[x]=max(mp[x][j].second,res[x]);
}
}
ll ans=LLONG_MAX;
ll idx=0;
for(ll i=1;i<res.size();i++){//注意不要越界了,res.size()==n+1,写i<=res.size()会越界
if(res[i]<ans){
ans=res[i];
idx=i;
}
}
cout<<idx;
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dis[1200000];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int h=n-1;
while(h--)
{
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
dis[x]=max(dis[x],z);
dis[y]=max(dis[y],z);
}
int ans=1;
for(int t=1;t<=n;t++)
if(dis[ans]>dis[t]) ans=t;
cout<<ans;
}
其实题目已经告诉我们答案了,只是又多说了&运算,可能对做题过程中造成一定困扰,下面让我们来具体解释一下。 
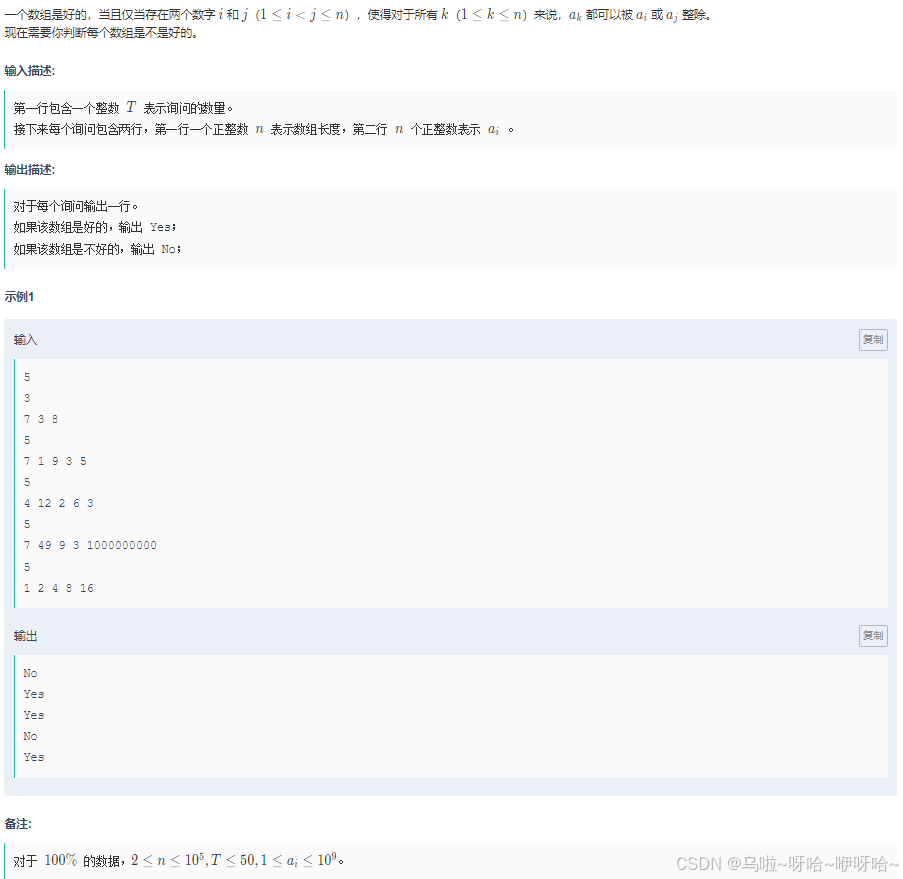
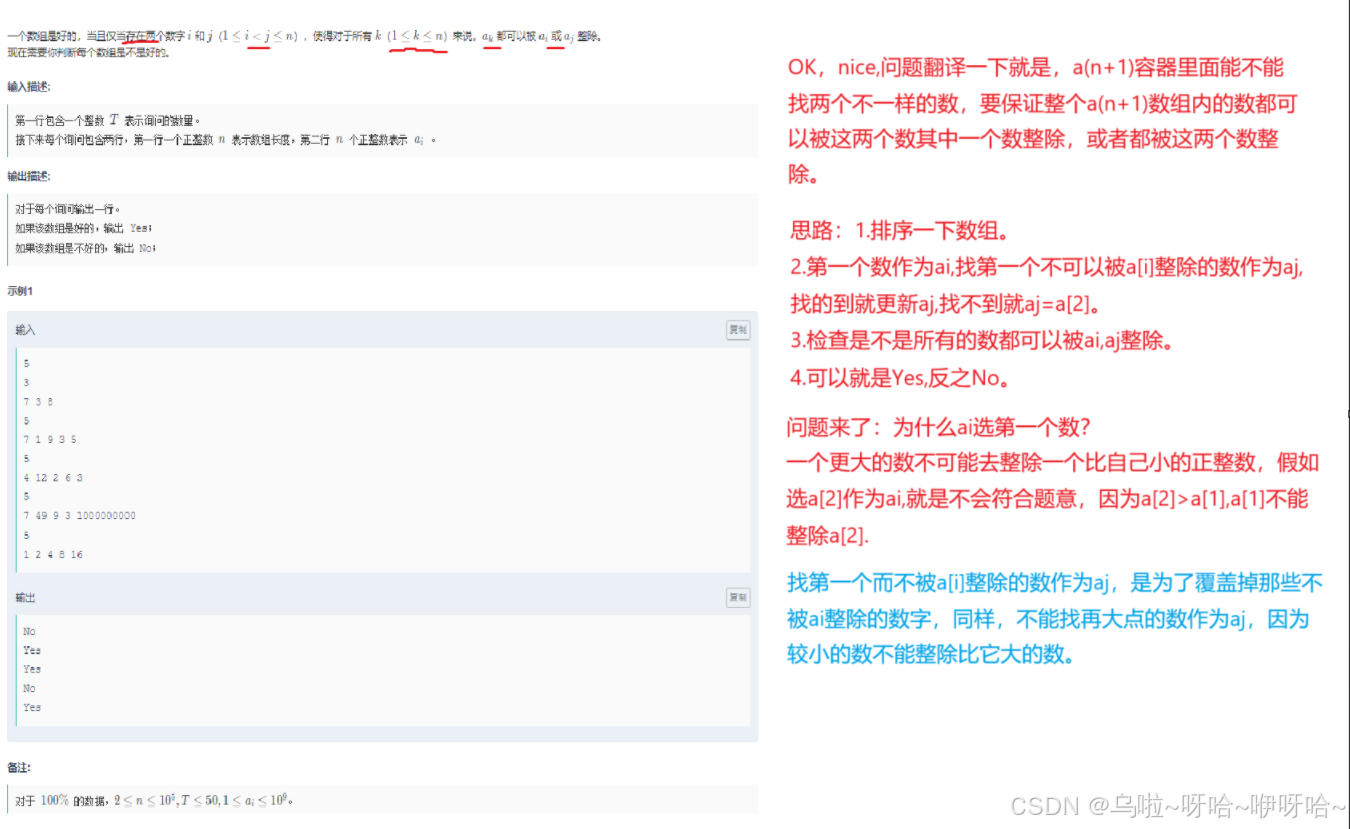
B.什么是好数组
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);//要加上,不然会超时
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n;cin>>n;
vector<ll> a(n+1,0);
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
if(n==2){
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}else{
