一.Sentinel的简介
Sentinel (分布式系统的流量防卫兵) 是阿里开源的一套用于服务容错的综合性解决方案。它以流量为切入点, 从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度来保护服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景, 例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
完备的实时监控:Sentinel 提供了实时的监控功能。通过控制台可以看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据, 甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块, 例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口快
速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等
二、微服务集成Sentinel
1.加pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.编写消费者的controller并调用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("test")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping
public String test(){
return "test";
}
}

三、安装Sentinel控制台
1.下载并解压

2.启动控制台
java -Dserver.port=8888 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8888 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.1.jar
或者进入到bin中
java -jar xxx(jar包名)
3.修改配置文件,在里面加入有关控制台的配置
消费者配置
#客户端与服务端进行交互的时候 交互使用的端口号
spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.port=9999
#sentinal服务所在的地址和端口号
spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.dashboard=localhost:8080
通过浏览器访问
用户,密码为:sentinel

四、流控规则
1.流控
流量控制,其原理是监控应用流量的QPS(每秒查询率) 或并发线程数等指标,当达到指定的阈值时对流量进行控制,以避免被瞬时的流量高峰冲垮,从而保障应用的高可用性。

被流控报出的(需要多刷新两次)

2.修改限流报出的异常
Result
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Result<T> {
private Integer code = 200;
private String msg = "success";
private T data;
public static <T> Result success(T data){
return new Result<T>(200,"SUCCESS",data);
}
public static <T> Result fail(){
return new Result<T>(200,"FAIL",null);
}
public static <T> Result forbidden(){
return new Result<T>(403,"Forbidden",null);
}
}MyException
@Component
public class MyException implements BlockExceptionHandler {
@Resource
private ObjectMapper ordApp;
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, BlockException e) throws Exception {
if (e instanceof FlowException) {
Result r = null;
if (e instanceof FlowException) {
r = new Result(100, "限流了", "");
}
//返回json数据
response.setStatus(500);
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
ordApp.writeValue(response.getWriter(),r);
}
}
}

3.配置流控模式
直接(默认):接口达到限流条件时,开启限流
关联:当关联的资源达到限流条件时,开启限流 [适合做应用让步]
链路:当从某个接口过来的资源达到限流条件时,开启限流
1.关联模式
@RestController
public class GuanController {
@GetMapping("mag1")
public Result msg1(){
return Result.success("msg1");
}
@GetMapping("mag2")
public Result msg2(){
return Result.success("msg2");
}
}

2.链路
controller
@RestController
public class LianController {
@Resource
private SentinelService service;
@GetMapping("lianlu1")
public Result aaa() {
service.msg();
return Result.success("");
}
@GetMapping("lianlu2")
public Result aaa2() {
service.msg();
return Result.success("");
}
}
service
@Service
public class SentinelService {
@SentinelResource("msg")
public void msg(){
System.out.println("----------");
}
}
配置文件加
#区分不同的url
spring.cloud.sentinel.web-context-unify=false

3.服务熔断测试
controller
@GetMapping("test3")
@SentinelResource(value = "test3",
blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class,
blockHandler = "handlerException2")
public Result customerBlockHandler() {
return new Result(200, "成功", null);
}
业务类
public class CustomerBlockHandler {
public static Result handlerException(BlockException exception) {
return new Result(500, "限流","");
}
}
4.配置流控效果
1.Warm up
Warm Up:它从开始阈值到最大QPS阈值会有一个缓冲阶段,一开始的阈值是最大QPS阈值的1/3,然后慢慢.增长,直到最大阈值,适用于将突然增大的流量转换为缓步增长的场景

初始阈值 = 阈值上限 / coldFactor, coldFactor 是冷加载因子,默认为3
所以本图效果为:五秒内最大阈值为2,五秒后最大阈值6
2.排队等待
排队等待:匀速排队,让请求以匀速的速度通过,阈值类型必须设置为QPS,否则无效(QPS>1000无效)

本图效果为1000毫秒内平均通过两次(相当于500毫秒通过一次)
五、降级规则
1.慢比例调用
RT:平均响应时间注:RT最大4900(更大的需要通过-Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=XXXX才能生效)
比例阈值:指触发降级的比例阈值,当响应时间超过了设定的比例阈值,就会触发降级
取值范围在0.0~1.0
熔断时长:慢调用比例和异常比例规则中,一旦触发降级,将在设定的熔断时长内对服务进行降级处理。

规定每个请求最大的时间是50ms超过这个时间就认为是慢调用
当慢调用的比例=0.5(最小的请求是2 慢调用/总调用) 的时候 触发熔断 熔断时长为1s
2.异常比例

本图效果:在两秒内发出请求个数6个,有三个异常就会触发熔断,熔断时长两秒
3.异常个数

本图效果:在两秒内发出请求个数2个,有1个异常就会触发熔断,熔断时长1秒
六、热点规则
1.热点规则
参数索引从 0 开始
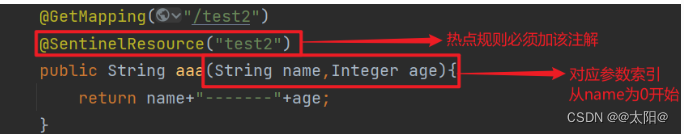


代表对name限制
2.热点规则参数例外项

七、授权规则
若配置白名单,则只有请求来源位于白名单内时才可通过; 若配置黑名单,则请求来源位于黑名单时不通过,其余的请求通过

自定义来源处理规则
@Component
public class RequestOriginParserDefinition implements RequestOriginParser{
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
String serviceName = request.getParameter("serviceName");
return serviceName;
}
}
访问路径加 serviceName=test

八、 Sentinel规则持久化
config
public class FilePersistence implements InitFunc {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String appcationName;
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
String ruleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/sentinel-rules/" + appcationName;
String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json";
String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json";
String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json";
String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json";
String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json";
this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir);
this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath);
// 流控规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
flowRuleListParser
);
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);
// 降级规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
degradeRuleListParser
);
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);
// 系统规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
systemRuleListParser
);
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);
// 授权规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
authorityRuleListParser
);
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS);
// 热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
paramFlowRuleListParser
);
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);
}
private Converter<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>() {
}
);
private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
private <T> String encodeJson(T t) {
return JSON.toJSONString(t);
}
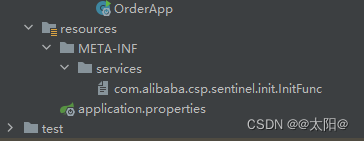
}在对应的微服务下面的resources里面创建一个目录
META-INF/services
并在目录下面写一个文件 ,,文件的内容







 本文详细阐述了Sentinel作为分布式系统流量防卫兵的重要特性,如应用场景、监控、与主流框架集成、流控规则配置、降级策略和规则持久化方法。
本文详细阐述了Sentinel作为分布式系统流量防卫兵的重要特性,如应用场景、监控、与主流框架集成、流控规则配置、降级策略和规则持久化方法。
















 282
282

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








