Given a binary search tree, you are supposed to find the node that contains the K-th largest key.
Format of function:
BinTree KthLargest ( BinTree T, int K );
where BinTree is defined as the following:
typedef struct TNode *BinTree;
struct TNode{
int Key;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
};
The function KthLargest is supposed to return the pointer that points to the node that contains the K-th largest key in the binary search tree T.
Here T is not empty and all its keys are distinct positive integers. K is positive and is never more than the total number of nodes in the tree.
Sample program of judge:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct TNode *BinTree;
struct TNode{
int Key;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
};
BinTree BuildTree(); /* details omitted */
BinTree KthLargest ( BinTree T, int K );
int main()
{
BinTree T, P;
int K;
T = BuildTree();
scanf("%d", &K);
P = KthLargest(T, K);
printf("%d\n", P->Key);
if (P->Left) printf("%d\n", P->Left->Key);
else printf("NULL\n");
if (P->Right) printf("%d\n", P->Right->Key);
else printf("NULL\n");
return 0;
}
/* Your function will be put here */
Sample Input: (for the following tree)
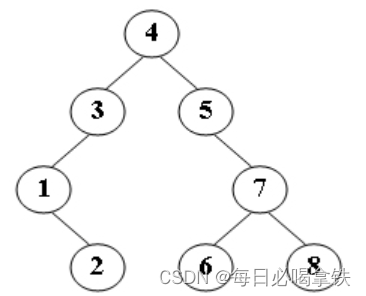
4
Sample Output:
5
NULL
7
Analysis:
用中序遍历得到序列,因为是二叉搜索树,则该序列一定是递增的,所以直接返回序列中倒数第k个数(下标为count-k),count为序列总数。
Notice:
- 如果不知道怎么用中序遍历得到序列,可以去看是否二叉搜索树,在这篇文章中,我具体分析了中序遍历得到序列。
- 序列中储存的是地址,因此直接返回即可。
Code:
BinTree KthLargest ( BinTree T, int K )
{
BinTree BT=T;
BinTree a[100]={NULL},b[100]={NULL};
int ai=0,bi=0;
while(BT||ai!=0)
{
while(BT)
{
a[ai++]=BT;
BT=BT->Left;
}
if(a[ai-1]==NULL)
ai--;
int top=--ai;
b[bi++]=a[top];
BT=a[top];
a[top]=NULL;
BT=BT->Right;
}
return b[bi-K];
}
























 1803
1803

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