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
ll ai=a[1],aj=-1;
for(ll i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i]%ai!=0){
aj=a[i];
break;
}
}
if(aj==-1)aj=a[2];
ll flag=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i]%ai!=0&&a[i]%aj!=0){
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
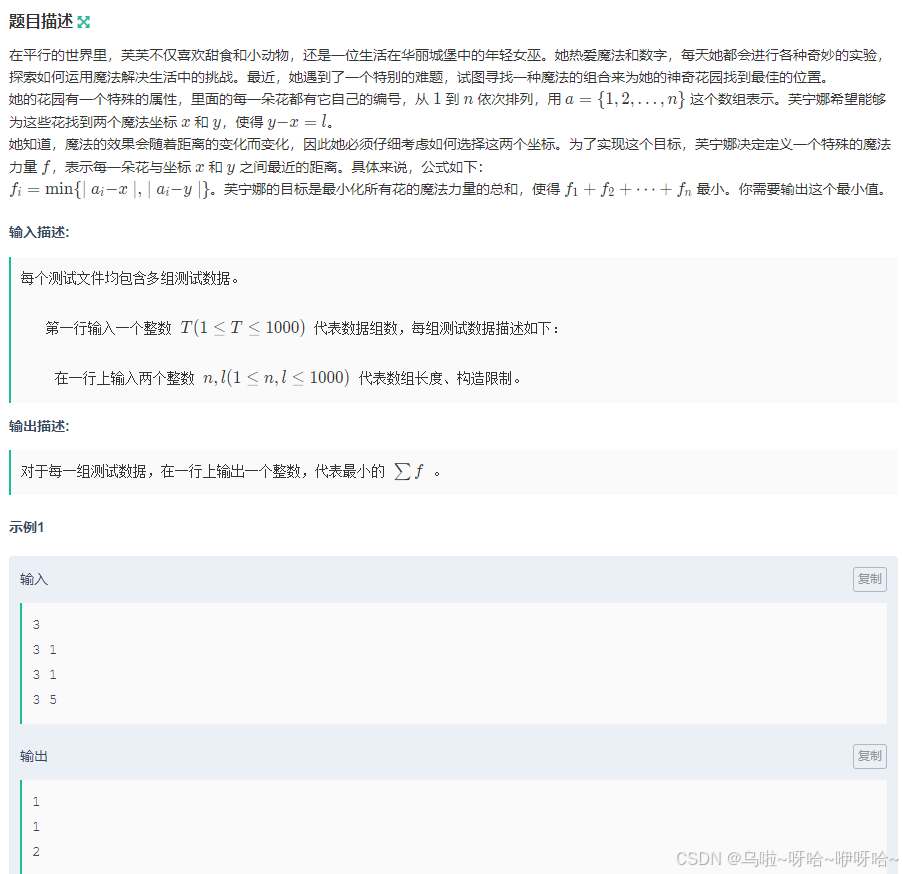
C.快来帮芙芙吧* I
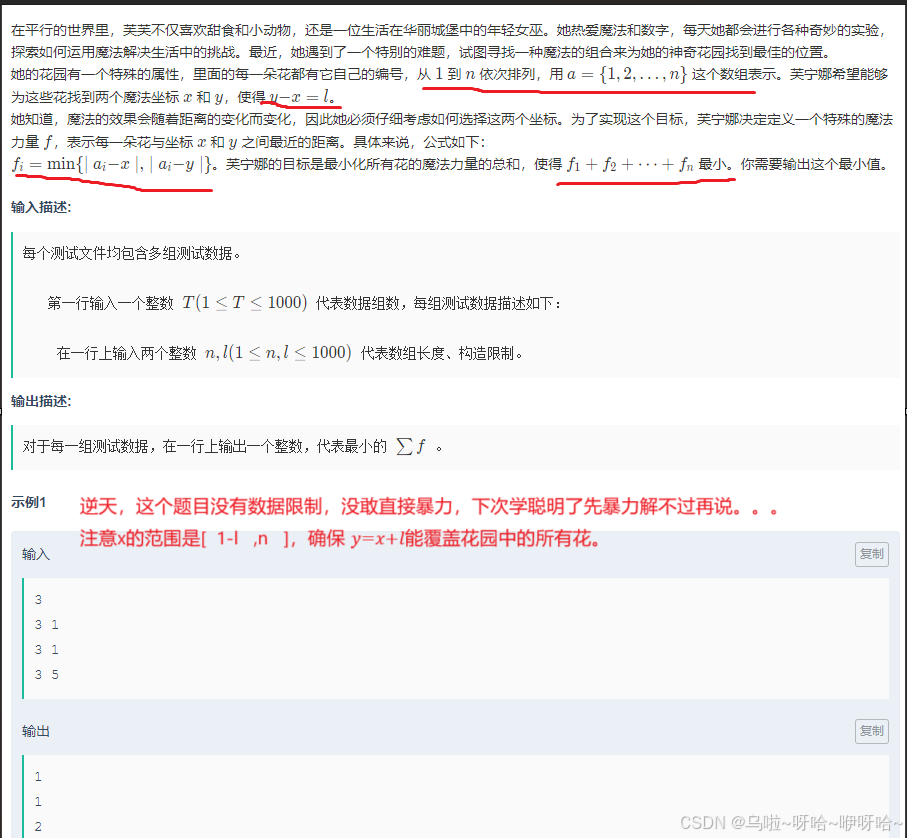
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n,l;cin>>n>>l;
ll min_sum=LLONG_MAX;
for(ll x=1-l;x<=n;x++){
ll flag=0;
ll current_sum=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
current_sum+=min(abs(i-x),abs(i-x-l));
if(current_sum>=min_sum){
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0){
if(current_sum<min_sum){
min_sum=current_sum;
}
}
}
cout<<min_sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
D.快来帮芙芙吧* II
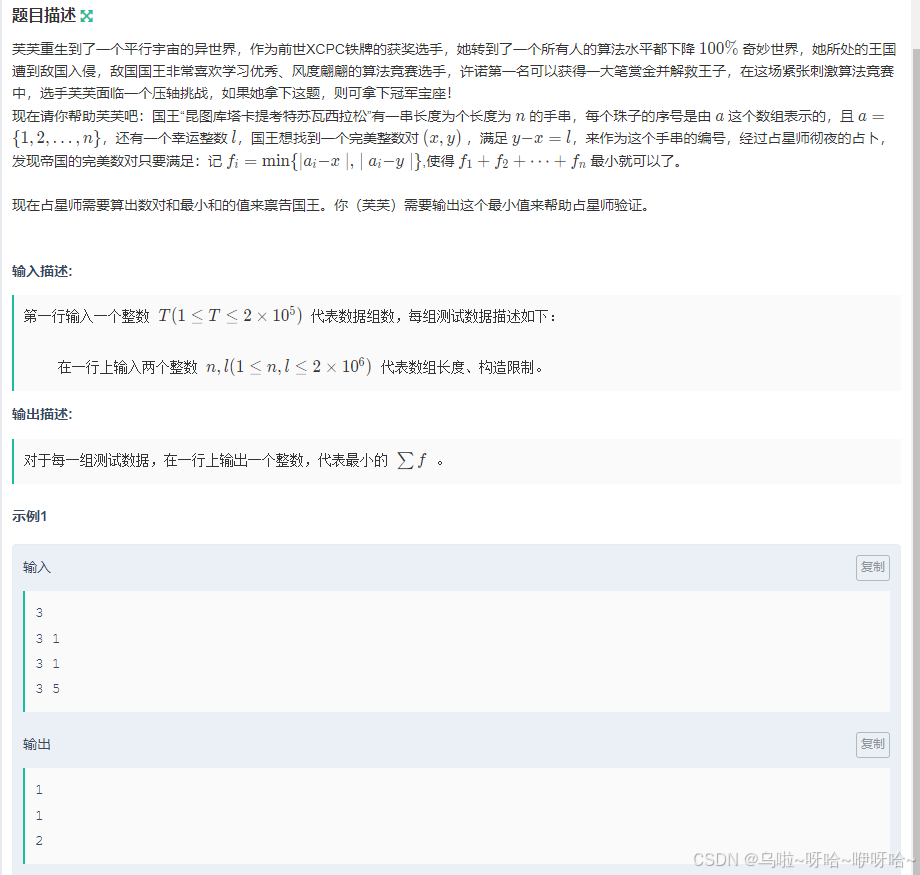
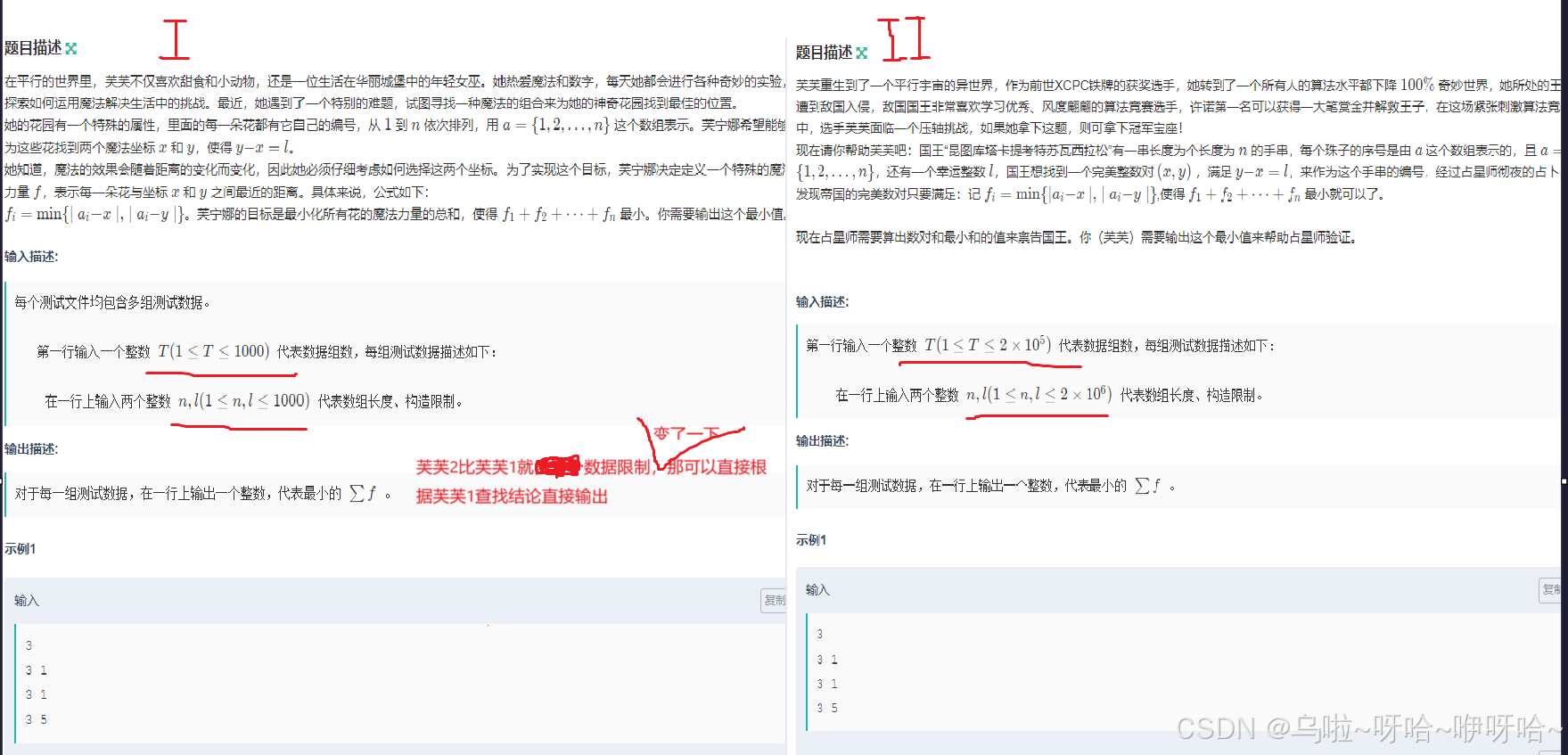
