1. scrapy的概念
Scrapy是一个Python编写的开源网络爬虫框架。它是一个被设计用于爬取网络数据、提取结构性数据的框架。
Scrapy 使用了Twisted['twɪstɪd]异步网络框架,可以加快我们的下载速度。
Scrapy文档地址:http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/1.0/intro/overview.html
2. scrapy框架的作用
少量的代码,就能够快速的抓取
3. scrapy的工作流程
 上面的流程可以改写为
上面的流程可以改写为

最后可以得到 scrapy的流程 :
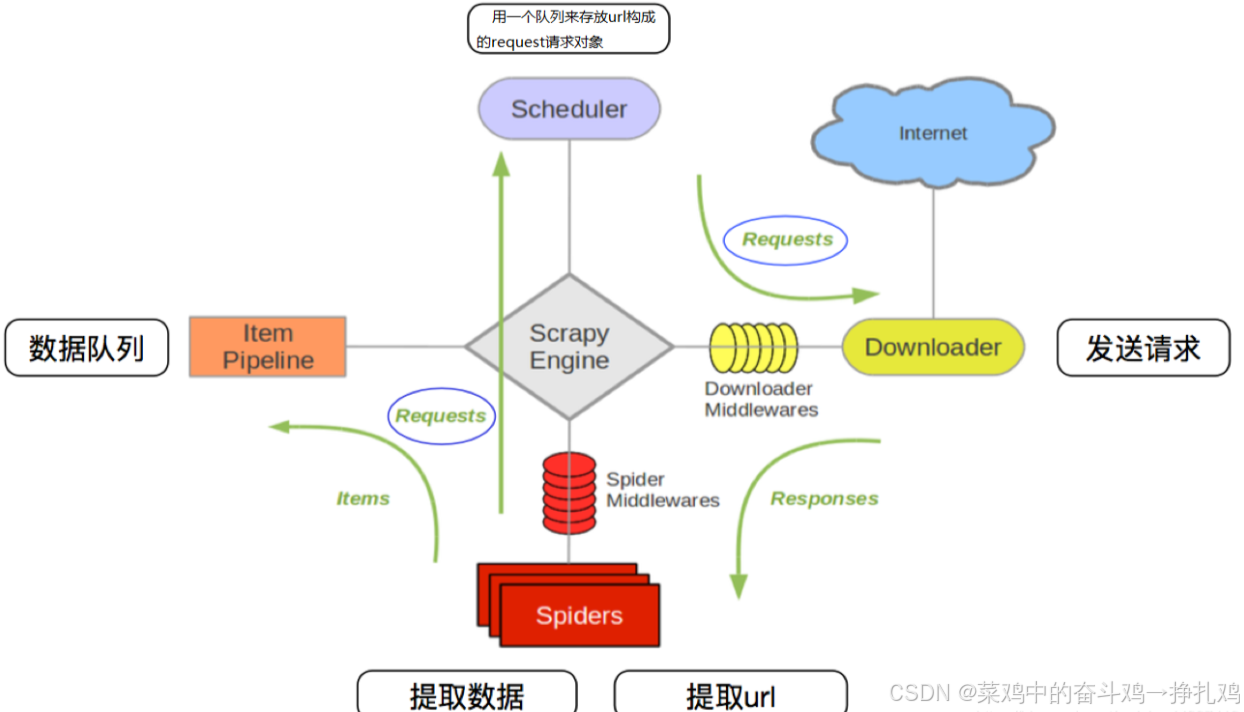
其流程可以描述如下:
爬虫中起始的url构造成request对象–>爬虫中间件–>引擎–>调度器
调度器把request–>引擎–>下载中间件—>下载器
下载器发送请求,获取response响应---->下载中间件---->引擎—>爬虫中间件—>爬虫
爬虫提取url地址,组装成request对象---->爬虫中间件—>引擎—>调度器,重复步骤2
爬虫提取数据—>引擎—>管道处理和保存数据
注意:
图中中文是为了方便理解后加上去的
图中绿色线条的表示数据的传递
注意图中中间件的位置,决定了其作用
注意其中引擎的位置,所有的模块之前相互独立,只和引擎进行交互
4.scrapy的三个内置对象
request请求对象:由url method post_data headers等构成
response响应对象:由url body status headers等构成
item数据对象:本质是个字典
每个模块的具体作用:

总结:
1.scrapy的概念:Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架
2.scrapy框架的运行流程以及数据传递过程:
爬虫中起始的url构造成request对象–>爬虫中间件–>引擎–>调度器
调度器把request–>引擎–>下载中间件—>下载器
下载器发送请求,获取response响应---->下载中间件---->引擎—>爬虫中间件—>爬虫
爬虫提取url地址,组装成request对象---->爬虫中间件—>引擎—>调度器,重复步骤2
爬虫提取数据—>引擎—>管道处理和保存数据
3.scrapy框架的作用:通过少量代码实现快速抓取
4.掌握scrapy中每个模块的作用:
引擎(engine):负责数据和信号在不腰痛模块间的传递
调度器(scheduler):实现一个队列,存放引擎发过来的request请求对象
下载器(downloader):发送引擎发过来的request请求,获取响应,并将响应交给引擎
爬虫(spider):处理引擎发过来的response,提取数据,提取url,并交给引擎
管道(pipeline):处理引擎传递过来的数据,比如存储
下载中间件(downloader middleware):可以自定义的下载扩展,比如设置代理ip
爬虫中间件(spider middleware):可以自定义request请求和进行response过滤,与下载中间件作用重复
5.scrapy项目开发流程
安装:pip install -i Simple Index scrapy
终端输入:scrapy version 查看是否安装成功
5.1 创建scrapy项目(需要先切换到想要放置的文件夹下):
1. scrapy startproject mypider(自己取名)

