2.题目分析
由题,显然是一道典型的搜索题。这里我使用的广度优先搜索,不过限制条件比较特殊,是每次只能走不同符号的地方,不过也很好解决,在结构体新加一个属性就可以解决。剩下的就是常规的bfs模版了。
3.代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
char map[101][101];
int n;
int book[101][101];
int nextgo[4][2] = { 0,1,1,0,0,-1,-1,0 };
int start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y;
typedef struct Node
{
int x, y, step;
char flag;
}node;
int bfs(int x, int y)
{
queue<node>q;
q.push({ x,y,0,'.' });
while (q.size())
{
node d = q.front();
q.pop();
if (d.x == end_x && d.y == end_y)
{
return d.step;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int tx = d.x + nextgo[i][0];
int ty = d.y + nextgo[i][1];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n && !book[ty][tx])
{
if (d.flag != map[ty][tx])
{
book[ty][tx] = 1;
q.push({ tx,ty,d.step + 1,map[ty][tx] });
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] == 'A')
{
start_x = j;
start_y = i;
}
if (map[i][j] == 'B')
{
end_x = j;
end_y = i;
}
}
}
book[start_y][start_x] = 1;
cout << bfs(start_x, start_y);
return 0;
}具体代码实现如上,接下来对每个操作进行解释。

这是对每个节点属性的创建,记录了该点的坐标以及走到该点需要的步数,还有flag记录该点的符号,便于之后进行判断。
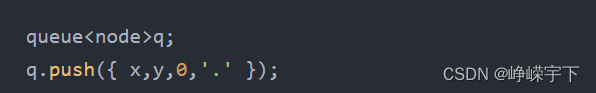
bfs函数的开头,先创建一个队列,然后把起始位置存进去。

之后在队列不为空的基础上对队列首个元素依次进行分析,如果该元素的坐标就是终点坐标,我们就可以返回该坐标的步数。
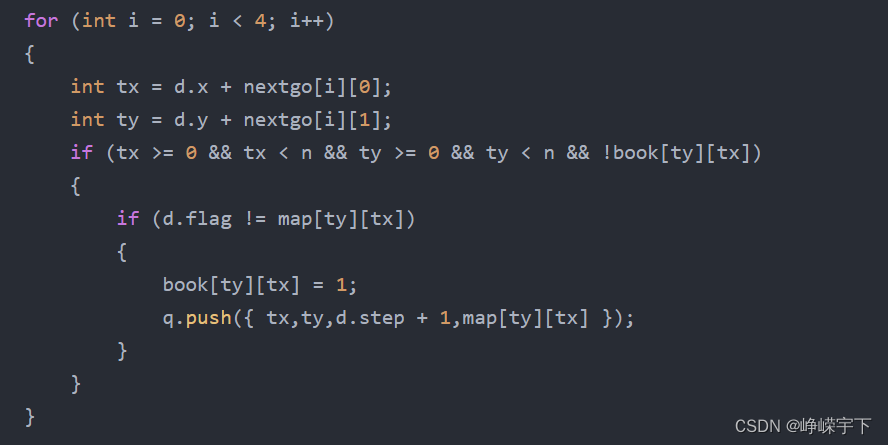
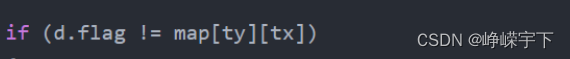
然后就是正常的搜索操作,不过额外加了一个判断(如下),寻找与该节点符号不同的节点,从而进行下一步搜索。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