下面开始数据模拟,四种情况每样一个。
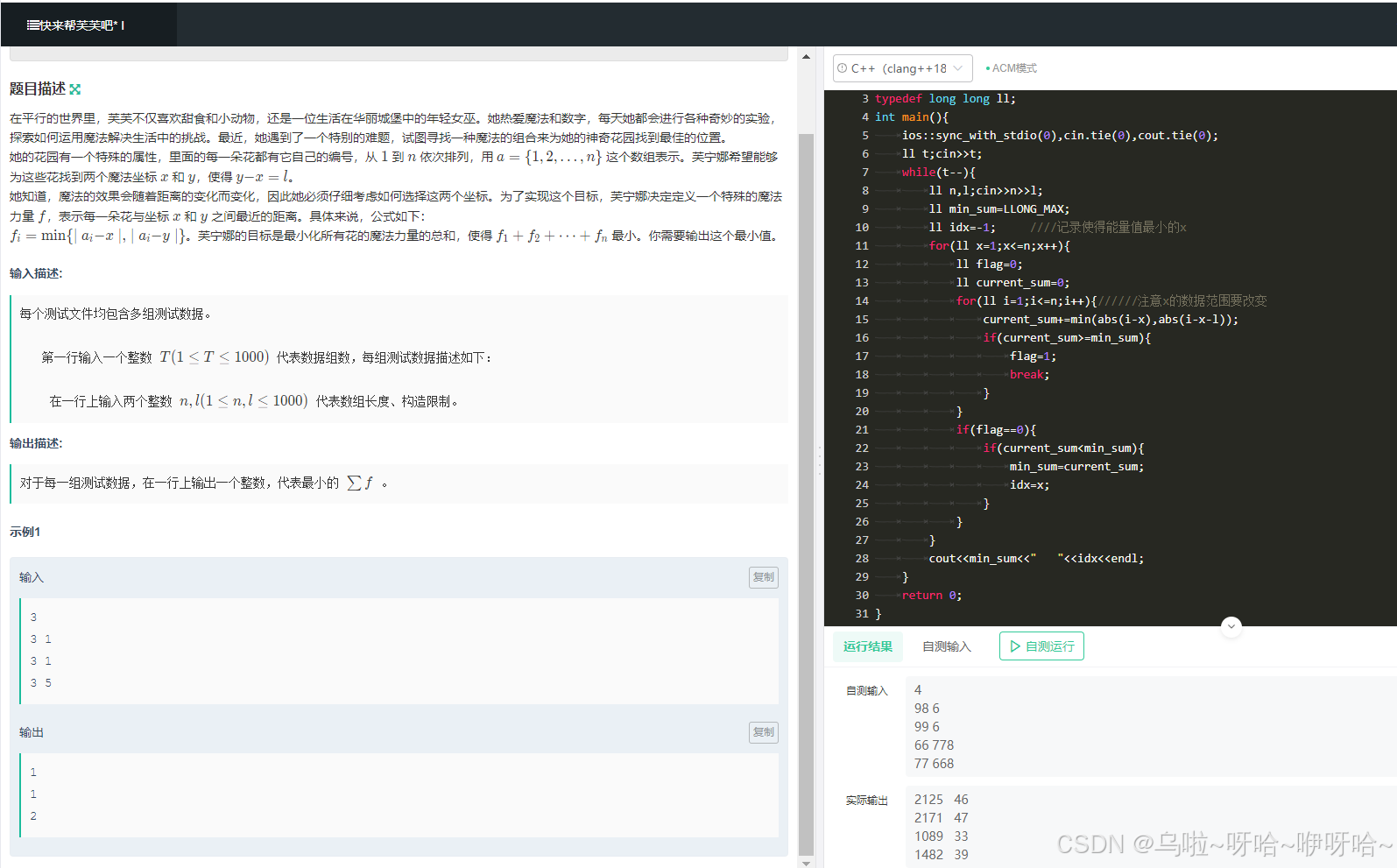
模拟数据的芙芙1代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n,l;cin>>n>>l;
ll min_sum=LLONG_MAX;
ll idx=-1; /////
for(ll x=1;x<=n;x++){ ////注意范围
ll flag=0;
ll current_sum=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
current_sum+=min(abs(i-x),abs(i-x-l));
if(current_sum>=min_sum){
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0){
if(current_sum<min_sum){
min_sum=current_sum;
idx=x;
}
}
}
cout<<min_sum<<" "<<idx<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
此时也就后两种情况的规律比较容易看出来,现在来验证后两种规律是否正确。
/*
根据数据模拟发现规律
<1> if(n>l && n%2==0)
x=
<2> if(n>l && n%2!=0)
x=
<3> if(l>n && n%2==0)
x=n/2
<4> if(l>n && n%2!=0)
x=n/2+1
*/
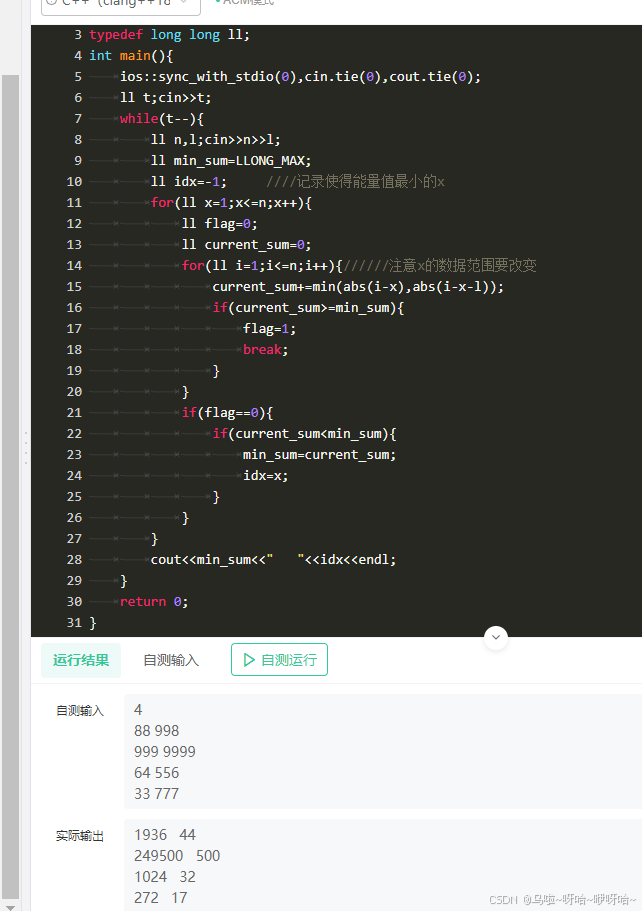
OK ,nice 现在找前两种规律 。
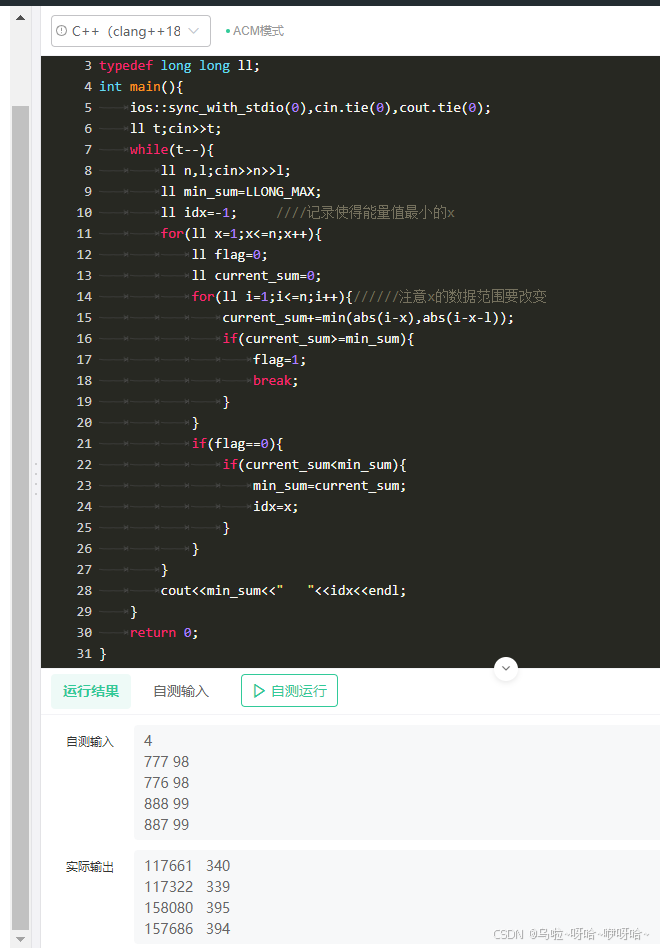
/*
根据数据模拟发现规律
<1> if(n>l && n%2==0)
x=(n-l+1)/2
<2> if(n>l && n%2!=0)
x=(n-l+1)/2
<3> if(l>n && n%2==0)
x=n/2
