文章目录
前言
原生的Spring在构造ApplicationContext时,会调用refresh方法。其中就包含了扫描所有包含@Component及其子注解的类(注解模式)或解析xml配置文件(xml模式)将其注册为BeanDefinition的逻辑。
一、scanCandidateComponents
scanCandidateComponents是扫描指定路径下的类,并且将符合要求的类进行解析,注册成BeanDefinition的逻辑。
在该方法中:
- 将传入的类路径进行格式转换。
- 获取指定类路径下的所有.class文件。
- 通过MetadataReader 解析.class的元数据信息。
获得类的元数据信息,判断类上是否有相关注解的方式有两种,第一是通过JVM的类加载,第二是MetadataReader 。为什么Spring选择的是后者?因为JVM的类是懒加载的,如果在Spring启动时就将所有目标路径下的类全部通过JVM加载,那么就违背了JVM类加载的机制。并且如果目标路径下的类很多,对于性能也有一定的损失。而MetadataReader 使用的是ASM技术 最终。得到的是BeanDefinition对象而不是在JVM中加载.class文件。
/**
* 参数:需要扫描的类路径 例:com.itbaima
* 返回值:BeanDefinition的集合
**/
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
//将参数中的类路径进行转换 com.itbaima->classpath*:com/itbaima/**/*.class
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
//得到指定类路径下的所有资源文件(类的.class文件)
//例:file [D:\Idea_workspace\2024\springplus\target\classes\com\itbaima\AppConfig.class]
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//遍历这些资源文件
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
try {
//通过MetadataReader 对某个.class文件的元数据进行解析
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
//1.1 isCandidateComponent
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
//创建BeanDefinition
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
//设置BeanDefinition的source属性 file [D:\Idea_workspace\2024\springplus\target\classes\com\itbaima\AppConfig.class]
sbd.setSource(resource);
//再次进行判断,对应的类是不是接口或抽象类(和上面的isCandidateComponent是重载的方法)
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
//将该BeanDefinition放入集合中
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored non-readable " + resource + ": " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
1.1 isCandidateComponent
在ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider中,isCandidateComponent有两个,第一个主要是用于判断类元信息中是否需要排除/包含注解:
 ExcludeFilter表示排除过滤器,IncludeFilter表示包含过滤器
ExcludeFilter表示排除过滤器,IncludeFilter表示包含过滤器
1.1.1、排除/包含过滤器
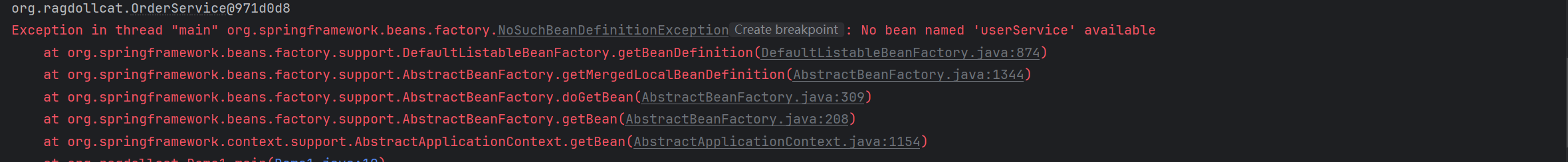
ExcludeFilter的作用:被排除在外的类,即使类上加入了@Component及其子注解,也不会被扫描到:
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
@Component
public class UserService {
}
@ComponentScan(value = "org.ragdollcat",
excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(
type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
classes = UserService.class)})
public class AppConfig {
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
System.out.println(context.getBean("orderService"));
System.out.println(context.getBean("userService"));
}
}
IncludeFilter的作用:被包含的类,即使类上没有加入@Component及其子注解,也会被扫描到:
@ComponentScan(value = "org.ragdollcat",
includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(
type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
classes = UserService.class)})
public class AppConfig {
}
public class UserService {
}