输入tree /f myspider 查看项目框架:


5.2 创建scrapy爬虫
在项目路径下执行(cd 刚刚创建的myspider):
scrapy genspider <爬虫名字> <允许爬取的域名>
cd myspider
scrapy genspider itcast itcast.cn

5.3 简单运行scrapy

命令:在项目目录下(有scrapy.cfg文件目录)执行scrapy crawl <爬虫名字>

得到运行结果:

5.4 完善爬虫
步骤:
1.修改起始的url
2.检查修改允许的域名
3.在parse方法中实现爬取逻辑
不显示日志信息:
scrapy crawl itcast --nolog

# xpath结果为只含有一个值的列表,可以使用extract_first(),用[0].extract()如果空或者无会报错,如果为多个值则使用extract()
response响应对象的常用属性:
response.url:当前响应的url地址
response.request.url:当前响应对应的请求的url地址
response.headers:响应头
response.requests.headers:当前响应的请求头
response.body:响应体,也就是html代码,byte类型
response.status:响应状态码

对象写法:
itcast.py
import scrapy
from myspider.items import MyspiderItem
class ItcastSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫名字
name = "itcast"
# 2.检查域名
allowed_domains = ["itcast.cn"]
# 1.修改起始url
start_urls = ["https://www.itheima.com/teacher.html"]
# 3.在parse方法中实现爬取逻辑
def parse(self, response):
# 定义对于网站的相关操作
# with open('itcast.html','wb') as f:
# f.write(response.body)
# 获取所有教师节点
node_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="li_txt"]')
# print(len(node_list))
# 遍历教师节点列表
for node in node_list:
# temp = {}
temp = MyspiderItem()
# xpath方法返回的是选择器对象列表, extract()用于从选择器对象中提取数据
temp['name'] = node.xpath('./h3/text()').extract_first()
temp['title'] = node.xpath('./h4/text()')[0].extract()
temp['desc'] = node.xpath('./p/text()')[0].extract()
# xpath结果为只含有一个值的列表,可以使用extract_first(),如果为多个值则使用extract()
# print(temp)
# break
yield temp
# print(response.url)
# print(response.request.url)
# print(response.headers)
# print(response.request.headers)items.py
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class MyspiderItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
name = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
desc = scrapy.Field()
# pass非对象写法:
itcast.py
import scrapy
class ItcastSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫名字
name = "itcast"
# 2.检查域名
allowed_domains = ["itcast.cn"]
# 1.修改起始url
start_urls = ["https://www.itheima.com/teacher.html"]
# 3.在parse方法中实现爬取逻辑
def parse(self, response):
# 定义对于网站的相关操作
# with open('itcast.html','wb') as f:
# f.write(response.body)
# 获取所有教师节点
node_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="li_txt"]')
# print(len(node_list))
# 遍历教师节点列表
for node in node_list:
temp = {}
# xpath方法返回的是选择器对象列表, extract()用于从选择器对象中提取数据
temp['name'] = node.xpath('./h3/text()').extract_first()
temp['title'] = node.xpath('./h4/text()')[0].extract()
temp['desc'] = node.xpath('./p/text()')[0].extract()
# xpath结果为只含有一个值的列表,可以使用extract_first(),如果为多个值则使用extract()
# print(temp)
# break
yield temp
# print(response.url)
# print(response.request.url)
# print(response.headers)
# print(response.request.headers)items.py
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class MyspiderItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
# name = scrapy.Field()
# title = scrapy.Field()
# desc = scrapy.Field()
pass5.5 scrapy命令操作
1. 进入 Scrapy Shell
scrapy shell <url> 如果单个项目直接scrapy shell,再单个发送url, fetch('https://example.com')

这将启动一个交互式 Python shell,并对提供的 URL 执行初步的 HTTP 请求,结果会存储在
response对象中。
2. 退出 Scrapy Shell
输入 exit() 或 quit():
3. Scrapy Shell 常见操作
1. 查看请求的响应内容
-
查看 HTML 源码
>>> response.text -
查看响应头信息
>>> response.headers -
查看状态码
>>> response.status
2. 使用 XPath 或 CSS 选择器提取内容
-
XPath 查询 使用 XPath 提取特定内容:
>>> response.xpath('//title/text()').get()获取所有匹配的结果:
>>> response.xpath('//a/@href').getall() -
CSS 选择器查询 使用 CSS 选择器提取内容:
>>> response.css('title::text').get()获取所有匹配的结果:
>>> response.css('a::attr(href)').getall()
5.6 保存数据
5.5.1 在pipelines.py文件中定义对数据的操作
- 定义一个管道类
- 重写管道类的process_item方法
- process_item方法处理完item之后必须返回给引擎
import json
class ItcastPipeline():
# 爬虫文件中提取数据的方法每yield一次item,就会运行一次
# 该方法为固定名称函数
def process_item(self, item, spider):
print(item)
return item
5.5.2 在settings.py配置启用管道
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'myspider.pipelines.ItcastPipeline': 400
}
配置项中键为使用的管道类,管道类使用.进行分割,第一个为项目目录,第二个为文件,第三个为定义的管道类。
配置项中值为管道的使用顺序,设置的数值约小越优先执行,该值一般设置为1000以内。























 64万+
64万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