<4> if(l>n && n%2!=0)
x=n/2+1
*/
OK ,nice 直接把规律输出,时间复杂度O(n)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int t;
int n,l;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>t;
int x,y;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>l;
if(l>=n){
if(n%2){
x=(n+1)/2;
y=x+l;
}
else{
x=n/2;
y=x+l;
}
}
else{
x=(n-l+1)/2;
y=x+l;
}
int sum=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
sum+=min(abs(j-x),abs(y-j));
}
cout<<sum<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
E. BF* I
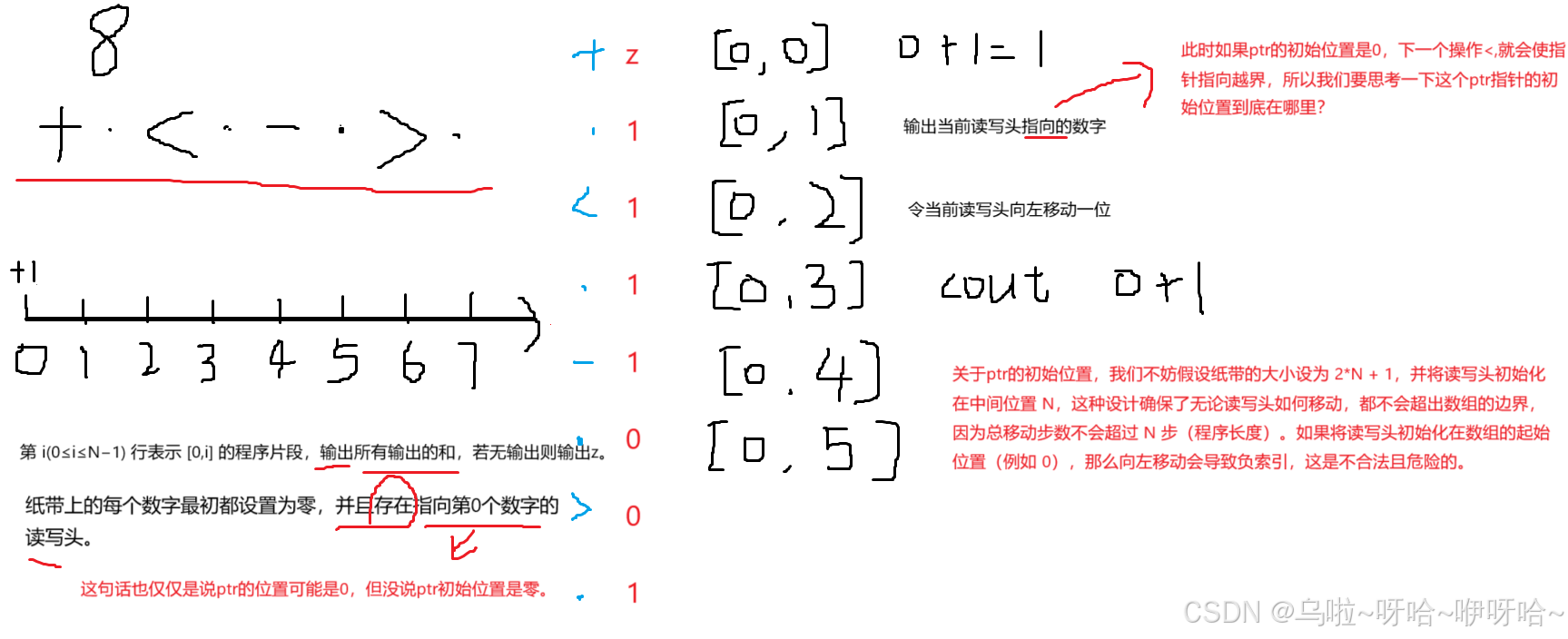
逆天代码竟然超时了,不过有知道了一个细节,我只能说,不积跬步无以至千里,不积小流无以成江河。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N=1e6;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
ll n;cin>>n;
string s;cin>>s;
vector<ll> a(2*N+5,0);
ll ptr=N;
ll cur_sum=0;
ll flag=0;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]=='.'){
cur_sum+=a[ptr];
flag=1;
}
else if(s[i]=='+')a[ptr]++;
else if(s[i]=='-')a[ptr]--;