1.1.2、条件装配
这里还有一个条件装配的概念,我们可以自定义一个类,实现Condition 接口,重写matches方法,自定义匹配的逻辑
@Component
public class MyConditional implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return false;
}
}
并且在需要条件装配的类上,加入@Conditional注解:
@Component
@Conditional(MyConditional.class)
public class UserService {
}
1.1.3、重载一
在isCandidateComponent方法中:
- 判断判断类元信息中是否需要排除/包含注解。
- 如果类元信息中需要包含某个注解,能匹配的上,如果还有
@Conditional注解,则需要再次判断是否符合条件。
/**
* 判断类元信息中是否需要排除/包含注解
* 参数:类元信息
*/
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
//如果当前元数据中的注解 有符合需要排除的注解 则返回false
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return false;
}
}
//如果当前元数据中的注解 有符合包含的注解 则再次进入判断
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return isConditionMatch(metadataReader);
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 主要用于判断条件装配
*
*/
private boolean isConditionMatch(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
if (this.conditionEvaluator == null) {
this.conditionEvaluator =
new ConditionEvaluator(getRegistry(), this.environment, this.resourcePatternResolver);
}
return !this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata());
}
public boolean shouldSkip(@Nullable AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, @Nullable ConfigurationPhase phase) {
//元数据为空 或者类上没有加@Conditional注解 无需判断 直接返回false
if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) {
return false;
}
if (phase == null) {
if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata &&
ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) {
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList<>();
//得到所有实现了Condition接口的类
for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) {
for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) {
//转换为Condition 对象
Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this.context.getClassLoader());
//加入到集合中
conditions.add(condition);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions);
for (Condition condition : conditions) {
ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null;
if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) {
requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase();
}
//关键点:调用自定义实现了Condition接口的类 的match方法 查看返回结果
if ((requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) && !condition.matches(this.context, metadata)) {
//如果自定义实现了Condition接口的类 的match方法 返回的是false 则 这里返回的true 表示需要跳过加上了@Condition注解的类的扫描
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
在进行匹配时,调用的核心方法:
@Override
protected boolean matchSelf(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
//首先获取类元数据上的注解信息
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
//返回判断的结果:
//1、类上有@Component及其子注解 或 2、considerMetaAnnotations 为true 并且类上有@Component及其子注解
return metadata.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()) ||
(this.considerMetaAnnotations && metadata.hasMetaAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()));
}
1.1.4、重载二
第二个isCandidateComponent方法,主要是判断当前类是否是接口或者抽象类,有一种特殊情况,即该类是抽象类,但是有@Lookup注解,也会被装配。
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
return (metadata.isIndependent() && (metadata.isConcrete() ||
(metadata.isAbstract() && metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Lookup.class.getName()))));
}
default boolean isConcrete() {
//如果是接口或者抽象类 则返回false
return !(isInterface() || isAbstract());
}
1.1.5、补充:@Lookup注解
如果某个单例bean中有个属性是多例的,在初始化单例后,每次获取到的属性的地址值都是一样的:
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class User {
}
@Component
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private User user;
public void test(){
System.out.println(user);
}
// @Lookup("user")
// public User m1(){
// return null;
// }
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
OrderService orderService = (OrderService) context.getBean("orderService");
orderService.test();
orderService.test();
orderService.test();
}
}
 如果要每次获取不同的属性,可以使用
如果要每次获取不同的属性,可以使用@Lookup注解实现:
@Component
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private User user;
public void test(){
System.out.println(m1());
}
@Lookup("user")
public User m1(){
return null;
}
}

总结
在Scan方法中主要做了:
- 将传入参数的路径进行转换,转换为classpath的格式。
- 获取路径下的所有资源文件(.class)。
- 通过MetadataReader 解析.class的元数据信息。
- 判断被扫描到的类上是否存在@Component及其子注解,并且有无需要排除某个类的情况。还需要判断类上是否加入了@Conditional注解。如果有,调用@Conditional注解value中的类的.matches方法,判断是否需要跳过该类。
- 将被扫描的类包装成BeanDefinition对象。
- 再次判断被扫描的类是否是接口/抽象类。如果是则不将其创建为BeanDefinition。有加入了@Lookup的抽象类的特殊情况。
- 将BeanDefinition对象加入集合。





















 1024
1024

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