else if(s[i]=='<')ptr--;
else if(s[i]=='>')ptr++;
if(flag==1)cout<<cur_sum<<endl;
else cout<<'z'<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
正确代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N=1e6;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
ll n;cin>>n;
string s;cin>>s;
vector<ll> a(2*N+5,0);
ll ptr=N;
ll cur_sum=0;
ll flag=0;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]=='.'){
cur_sum+=a[ptr];
flag=1;
}
else if(s[i]=='+')a[ptr]++;
else if(s[i]=='-')a[ptr]--;
else if(s[i]=='<')ptr--;
else if(s[i]=='>')ptr++;
if(flag==1)cout<<cur_sum<<'\n';
else cout<<'z'<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}

F.average
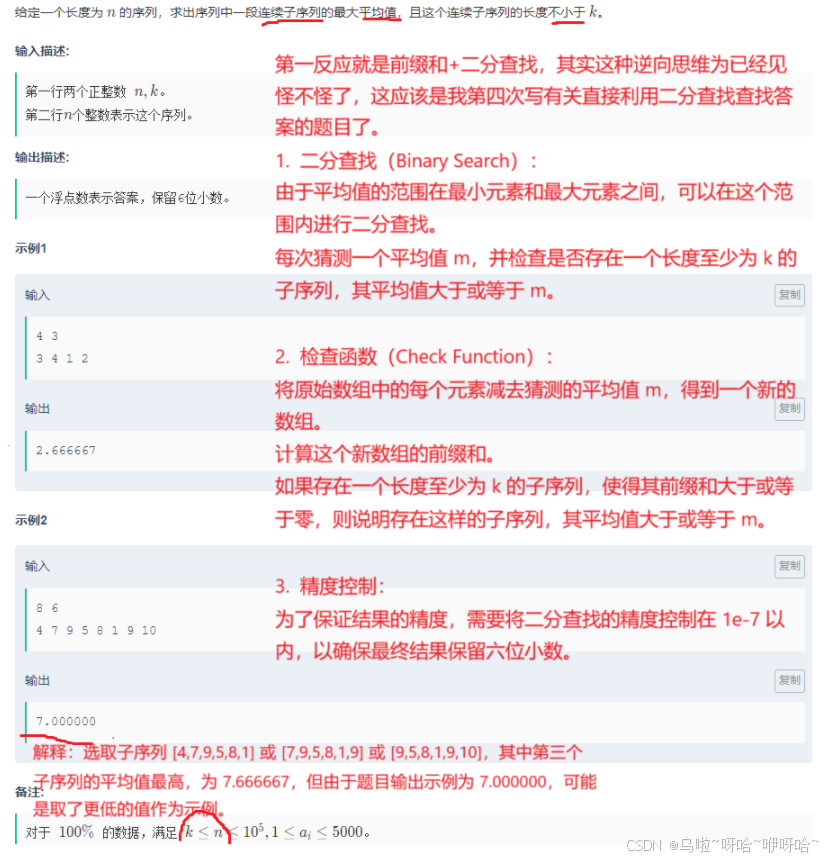
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef double ll;
ll n,k;
bool check(ll mid,vector<ll> &s,vector<ll> &a){
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
s[i]=s[i-1]+(a[i]-mid);
}
ll xiao_v=1e17;
for(ll i=k;i<=n;i++){
xiao_v=min(xiao_v,s[i-k]);
if(s[i]-xiao_v>=0)return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>k;
vector<ll> a(n+1,0);
vector<ll> s(n+1,0);
ll MIN=-1e17,MAX=1e17;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
MIN=min(MIN,a[i]);
MAX=max(MAX,a[i]);
}
ll l=MIN,r=MAX;
ll mid=0;
while(r-l>1e-6){
mid=(r+l)/2;
if(check(mid,s,a)){
l=mid;
}else r=mid;
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(6)<<l<<'\n';
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
double a[120000],s[120000];
int n,k;
int check(double x)
{
for(int t=1;t<=n;t++) s[t]=s[t-1]+a[t]-x;
double v=1e17;
for(int t=k;t<=n;t++)
{
v=min(v,s[t-k]);
if(s[t]-v>=0) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>k;
for(int t=1;t<=n;t++) cin>>a[t];
double l=0,r=5000;
while(r-l>1e-6)
{
double mid=(l+r)/2;
if(check(mid)) l=mid;
else r=mid;
}
printf("%.6lf",l);
}
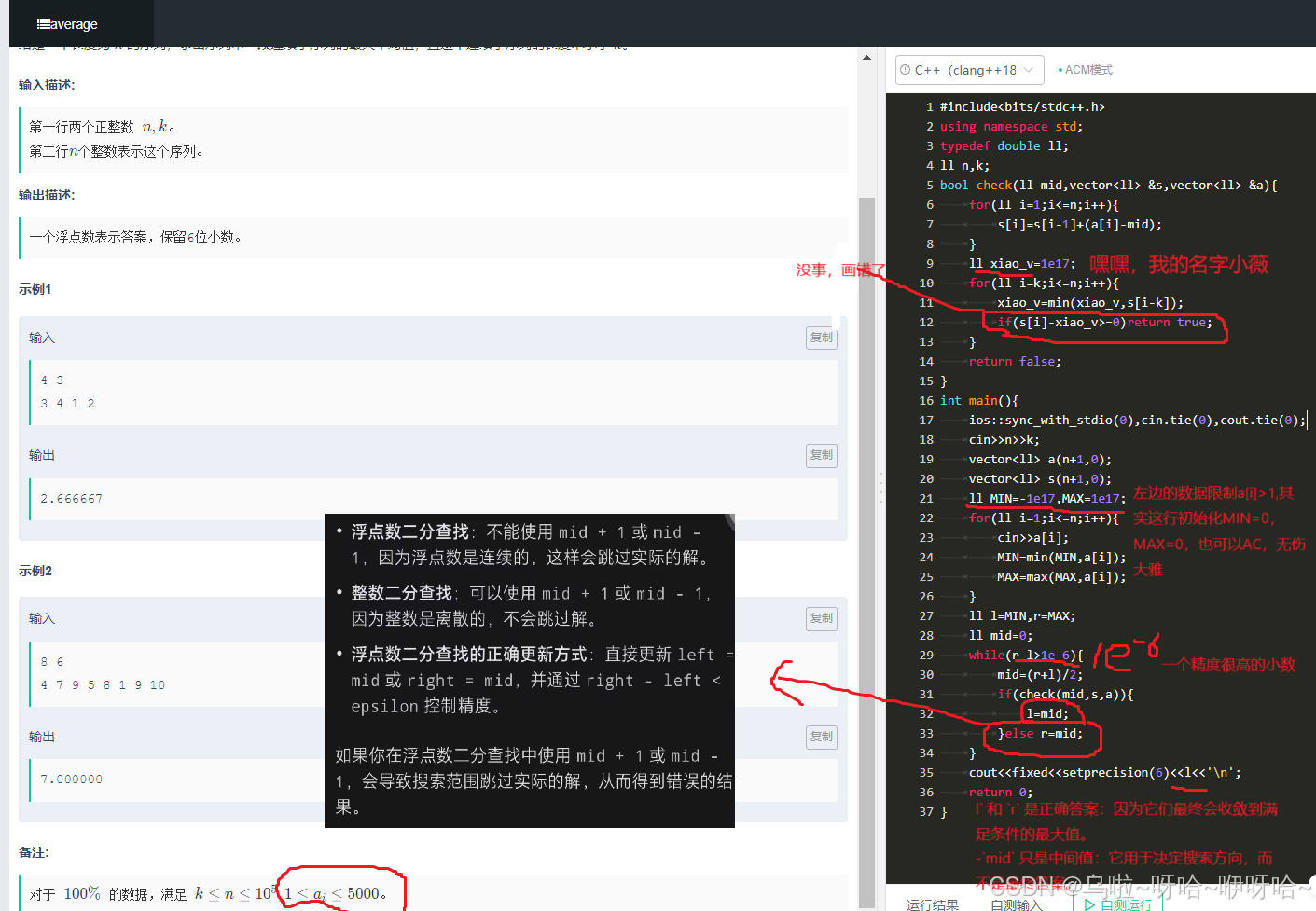

为什么不需要单独检查更长的子序列?
当我们遍历到位置 i并更新 xiao_v,实际上已经隐含地检查了所有长度从 k 到 i 的子序列。具体原因如下:
- 任意长度 ≥ k的子序列 都可以被分解为至少一个长度为 k 的子序列加上额外的元素。因此,只要存在一个长度为 k的子序列满足条件,或更长的子序列通过包含长度为 k 的子序列来满足条件,s
[i] - xiao_v>= 0就会捕捉到这一点。 - 维护 xiao_v确保我们考虑了所有可能的起始位置 j≤i−k,覆盖了所有长度至少为 k的子序列。
具体示例解析
让我们通过具体的例子来更好地理解这一点。

G.操作
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main() {
ll n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
while (k--) {
if (n % 200 == 0) {
n /= 200;
} else {
n = stoll(to_string(n) + "200");
}
}
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}
H.path
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
vector adj(n+1,vector<pair<int,ll>>());
int u,v,w;
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
cin>>u>>v>>w;
adj[u].push_back({v,w});
adj[v].push_back({u,w});
}
vector dist(n+1,vector<ll>(4,1e18));
dist[1][0] = 0;
priority_queue<pair<ll,pair<int,int>>,vector<pair<ll,pair<int,int>>>,greater<pair<ll,pair<int,int>>>> pq;
pq.push({0,{1,0}});
while(!pq.empty()){
auto it = pq.top();
ll d = it.first;
int u = it.second.first, wt = it.second.second;
pq.pop();
for(auto [v,w]:adj[u]){
if(d+w<dist[v][wt]){
dist[v][wt]= d+w;
pq.push({d+w,{v,wt}});
}
if((wt&1)==0){ // 2 times
if(d+w+w<dist[v][wt+1]){
dist[v][wt+1] = d+w+w;
pq.push({d+w+w,{v,wt+1}});
}
}
if((wt&2)==0){ // 0 times
if(d<dist[v][wt+2]){
dist[v][wt+2] = d;
pq.push({d,{v,wt+2}});
}
}
}
}
for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++){
cout<<min(dist[i][0],dist[i][3])<<" ";
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int testcase = 1;
while (testcase--)
solve();
return 0;
}


for (auto [v, w] : adj[u]) {
// 1) 普通走法
if (d + w < dist[v][wt]) {
dist[v][wt] = d + w;
pq.push({d + w, {v, wt}});
}
// 2) 如果可以用“多加一次” (bit0 == 0)
if ((wt & 1) == 0) {
// d + w + w
if (d + 2LL*w < dist[v][wt + 1]) {
dist[v][wt + 1] = d + 2LL*w;
pq.push({d + 2LL*w, {v, wt + 1}});
}
}
// 3) 如果可以用“少加一次” (bit1 == 0)
if ((wt & 2) == 0) {
// d + 0
if (d < dist[v][wt + 2]) {
dist[v][wt + 2] = d;
pq.push({d, {v, wt + 2}});
}
}
}


I.lucky number
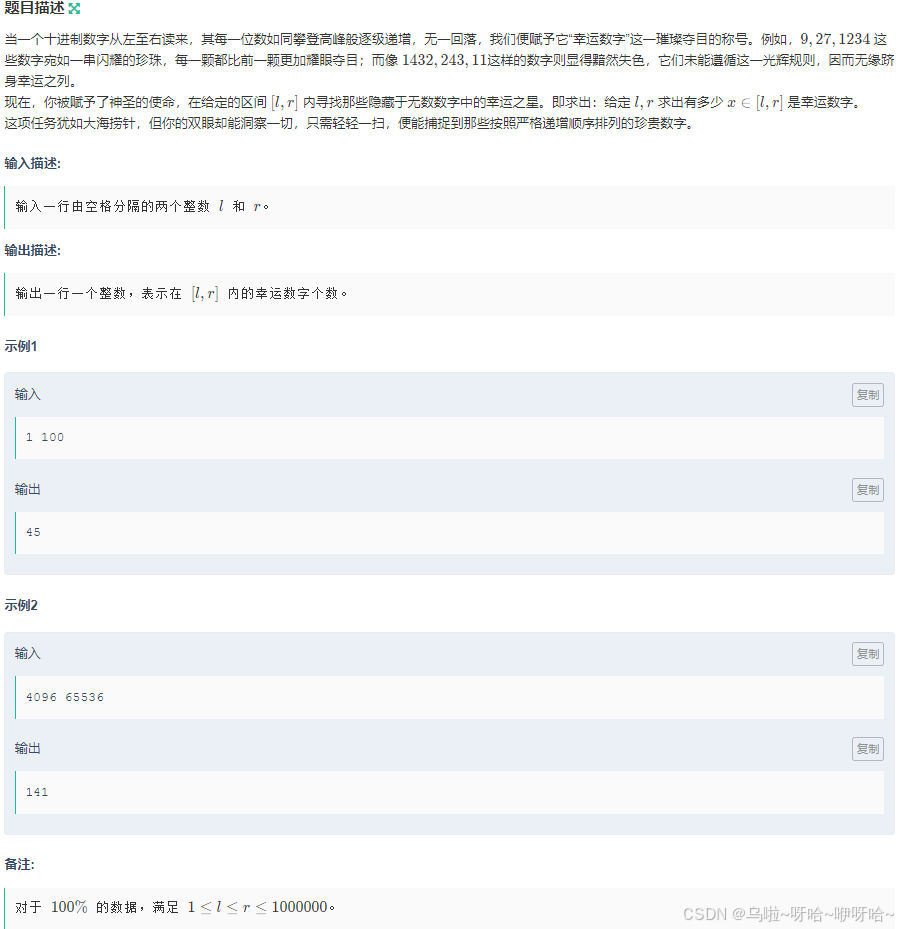
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
bool find(ll num){
if(num>=1&&num<=9)return true;
if(num%10==0)return false;
vector<ll> a;
while(num--){
ll temp=num%10;
a.push_back(temp);
num/=10;
}
for(ll i=0;i<a.size()-1;i++){
if(a[i]<=a[i+1])return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
ll l,r;cin>>l>>r;
ll sum=0;
for(ll i=l;i<=r;i++){
if(find(i)){
//cout<<i<<endl;
sum++;
}
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
J.sequence
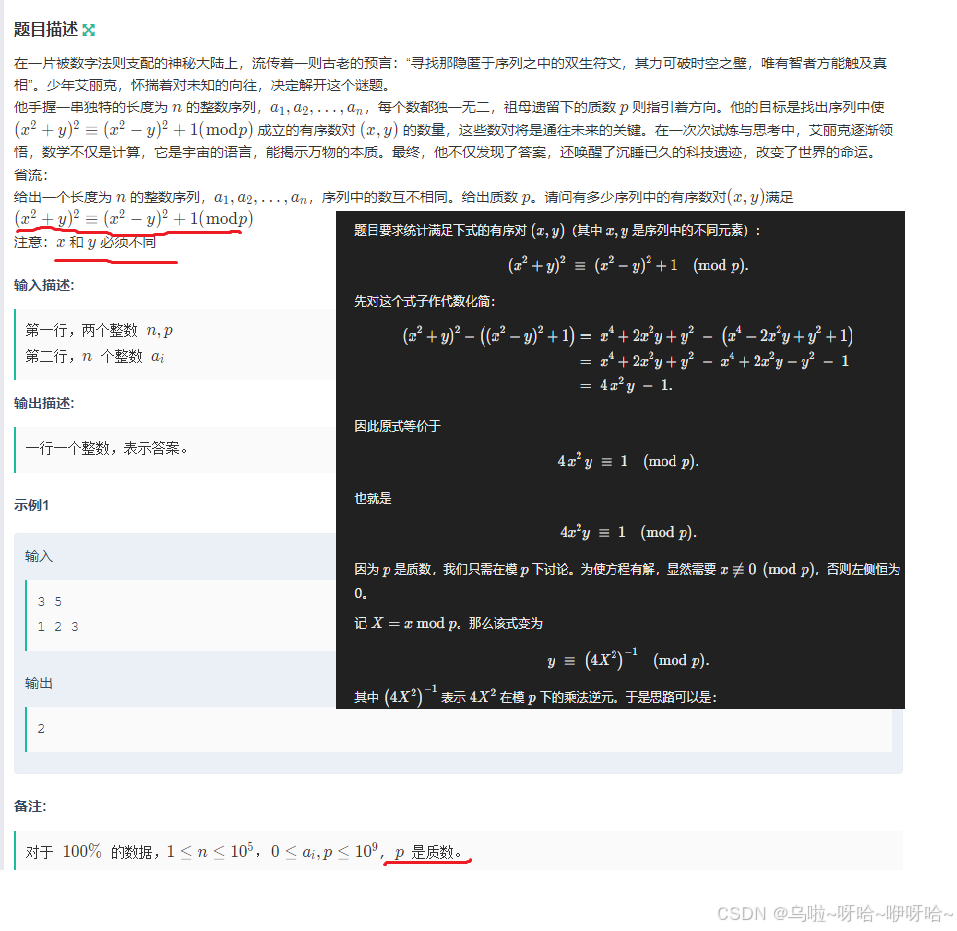



//y, (4x*x)^(-1) mod p是同一个余数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll n,p;
map<ll,ll> modmod;
ll qsm(ll a,ll b){
ll res=1;
a%=p;
while(b){
if(b&1)res=a*res%p;
a=a*a%p;
b/=2;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>p;
vector<ll> a(n);
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
modmod[4*a[i]%p*a[i]%p]++;
}
ll sum=0;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
ll x=qsm(a[i],p-2);
// 需要确定是否当前的 y 在序列中等于当前的 a[i]
// 因为 y ≡ (4x^2)^(-1) mod p,且 a[i] ≠ y 仅当 a[i] ≠ y
// 检查 a[i] 是否恰好等于 y
// 由于 y 是模 p 的逆元,且序列中元素互不相同
// 如果 y 在序列中存在且 y == a[i], 则需要减 1
// 但 y 可能对应多个不同的元素在模 p 下同余于 y
// 这里我们需要明确 y 是否等于当前 a[i]也即x
// 因为 y = (4x^2)^(-1) mod p, 且y!=x
// 所以 y == x 只有当 a[i] ≡ (4a[i]^2)^(-1) mod p 时
if(x==0)continue;//无逆元,跳过
if(x==(4*a[i]%p*a[i]%p))sum+=modmod[x]-1;
//括号里条件判断记得要注意优先级,还需要排除自身
else sum+=modmod[x];
}
cout<<sum;
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
// 快速幂计算 base^(exp) mod p (p 为质数)
// 用来求逆元时,exp = p-2
ll modExp(ll base, ll exp, ll p) {
ll result = 1 % p; // 应对 p=1 情况,不过题意p是质数且>=2
base = (base % p + p) % p;
while(exp > 0) {
if(exp & 1) result = ( (__int128)result * base ) % p;
base = ( (__int128)base * base ) % p;
exp >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
long long p;
cin >> n >> p; // n,p
vector<long long> arr(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> arr[i];
}
// 如果 p=1 或 p=2,特殊快速判断
// - p=1不可能,因为p是质数
// - p=2也很简单: 4*x^2*y mod 2=0 => 无法等于1 =>答案=0
if(p == 2){
cout << 0 << "\n";
return 0;
}
// 统计每个模值出现次数
// p 可达1e9, 无法直接开数组,只能用unordered_map或 map
unordered_map<ll,int> freq;
freq.reserve(n*2); // 以防止频繁 rehash
freq.max_load_factor(0.7f);
auto modVal = [&](long long x){
long long r = x % p;
if(r < 0) r += p;
return r;
};
for(auto &x : arr){
ll r = modVal(x);
freq[r]++;
}
long long ans = 0;
// 遍历每个 x,计算可配对的 y 数量
for(auto &x : arr){
ll X = modVal(x);
if(X == 0) {
// 4*x^2 = 0 (mod p) => 不可能=1 => 跳过
continue;
}
// T = 4 * X^2 mod p
// 注意可能溢出,用 128 位中间量或先做 modMul
// 这里做一步一步:
long long X2 = ( (long long)X * X ) % p; // x^2 mod p
long long T = (4LL * X2) % p; // 4 x^2 mod p
if(T == 0) {
// 依然不可能得到1
continue;
}
// T_inv = T^(p-2) mod p
long long T_inv = modExp(T, p-2, p);
// freq[T_inv] => 多少 y 的值 mod p = T_inv
// 如果 X == T_inv, 需要排除 x 本身
auto it = freq.find(T_inv);
if(it == freq.end()){
// 没有任何元素 y 满足 y mod p= T_inv
continue;
}
long long cnt = it->second;
if(X == T_inv) {
// 要排除 x 本身(1个)
cnt -= 1;
}
ans += cnt;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
path仔细看看,其他大部分转换一下不是很难,请继续前进。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








